Azinphos-Methyl
An organothiophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitor. It has been used as an acaricide and as an insecticide.
General
Type : Insecticide,Organophosphate,Sulfur Compound,Organothiophosphate,Triazine
Chemical_Nomenclature : 3-(dimethoxyphosphinothioylsulfanylmethyl)-1,2,3-benzotriazin-4-one
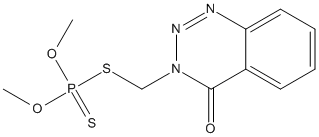
Canonical SMILES : COP(=S)(OC)SCN1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2N=N1
InChI : InChI=1S\/C10H12N3O3PS2\/c1-15-17(18,16-2)19-7-13-10(14)8-5-3-4-6-9(8)11-12-13\/h3-6H,7H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : CJJOSEISRRTUQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Phosphorodithioic acid O,O-dimethyl S-[4-oxo-1,2,3-benzotriazin-3(4H)-yl)methyl]ester,Phosphorodithioic acid O,O-dimethyl ester S ester with 3-mercaptomethyl-1,2,3-benzotriazin-4(3H)-one,Gusathion M,Gusathion,Gution zimil,Bay 9027,Bay 17147,Bayer 17147,Carfene,Cotnion-methyl,Guthion,Methyl-Guthion.
MW : 317.33
Formula : C10H12N3O3PS2
CAS_number : 86-50-0
PubChem : 2268
UniChem : CJJOSEISRRTUQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Azinphos-methyl
Target
References (20)
| Title : Environmental concentrations of azinphos-methyl cause different toxic effects without affecting the main target (cholinesterases) in the freshwater gastropod Biomphalaria straminea - Cossi_2018_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_162_287 |
| Author(s) : Cossi PF , Herbert LT , Yusseppone MS , Perez AF , Kristoff G |
| Ref : Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety , 162 :287 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Cossi_2018_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_162_287 |
| ESTHER : Cossi_2018_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_162_287 |
| PubMedSearch : Cossi_2018_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_162_287 |
| PubMedID: 30005401 |
| Title : The relationship between maternal and fetal effects following maternal organophosphate exposure during gestation in the rat - Astroff_1998_Toxicol.Ind.Health_14_869 |
| Author(s) : Astroff AB , Young AD |
| Ref : Toxicol Ind Health , 14 :869 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Astroff_1998_Toxicol.Ind.Health_14_869 |
| ESTHER : Astroff_1998_Toxicol.Ind.Health_14_869 |
| PubMedSearch : Astroff_1998_Toxicol.Ind.Health_14_869 |
| PubMedID: 9891917 |
| Title : Subchronic neurotoxicity screening studies with six organophosphate insecticides: an assessment of behavior and morphology relative to cholinesterase inhibition - Sheets_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_35_101 |
| Author(s) : Sheets LP , Hamilton BF , Sangha GK , Thyssen JH |
| Ref : Fundamental & Applied Toxicology , 35 :101 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Sheets_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_35_101 |
| ESTHER : Sheets_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_35_101 |
| PubMedSearch : Sheets_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_35_101 |
| PubMedID: 9024678 |
| Title : Risk factors for systemic illnesses following agricultural exposures to restricted organophosphates in California, 1984-1988 - Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| Author(s) : Weinbaum Z , Schenker MB , Gold EB , Samuels SJ , O'Malley MA |
| Ref : American Journal of Industrial Medicine , 31 :572 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| ESTHER : Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| PubMedSearch : Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| PubMedID: 9099360 |
| Title : Selective, solid-matrix dispersion extraction of organophosphate pesticide residues from milk - Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| Author(s) : Di Muccio A , Pelosi P , Camoni I , Attard Barbini D , Dommarco R , Generali T , Ausili A |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 754 :497 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| ESTHER : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedSearch : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedID: 8997741 |
| Title : A Point Mutation of Acetylcholinesterase Associated with Azinphosmethyl Resistance and Reduced Fitness in Colorado Potato Beetle - Zhu_1996_Pestic.Biochem.Physiol_55_100 |
| Author(s) : Zhu KY , Lee SH , Clark JM |
| Ref : Pestic Biochem Physiol , 55 :100 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Zhu_1996_Pestic.Biochem.Physiol_55_100 |
| ESTHER : Zhu_1996_Pestic.Biochem.Physiol_55_100 |
| PubMedSearch : Zhu_1996_Pestic.Biochem.Physiol_55_100 |
| PubMedID: 8980034 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: lepde-ACHE |
| Title : Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction procedure for multiresidue pesticide analysis in oranges - Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| Author(s) : Torres CM , Pico Y , Redondo MJ , Manes J |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 719 :95 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| ESTHER : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedSearch : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedID: 8589838 |
