ARN14140
balanced inhibiting profile against the acetylcholinesterase enzyme (galantamine) and the NMDA receptor (memantine): AChE IC50 =0.695 muM; NMDAR Ki 2.32 muM
General
Type : Adamantyl,Multitarget,Derivative of Galanthamine,NMDA-Ligand,Alkyl linked bis-ligand
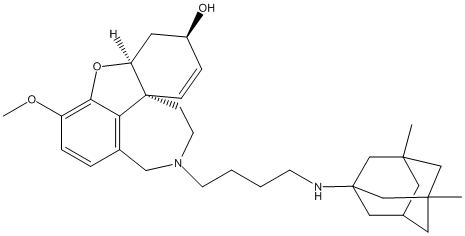
Chemical_Nomenclature : (1S,12S,14R)-4-[4-[(3,5-dimethyl-1-adamantyl)amino]butyl]-9-methoxy-11-oxa-4-azatetracyclo[8.6.1.01,12.06,17]heptadeca-6(17),7,9,15-tetraen-14-ol
Canonical SMILES : CC12CC3CC(C1)(CC(C3)(C2)NCCCCN4CCC56C=CC(CC5OC7=C(C=CC(=C67)C4)OC)O)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C32H46N2O3\/c1-29-15-22-16-30(2,19-29)21-31(17-22,20-29)33-11-4-5-12-34-13-10-32-9-8-24(35)14-26(32)37-28-25(36-3)7-6-23(18-34)27(28)32\/h6-9,22,24,26,33,35H,4-5,10-21H2,1-3H3\/t22?,24-,26-,29?,30?,31?,32-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : SQNFGAWWNIPHLE-WBIOMSNFSA-N
Other name(s) : CHEMBL2178782,BDBM50398930
MW : 506.73
Formula : C32H46N2O3
CAS_number :
PubChem : 71460880
UniChem : SQNFGAWWNIPHLE-WBIOMSNFSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (3)
| Title : Controlled Iontophoretic Delivery in Vitro and in Vivo of ARN14140-A Multitarget Compound for Alzheimer's Disease - Singhal_2019_Mol.Pharm_16_3460 |
| Author(s) : Singhal M , Merino V , Rosini M , Cavalli A , Kalia YN |
| Ref : Mol Pharm , 16 :3460 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Singhal_2019_Mol.Pharm_16_3460 |
| ESTHER : Singhal_2019_Mol.Pharm_16_3460 |
| PubMedSearch : Singhal_2019_Mol.Pharm_16_3460 |
| PubMedID: 31241959 |
| Title : In Vivo Characterization of ARN14140, a Memantine\/Galantamine-Based Multi-Target Compound for Alzheimer's Disease - Reggiani_2016_Sci.Rep_6_33172 |
| Author(s) : Reggiani AM , Simoni E , Caporaso R , Meunier J , Keller E , Maurice T , Minarini A , Rosini M , Cavalli A |
| Ref : Sci Rep , 6 :33172 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Reggiani_2016_Sci.Rep_6_33172 |
| ESTHER : Reggiani_2016_Sci.Rep_6_33172 |
| PubMedSearch : Reggiani_2016_Sci.Rep_6_33172 |
| PubMedID: 27609215 |
| Title : Combining galantamine and memantine in multitargeted, new chemical entities potentially useful in Alzheimer's disease - Simoni_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_9708 |
| Author(s) : Simoni E , Daniele S , Bottegoni G , Pizzirani D , Trincavelli ML , Goldoni L , Tarozzo G , Reggiani A , Martini C , Piomelli D , Melchiorre C , Rosini M , Cavalli A |
| Ref : Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 55 :9708 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Simoni_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_9708 |
| ESTHER : Simoni_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_9708 |
| PubMedSearch : Simoni_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_9708 |
| PubMedID: 23033965 |