Aldicarb
Insecticide, acaricide, nematocide
General
Type : Insecticide,Carbamate,Sulfur Compound
Chemical_Nomenclature : [(E)-(2-methyl-2-methylsulfanylpropylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate
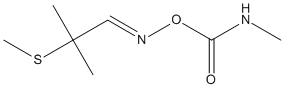
Canonical SMILES : CC(C)(C=NOC(=O)NC)SC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C7H14N2O2S\/c1-7(2,12-4)5-9-11-6(10)8-3\/h5H,1-4H3,(H,8,10)\/b9-5+
InChIKey : QGLZXHRNAYXIBU-WEVVVXLNSA-N
Other name(s) : 2-Methyl-2-(methylthio)propanal O-[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxime,2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propionaldehyde O-methylcarbamoyloxime,aldicarbe,Temik,UC21149,temik g10,temik 10 g,UNII-OR2E6B4F2X
MW : 190.27
Formula : C7H14N2O2S
CAS_number : 116-06-3
PubChem : 9570071
UniChem : QGLZXHRNAYXIBU-WEVVVXLNSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Aldicarb
Target
References (34)
| Title : Aldicarb-related suicide attempt cases in North of France (2012-2021) - Lenski_2022_Toxicol.Res.(Camb)_11_529 |
| Author(s) : Lenski M , Letrillart A , Gish A , Nisse P , Gaulier JM , Allorge D |
| Ref : Toxicol Res (Camb) , 11 :529 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Lenski_2022_Toxicol.Res.(Camb)_11_529 |
| ESTHER : Lenski_2022_Toxicol.Res.(Camb)_11_529 |
| PubMedSearch : Lenski_2022_Toxicol.Res.(Camb)_11_529 |
| PubMedID: 35782643 |
| Title : Potential enhancement of degradation of the nematicides aldicarb, oxamyl and fosthiazate in UK agricultural soils through repeated applications - Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| Author(s) : Osborn RK , Edwards SG , Wilcox A , Haydock PP |
| Ref : Pest Manag Sci , 66 :253 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| ESTHER : Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| PubMedSearch : Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| PubMedID: 19862790 |
| Title : Comparison of aldicarb and methamidophos neurotoxicity at different ages in the rat: behavioral and biochemical parameters - Moser_1999_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_157_94 |
| Author(s) : Moser VC |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 157 :94 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Moser_1999_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_157_94 |
| ESTHER : Moser_1999_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_157_94 |
| PubMedSearch : Moser_1999_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_157_94 |
| PubMedID: 10366542 |
| Title : A case of aldicarb poisoning: a possible murder attempt - Covaci_1999_J.Anal.Toxicol_23_290 |
| Author(s) : Covaci A , Manirakiza P , Coucke V , Beckers R , Jorens PG , Schepens P |
| Ref : J Anal Toxicol , 23 :290 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Covaci_1999_J.Anal.Toxicol_23_290 |
| ESTHER : Covaci_1999_J.Anal.Toxicol_23_290 |
| PubMedSearch : Covaci_1999_J.Anal.Toxicol_23_290 |
| PubMedID: 10445493 |
| Title : In vitro sulfoxidation of aldicarb by hepatic microsomes of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus - Perkins_1999_Toxicol.Sci_48_67 |
| Author(s) : Perkins EJ , el-Alfy A , Schlenk D |
| Ref : Toxicol Sci , 48 :67 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Perkins_1999_Toxicol.Sci_48_67 |
| ESTHER : Perkins_1999_Toxicol.Sci_48_67 |
| PubMedSearch : Perkins_1999_Toxicol.Sci_48_67 |
| PubMedID: 10330685 |
| Title : Potential mechanisms of the enhancement of aldicarb toxicity to japanese medaka, oryzias latipes, at high salinity - El-Alfy_1998_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_152_175 |
| Author(s) : el-Alfy A , Schlenk D |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 152 :175 , 1998 |
| Abstract : El-Alfy_1998_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_152_175 |
| ESTHER : El-Alfy_1998_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_152_175 |
| PubMedSearch : El-Alfy_1998_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_152_175 |
| PubMedID: 9772213 |
| Title : Effects of hexamethonium, phenothiazines, propranolol and ephedrine on acetylcholinesterase carbamylation by physostigmine, aldicarb and carbaryl: interaction between the active site and the functionally distinct peripheral sites in acetylcholinesterase - Singh_1998_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_119_97 |
| Author(s) : Singh AK , Spassova D |
| Ref : Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology C Pharmacology Toxicology & Endocrinology , 119 :97 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Singh_1998_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_119_97 |
| ESTHER : Singh_1998_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_119_97 |
