GV
General
Type : Chemical Warfare Agent,Organophosphate,Nerve Agent G-series
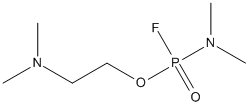
Chemical_Nomenclature : 2-[dimethylamino(fluoro)phosphoryl]oxy-N,N-dimethylethanamine
Canonical SMILES : CN(C)CCOP(=O)(N(C)C)F
InChI : InChI=1S\/C6H16FN2O2P\/c1-8(2)5-6-11-12(7,10)9(3)4\/h5-6H2,1-4H3
InChIKey : SQOVUABAJBECMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 2-dimethylaminoethyl-(dimethylamido)fluorophosphate,2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl N,N-dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate,GV-Substance,GV Substance,GV-Phosphoramidofluoridate,SCHEMBL16428101,GP,DMAEDMAPP
MW : 198.18
Formula : C6H16FN2O2P
CAS_number : 141102-74-1
PubChem : 132333
UniChem : SQOVUABAJBECMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
References (5)
| Title : Structural and Biochemical Insights into the Inhibition of Human Acetylcholinesterase by G-Series Nerve Agents and Subsequent Reactivation by HI-6 - McGuire_2021_Chem.Res.Toxicol_34_804 |
| Author(s) : McGuire JR , Bester SM , Guelta MA , Cheung J , Langley C , Winemiller MD , Bae SY , Funk V , Myslinski JM , Pegan SD , Height JJ |
| Ref : Chemical Research in Toxicology , 34 :804 , 2021 |
| Abstract : McGuire_2021_Chem.Res.Toxicol_34_804 |
| ESTHER : McGuire_2021_Chem.Res.Toxicol_34_804 |
| PubMedSearch : McGuire_2021_Chem.Res.Toxicol_34_804 |
| PubMedID: 33538594 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-ACHE |
| Title : Therapeutic efficacy of obidoxime or HI-6 with atropine against intoxication with some nerve agents in mice - Kassa_1996_Acta.Medica.(Hradec.Kralove)_39_27 |
| Author(s) : Kassa J , Bajgar J |
| Ref : Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) , 39 :27 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Kassa_1996_Acta.Medica.(Hradec.Kralove)_39_27 |
| ESTHER : Kassa_1996_Acta.Medica.(Hradec.Kralove)_39_27 |
| PubMedSearch : Kassa_1996_Acta.Medica.(Hradec.Kralove)_39_27 |
| PubMedID: 9106387 |
| Title : [Comparison of the effect of selected anticholinergic agents on cholinergic and noncholinergic effects of GV substances during acute poisoning in rats]. [Czech] - Kassa_1994_Ceska.Slov.Farm_43_222 |
| Author(s) : Kassa J , Bajgar J |
| Ref : Ceska a Slovenska Farmacie , 43 :222 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Kassa_1994_Ceska.Slov.Farm_43_222 |
| ESTHER : Kassa_1994_Ceska.Slov.Farm_43_222 |
| PubMedSearch : Kassa_1994_Ceska.Slov.Farm_43_222 |
| PubMedID: 7982005 |
| Title : Treatment of intoxication with GV compound in laboratory rats - Fusek_1994_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_37_57 |
| Author(s) : Fusek J , Bajgar J |
| Ref : Sb Ved Pr Lek Fak Karlovy Univerzity Hradci Kralove , 37 :57 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Fusek_1994_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_37_57 |
| ESTHER : Fusek_1994_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_37_57 |
| PubMedSearch : Fusek_1994_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_37_57 |
| PubMedID: 7784799 |
| Title : Anticholinesterase action of organophosphates: importance of the liver - Skopec_1993_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_36_83 |
| Author(s) : Skopec F , Bajgar J |
| Ref : Sb Ved Pr Lek Fak Karlovy Univerzity Hradci Kralove , 36 :83 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Skopec_1993_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_36_83 |
| ESTHER : Skopec_1993_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_36_83 |
| PubMedSearch : Skopec_1993_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove_36_83 |
| PubMedID: 8165434 |