| Title : Effect of pesticide mixtures on in vitro nervous cells: comparison with single pesticides - Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| Author(s) : Marinovich M , Ghilardi F , Galli CL |
| Ref : Toxicology , 108 :201 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| ESTHER : Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| PubMedSearch : Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| PubMedID: 8658539 |
| Title : Genotoxicity assay of five pesticides and their mixtures in Saccharomyces cerevisiae D7 - Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| Author(s) : Bianchi L , Zannoli A , Pizzala R , Stivala LA , Chiesara E |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 321 :203 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| ESTHER : Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| PubMedSearch : Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| PubMedID: 7515158 |
| Title : Mixtures of benomyl, pirimiphos-methyl, dimethoate, diazinon and azinphos-methyl affect protein synthesis in HL-60 cells differently - Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| Author(s) : Marinovich M , Guizzetti M , Galli CL |
| Ref : Toxicology , 94 :173 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| ESTHER : Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| PubMedSearch : Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| PubMedID: 7801320 |
| Title : Monitoring Peach Harvest Workers Exposed to Azinphosmethyl Residues in Sutter County, California, 1991 - Schneider_1994_Environ.Health.Perspect_102_580 |
| Author(s) : Schneider F , Steenland K , Hernandez B , Wilson B , Krieger R , Spencer J , Margetich S |
| Ref : Environmental Health Perspectives , 102 :580 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Schneider_1994_Environ.Health.Perspect_102_580 |
| ESTHER : Schneider_1994_Environ.Health.Perspect_102_580 |
| PubMedSearch : Schneider_1994_Environ.Health.Perspect_102_580 |
| PubMedID: 9679119 |
| Title : Safety\/risk assessment of pesticides: principles, procedures and examples - Lu_1992_Toxicol.Lett_64_783 |
| Author(s) : Lu FC , Dourson ML |
| Ref : Toxicol Lett , 64-65 :783 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Lu_1992_Toxicol.Lett_64_783 |
| ESTHER : Lu_1992_Toxicol.Lett_64_783 |
| PubMedSearch : Lu_1992_Toxicol.Lett_64_783 |
| PubMedID: 1471237 |
| Title : Determination of organophosphorous and carbamate insecticides by flow injection analysis - Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| Author(s) : Kumaran S , Tran-Minh C |
| Ref : Analytical Biochemistry , 200 :187 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| ESTHER : Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| PubMedSearch : Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| PubMedID: 1595894 |
| Title : Dialkylphosphorus metabolites in the urine and activities of esterases in the serum as biochemical indices for human absorption of organophosphorus pesticides - Drevenkar_1991_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_20_417 |
| Author(s) : Drevenkar V , Radic Z , Vasilic Z , Reiner E |
| Ref : Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 20 :417 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Drevenkar_1991_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_20_417 |
| ESTHER : Drevenkar_1991_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_20_417 |
| PubMedSearch : Drevenkar_1991_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_20_417 |
| PubMedID: 1650168 |
| Title : Monitoring Ontario-grown apples for pest control chemicals used in their production, 1978-86 - Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| Author(s) : Frank R , Braun HE , Ripley BD |
| Ref : Food Additives & Contaminants , 6 :227 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| ESTHER : Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| PubMedSearch : Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| PubMedID: 2924979 |
| Title : Sister-chromatid exchanges and cell-cycle delay in Chinese hamster V79 cells treated with 9 organophosphorus compounds (8 pesticides and 1 defoliant) - Chen_1982_Mutat.Res_103_307 |
| Author(s) : Chen HH , Sirianni SR , Huang CC |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 103 :307 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Chen_1982_Mutat.Res_103_307 |
| ESTHER : Chen_1982_Mutat.Res_103_307 |
| PubMedSearch : Chen_1982_Mutat.Res_103_307 |
| PubMedID: 6211614 |
| Title : Die insektiziden Phosphorsaureester - Schrader_1961_Angew.Chem_69_86 |
| Author(s) : Schrader G |
| Ref : Angewandte Chemie , 69 :86 , 1957 |
| Abstract : Schrader_1961_Angew.Chem_69_86 |
| ESTHER : Schrader_1961_Angew.Chem_69_86 |
| PubMedSearch : Schrader_1961_Angew.Chem_69_86 |
| PubMedID: |
| Title : Neuer spezifischer Nachweis des lnsektizides Bayer 17147 Gusathion - Wollenberg_1956_Angew.Chem_68_41 |
| Author(s) : Wollenberg O , Schrader G |
| Ref : Angewandte Chemie , 68 :41 , 1956 |
| Abstract : Wollenberg_1956_Angew.Chem_68_41 |
| ESTHER : Wollenberg_1956_Angew.Chem_68_41 |
| PubMedSearch : Wollenberg_1956_Angew.Chem_68_41 |
| PubMedID: |