| PubMedSearch : Singh_1998_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_119_97 |
| PubMedID: 9568379 |
| Title : Synaptic transmission deficits in Caenorhabditis elegans synaptobrevin mutants - Nonet_1998_J.Neurosci_18_70 |
| Author(s) : Nonet ML , Saifee O , Zhao H , Rand JB , Wei L |
| Ref : Journal of Neuroscience , 18 :70 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Nonet_1998_J.Neurosci_18_70 |
| ESTHER : Nonet_1998_J.Neurosci_18_70 |
| PubMedSearch : Nonet_1998_J.Neurosci_18_70 |
| PubMedID: 9412487 |
| Title : The caenorhabditis elegans unc-64 locus encodes a syntaxin that interacts genetically with synaptobrevin - Saifee_1998_Mol.Biol.Cell_9_1235 |
| Author(s) : Saifee O , Wei L , Nonet ML |
| Ref : Molecular Biology of the Cell , 9 :1235 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Saifee_1998_Mol.Biol.Cell_9_1235 |
| ESTHER : Saifee_1998_Mol.Biol.Cell_9_1235 |
| PubMedSearch : Saifee_1998_Mol.Biol.Cell_9_1235 |
| PubMedID: 9614171 |
| Title : Comparative Toxicity of Chlordane, Chlorpyrifos, and Aldicarb to Four Aquatic Testing Organisms - Moore_1998_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_34_152 |
| Author(s) : Moore MT , Huggett DB , Gillespie WB, Jr. , Rodgers JH, Jr. , Cooper CM |
| Ref : Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 34 :152 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Moore_1998_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_34_152 |
| ESTHER : Moore_1998_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_34_152 |
| PubMedSearch : Moore_1998_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_34_152 |
| PubMedID: 9469857 |
| Title : Rat brain acetylcholinesterase activity: developmental profile and maturational sensitivity to carbamate and organophosphorus inhibitors - Mortensen_1998_Toxicology_125_13 |
| Author(s) : Mortensen SR , Hooper MJ , Padilla S |
| Ref : Toxicology , 125 :13 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Mortensen_1998_Toxicology_125_13 |
| ESTHER : Mortensen_1998_Toxicology_125_13 |
| PubMedSearch : Mortensen_1998_Toxicology_125_13 |
| PubMedID: 9585096 |
| Title : Recovery following pulsed exposure to organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides in the midge, Chironomus riparius - Kallander_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_29 |
| Author(s) : Kallander DB , Fisher SW , Lydy MJ |
| Ref : Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 33 :29 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Kallander_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_29 |
| ESTHER : Kallander_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_29 |
| PubMedSearch : Kallander_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_29 |
| PubMedID: 9216867 |
| Title : Caenorhabditis elegans rab-3 mutant synapses exhibit impaired function and are partially depleted of vesicles - Nonet_1997_J.Neurosci_17_8061 |
| Author(s) : Nonet ML , Staunton JE , Kilgard MP , Fergestad T , Hartwieg E , Horvitz HR , Jorgensen EM , Meyer BJ |
| Ref : Journal of Neuroscience , 17 :8061 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Nonet_1997_J.Neurosci_17_8061 |
| ESTHER : Nonet_1997_J.Neurosci_17_8061 |
| PubMedSearch : Nonet_1997_J.Neurosci_17_8061 |
| PubMedID: 9334382 |
| Title : A sampling and analytical method for the simultaneous determination of multiple organonitrogen pesticides in air - Kennedy_1997_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_58_720 |
| Author(s) : Kennedy ER , Lin JJ , Reynolds JM , Perkins JB |
| Ref : American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal , 58 :720 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Kennedy_1997_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_58_720 |
| ESTHER : Kennedy_1997_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_58_720 |
| PubMedSearch : Kennedy_1997_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_58_720 |
| PubMedID: 9342832 |
| Title : Inhibition of 17 beta-estradiol and progesterone activity in human breast and endometrial cancer cells by carbamate insecticides - Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| Author(s) : Klotz DM , Arnold SF , McLachlan JA |
| Ref : Life Sciences , 60 :1467 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| ESTHER : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| PubMedSearch : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| PubMedID: 9126867 |
| Title : Poisonings associated with illegal use of aldicarb as a rodenticide -- New York City, 1994-1997 - NYCPCC_1997_MMWR.Morb.Mortal.Wkly.Rep_46_961 |
| Author(s) : NYCPCC |
| Ref : MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep , 46 :961 , 1997 |
| Abstract : NYCPCC_1997_MMWR.Morb.Mortal.Wkly.Rep_46_961 |
