DSF
organosulfur cannabinoid CB1 receptor ligand. NTE Neuropathy target esterase and general LYsophospholipase_carboxylesterase or lipase inhibitor
General
Type : Sulfur Compound,Sulfonyl,NTE inhibitor,Not A\/B H target,Lipase inhibitor
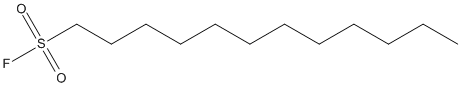
Chemical_Nomenclature : dodecane-1-sulfonyl fluoride
Canonical SMILES : CCCCCCCCCCCCS(=O)(=O)F
InChI : InChI=1S\/C12H25FO2S\/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-16(13,14)15\/h2-12H2,1H3
InChIKey : UVLRFDMRDPQRSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : CHEMBL97038,Dodecanesulfonyl fluoride,SCHEMBL1470419,DNC014029,LS-191509
MW : 252.38
Formula : C12H25FO2S
CAS_number :
PubChem : 18516661
UniChem : UVLRFDMRDPQRSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : DSF ligand of proteins in family: LYsophospholipase_carboxylesterase || Acidic_Lipase
Stucture :
Protein :
References (3)
| Title : Lysophospholipase inhibition by organophosphorus toxicants - Quistad_2004_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_196_319 |
| Author(s) : Quistad GB , Casida JE |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 196 :319 , 2004 |
| Abstract : Quistad_2004_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_196_319 |
| ESTHER : Quistad_2004_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_196_319 |
| PubMedSearch : Quistad_2004_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_196_319 |
| PubMedID: 15094302 |
| Title : Toxicological and structural features of organophosphorus and organosulfur cannabinoid CB1 receptor ligands - Segall_2003_Toxicol.Sci_76_131 |
| Author(s) : Segall Y , Quistad GB , Sparks SE , Nomura DK , Casida JE |
| Ref : Toxicol Sci , 76 :131 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Segall_2003_Toxicol.Sci_76_131 |
| ESTHER : Segall_2003_Toxicol.Sci_76_131 |
| PubMedSearch : Segall_2003_Toxicol.Sci_76_131 |
| PubMedID: 12944586 |
| Title : Novel trifluoromethyl ketones as potent gastric lipase inhibitors - Kokotos_2003_Chembiochem_4_90 |
| Author(s) : Kokotos G , Kotsovolou S , Verger R |
| Ref : Chembiochem , 4 :90 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Kokotos_2003_Chembiochem_4_90 |
| ESTHER : Kokotos_2003_Chembiochem_4_90 |
| PubMedSearch : Kokotos_2003_Chembiochem_4_90 |
| PubMedID: 12512081 |