Cyclipostin-P
General
Type : Organophosphate,Cyclic OP,Lipase inhibitor,Natural
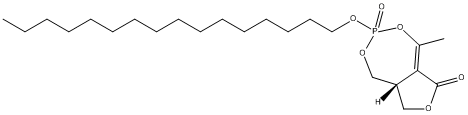
Chemical_Nomenclature : (8aR)-3-hexadecoxy-5-methyl-3-oxido-8,8a-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-e][1,3,2]dioxaphosphepin-3-ium-6-one
Canonical SMILES : CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCO[P+]1(OCC2COC(=O)C2=C(O1)C)[O-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C23H41O6P\/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-27-30(25)28-19-21-18-26-23(24)22(21)20(2)29-30\/h21H,3-19H2,1-2H3\/t21-,30?\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : LXXPVFWDVXTYTB-BPADPFCFSA-N
Other name(s) : (1beta)-4beta-(Hexadecyloxy)-6-methyl-8-oxo-3,5,9-trioxa-4-phosphabicyclo[5.3.0]deca-6-ene 4-oxide,(6S)-6alpha-(Hexadecyloxy)-8-methyl-3,3abeta-dihydro-1H,4H,6H-2,5,7-trioxa-6-phosphaazulene-1-one 6-oxide,Cyc18,Cyc 18,Cyc-18
MW : 444.54
Formula : C23H41O6P
CAS_number :
PubChem : 101182228
UniChem : LXXPVFWDVXTYTB-BPADPFCFSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : Cyclipostin-P ligand of proteins in family: Hormone-sensitive_lipase_like || Monoglyceridelipase_lysophospholip || Cutinase
Stucture :
Protein : ratno-hslip || myctu-rv0183 || myctu-Rv3097c || fusso-cutas
References (3)
| Title : Rat hormone sensitive lipase inhibition by cyclipostins and their analogs - Vasilieva_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_944 |
| Author(s) : Vasilieva E , Dutta S , Malla RK , Martin BP , Spilling CD , Dupureur CM |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry , 23 :944 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Vasilieva_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_944 |
| ESTHER : Vasilieva_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_944 |
| PubMedSearch : Vasilieva_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_944 |
| PubMedID: 25678014 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: ratno-hslip |
| Title : Synthesis and kinetic evaluation of cyclophostin and cyclipostins phosphonate analogs as selective and potent inhibitors of microbial lipases - Point_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_10204 |
| Author(s) : Point V , Malla RK , Diomande S , Martin BP , Delorme V , Carriere F , Canaan S , Rath NP , Spilling CD , Cavalier JF |
| Ref : Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 55 :10204 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Point_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_10204 |
| ESTHER : Point_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_10204 |
| PubMedSearch : Point_2012_J.Med.Chem_55_10204 |
| PubMedID: 23095026 |
| Title : The first total synthesis of (+\/-)-cyclophostin and (+\/-)-cyclipostin P: inhibitors of the serine hydrolases acetyl cholinesterase and hormone sensitive lipase - Malla_2011_Org.Lett_13_3094 |
| Author(s) : Malla RK , Bandyopadhyay S , Spilling CD , Dutta S , Dupureur CM |
| Ref : Org Lett , 13 :3094 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Malla_2011_Org.Lett_13_3094 |
| ESTHER : Malla_2011_Org.Lett_13_3094 |
| PubMedSearch : Malla_2011_Org.Lett_13_3094 |
| PubMedID: 21591624 |