| ESTHER : NYCPCC_1997_MMWR.Morb.Mortal.Wkly.Rep_46_961 |
| PubMedSearch : NYCPCC_1997_MMWR.Morb.Mortal.Wkly.Rep_46_961 |
| PubMedID: 9347907 |
| Title : Determination of the rate of aldicarb sulphoxidation in rat liver, kidney and lung microsomes - Pelekis_1997_Xenobiotica_27_1113 |
| Author(s) : Pelekis M , Krishnan K |
| Ref : Xenobiotica , 27 :1113 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Pelekis_1997_Xenobiotica_27_1113 |
| ESTHER : Pelekis_1997_Xenobiotica_27_1113 |
| PubMedSearch : Pelekis_1997_Xenobiotica_27_1113 |
| PubMedID: 9413915 |
| Title : Carbamate poisoning in early childhood and in adults - Lifshitz_1997_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_35_25 |
| Author(s) : Lifshitz M , Shahak E , Bolotin A , Sofer S |
| Ref : Journal of Toxicology Clinical Toxicology , 35 :25 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Lifshitz_1997_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_35_25 |
| ESTHER : Lifshitz_1997_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_35_25 |
| PubMedSearch : Lifshitz_1997_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_35_25 |
| PubMedID: 9022648 |
| Title : Categorical regression of toxicity data: a case study using aldicarb - Dourson_1997_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_25_121 |
| Author(s) : Dourson ML , Teuschler LK , Durkin PR , Stiteler WM |
| Ref : Regul Toxicol Pharmacol , 25 :121 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Dourson_1997_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_25_121 |
| ESTHER : Dourson_1997_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_25_121 |
| PubMedSearch : Dourson_1997_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_25_121 |
| PubMedID: 9185888 |
| Title : Solid-phase extraction of polar pesticides from environmental water samples on graphitized carbon and Empore-activated carbon disks and on- line coupling to octadecyl-bonded silica analytical columns - Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| Author(s) : Slobodnik J , Oztezkizan O , Lingeman H , Brinkman UA |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 750 :227 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| ESTHER : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| PubMedSearch : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| PubMedID: 8938388 |
| Title : Comparisons of the acute effects of cholinesterase inhibitors using a neurobehavioral screening battery in rats - Moser_1995_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_17_617 |
| Author(s) : Moser VC |
| Ref : Neurotoxicology & Teratology , 17 :617 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Moser_1995_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_17_617 |
| ESTHER : Moser_1995_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_17_617 |
| PubMedSearch : Moser_1995_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_17_617 |
| PubMedID: 8747743 |
| Title : Toxic interactions between copper sulphate and some organic agrochemicals - Ahmed_1994_Toxicol.Lett_70_109 |
| Author(s) : Ahmed HM , Shoka AA |
| Ref : Toxicology Letters , 70 :109 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Ahmed_1994_Toxicol.Lett_70_109 |
| ESTHER : Ahmed_1994_Toxicol.Lett_70_109 |
| PubMedSearch : Ahmed_1994_Toxicol.Lett_70_109 |
| PubMedID: 8310452 |
| Title : Aldicarb poisoning. A case report with prolonged cholinesterase inhibition and improvement after pralidoxime therapy - Burgess_1994_Arch.Intern.Med_154_221 |
| Author(s) : Burgess JL , Bernstein JN , Hurlbut K |
| Ref : Archives of Internal Medicine , 154 :221 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Burgess_1994_Arch.Intern.Med_154_221 |
| ESTHER : Burgess_1994_Arch.Intern.Med_154_221 |
| PubMedSearch : Burgess_1994_Arch.Intern.Med_154_221 |
| PubMedID: 8285817 |
| Title : Carbamate poisoning and oxime treatment in children: a clinical and laboratory study - Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| Author(s) : Lifshitz M , Rotenberg M , Sofer S , Tamiri T , Shahak E , Almog S |
| Ref : Pediatrics , 93 :652 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| ESTHER : Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| PubMedSearch : Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| PubMedID: 8134223 |
| Title : Analyte stability study of N-methylcarbamate pesticides in beef and poultry liver tissues by liquid chromatography - Ali_1993_J.AOAC.Int_76_1309 |
| Author(s) : Ali MS , White JD , Bakowski RS , Phillippo ET , Ellis RL |
| Ref : Journal of AOAC International , 76 :1309 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Ali_1993_J.AOAC.Int_76_1309 |
| ESTHER : Ali_1993_J.AOAC.Int_76_1309 |
| PubMedSearch : Ali_1993_J.AOAC.Int_76_1309 |
| PubMedID: 8286970 |
| Title : Zinc chloride-diphenylamine reagent for thin layer chromatographic detection of some organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides - Sevalkar_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_545 |
| Author(s) : Sevalkar MT , Patil VB , Katkar HN |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 74 :545 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Sevalkar_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_545 |
| ESTHER : Sevalkar_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_545 |
| PubMedSearch : Sevalkar_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_545 |
| PubMedID: 1874701 |
| Title : [Exposure to residues on plant surfaces following the use of plant pesticides in the greenhouse] - Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| Author(s) : Goedicke HJ , Hermes H , Wagner R |
| Ref : Z Gesamte Hyg , 35 :531 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| ESTHER : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| PubMedSearch : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| PubMedID: 2588705 |
| Title : Simplified multiresidue method for liquid chromatographic determination of N-methyl carbamate insecticides in fruits and vegetables - Chaput_1988_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_71_542 |
| Author(s) : Chaput D |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 71 :542 , 1988 |
| Abstract : Chaput_1988_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_71_542 |
| ESTHER : Chaput_1988_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_71_542 |
| PubMedSearch : Chaput_1988_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_71_542 |
| PubMedID: 3391959 |
| Title : Susceptibility of laboratory-reared northern fowl mites, Ornithonyssus sylviarum (Acari: Macronyssidae), to selected acaricides - Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| Author(s) : Crystal MM , DeMilo AB |
| Ref : Exp Appl Acarol , 4 :353 , 1988 |
| Abstract : Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| ESTHER : Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| PubMedSearch : Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| PubMedID: 3168660 |
| Title : Oxadiazolidinones: irreversible inhibition of cholinesterases and effects on acetylcholine receptors - Bakry_1986_Neurotoxicol_7_1 |
| Author(s) : Bakry NM , Sherby SM , Eldefrawi AT , Eldefrawi ME |
| Ref : Neurotoxicology , 7 :1 , 1986 |
| Abstract : Bakry_1986_Neurotoxicol_7_1 |
| ESTHER : Bakry_1986_Neurotoxicol_7_1 |
| PubMedSearch : Bakry_1986_Neurotoxicol_7_1 |
| PubMedID: 3822252 |
| Title : Liquid chromatographic determination of N-methylcarbamate insecticides and metabolites in crops. II. Analytical characteristics and residue findings - Krause_1985_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_68_734 |
| Author(s) : Krause RT |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 68 :734 , 1985 |
| Abstract : Krause_1985_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_68_734 |
| ESTHER : Krause_1985_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_68_734 |
| PubMedSearch : Krause_1985_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_68_734 |
| PubMedID: 4030646 |
| Title : Simple determination of oxime carbamates in soil and environmental water by high pressure liquid chromatography - Dekker_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_18_379 |
| Author(s) : Dekker A , Houx NW |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 18 :379 , 1983 |
| Abstract : Dekker_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_18_379 |
| ESTHER : Dekker_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_18_379 |
| PubMedSearch : Dekker_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_18_379 |
| PubMedID: 6875217 |
| Title : Observations on the influence of water and soil pH on the persistence of insecticides - Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| Author(s) : Chapman RA , Cole CM |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 17 :487 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| ESTHER : Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| PubMedSearch : Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| PubMedID: 7175098 |
| Title : [Radiometric determination of 11 carbamate pesticides in the nanogram and subnanongram ranges by means of cholinesterase inhibition] - Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| Author(s) : Schmid ER , Damboritz W , Markl P |
| Ref : Nahrung , 21 :311 , 1977 |
| Abstract : Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| ESTHER : Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| PubMedSearch : Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| PubMedID: 406567 |