Ladostigil
bifunctional compound: monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, rasagiline linked to a carbamate || Bifunctional drug derivative
General
Type : Monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor,Multitarget,Carbamate,Drug,Inden
Chemical_Nomenclature : [(3R)-3-(prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl] N-ethyl-N-methylcarbamate
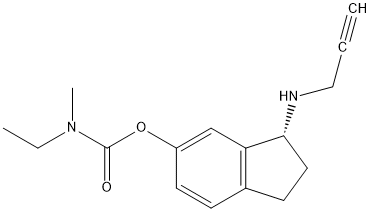
Canonical SMILES : CCN(C)C(=O)OC1=CC2=C(CCC2NCC#C)C=C1
InChI : InChI=1S\/C16H20N2O2\/c1-4-10-17-15-9-7-12-6-8-13(11-14(12)15)20-16(19)18(3)5-2\/h1,6,8,11,15,17H,5,7,9-10H2,2-3H3\/t15-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : LHXOCOHMBFOVJS-OAHLLOKOSA-N
Other name(s) : (N-propargyl-(3R) aminoindan-5-yl)-ethyl methyl carbamate,(3R)-3-(Prop-2-ynylamino)indan-5-yl ethyl(methyl)carbamate,TV3326,TV-3326
MW : 272.342
Formula : C16H20N2O2
CAS_number : 209394-27-4
PubChem : 208907
UniChem : LHXOCOHMBFOVJS-OAHLLOKOSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Ladostigil
Target
References (20)
| Title : TV 3326 for Alzheimer's dementia: a novel multimodal ChE and MAO inhibitors to mitigate Alzheimer's-like neuropathology - Uddin_2020_J.Pharm.Pharmacol__ |
| Author(s) : Uddin S , Kabir T , Rahman M , Mathew B , Shah MA , Ashraf GM |
| Ref : J Pharm Pharmacol , : , 2020 |
| Abstract : Uddin_2020_J.Pharm.Pharmacol__ |
| ESTHER : Uddin_2020_J.Pharm.Pharmacol__ |
| PubMedSearch : Uddin_2020_J.Pharm.Pharmacol__ |
| PubMedID: 32149402 |
| Title : The path from anti Parkinson drug selegiline and rasagiline to multifunctional neuroprotective anti Alzheimer drugs ladostigil and m30 - Youdim_2006_Curr.Alzheimer.Res_3_541 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB |
| Ref : Curr Alzheimer Res , 3 :541 , 2006 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2006_Curr.Alzheimer.Res_3_541 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2006_Curr.Alzheimer.Res_3_541 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2006_Curr.Alzheimer.Res_3_541 |
| PubMedID: 17168653 |
| Title : The neurochemical and behavioral effects of the novel cholinesterase-monoamine oxidase inhibitor, ladostigil, in response to L-dopa and L-tryptophan, in rats - Sagi_2005_Br.J.Pharmacol_146_553 |
| Author(s) : Sagi Y , Drigues N , Youdim MB |
| Ref : British Journal of Pharmacology , 146 :553 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Sagi_2005_Br.J.Pharmacol_146_553 |
| ESTHER : Sagi_2005_Br.J.Pharmacol_146_553 |
| PubMedSearch : Sagi_2005_Br.J.Pharmacol_146_553 |
| PubMedID: 16086033 |
| Title : Bifunctional drug derivatives of MAO-B inhibitor rasagiline and iron chelator VK-28 as a more effective approach to treatment of brain ageing and ageing neurodegenerative diseases - Youdim_2005_Mech.Ageing.Dev_126_317 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Fridkin M , Zheng H |
| Ref : Mech Ageing Dev , 126 :317 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2005_Mech.Ageing.Dev_126_317 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2005_Mech.Ageing.Dev_126_317 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2005_Mech.Ageing.Dev_126_317 |
| PubMedID: 15621213 |
| Title : Multi-functional drugs for various CNS targets in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders - Youdim_2005_Trends.Pharmacol.Sci_26_27 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Buccafusco JJ |
| Ref : Trends in Pharmacological Sciences , 26 :27 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2005_Trends.Pharmacol.Sci_26_27 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2005_Trends.Pharmacol.Sci_26_27 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2005_Trends.Pharmacol.Sci_26_27 |
| PubMedID: 15629202 |
| Title : CNS Targets for multi-functional drugs in the treatment of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases - Youdim_2005_J.Neural.Transm.(Vienna)_112_519 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Buccafusco JJ |
| Ref : J Neural Transm (Vienna) , 112 :519 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2005_J.Neural.Transm.(Vienna)_112_519 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2005_J.Neural.Transm.(Vienna)_112_519 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2005_J.Neural.Transm.(Vienna)_112_519 |
| PubMedID: 15666041 |
| Title : Recent approaches to novel anti-Alzheimer therapy - Carreiras_2004_Curr.Pharm.Des_10_3167 |
| Author(s) : Carreiras MC , Marco JL |
| Ref : Curr Pharm Des , 10 :3167 , 2004 |
| Abstract : Carreiras_2004_Curr.Pharm.Des_10_3167 |
| ESTHER : Carreiras_2004_Curr.Pharm.Des_10_3167 |
| PubMedSearch : Carreiras_2004_Curr.Pharm.Des_10_3167 |
| PubMedID: 15544506 |
| Title : Therapeutic applications of selective and non-selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A and B that do not cause significant tyramine potentiation - Youdim_2004_Neurotoxicol_25_243 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Weinstock M |
| Ref : Neurotoxicology , 25 :243 , 2004 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2004_Neurotoxicol_25_243 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2004_Neurotoxicol_25_243 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2004_Neurotoxicol_25_243 |
| PubMedID: 14697899 |
| Title : Potential cognitive actions of (n-propargly-(3r)-aminoindan-5-yl)-ethyl, methyl carbamate (tv3326), a novel neuroprotective agent, as assessed in old rhesus monkeys in their performance of versions of a delayed matching task - Buccafusco_2003_Neurosci_119_669 |
| Author(s) : Buccafusco JJ , Terry AV, Jr. , Goren T , Blaugrun E |
| Ref : Neuroscience , 119 :669 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Buccafusco_2003_Neurosci_119_669 |
| ESTHER : Buccafusco_2003_Neurosci_119_669 |
| PubMedSearch : Buccafusco_2003_Neurosci_119_669 |
| PubMedID: 12809688 |
| Title : Amyloid Processing and Signal Transduction Properties of Antiparkinson-Antialzheimer Neuroprotective Drugs Rasagiline and TV3326 - Youdim_2003_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_993_378 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Amit T , Bar-Am O , Weinstock M , Yogev-Falach M |
| Ref : Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences , 993 :378 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2003_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_993_378 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2003_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_993_378 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2003_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_993_378 |
| PubMedID: 12853332 |
| Title : Anti-apoptotic action of anti-Alzheimer drug, TV3326 [(N-propargyl)-(3R)-aminoindan-5-yl]-ethyl methyl carbamate, a novel cholinesterase-monoamine oxidase inhibitor - Maruyama_2003_Neurosci.Lett_341_233 |
| Author(s) : Maruyama W , Weinstock M , Youdim MB , Nagai M , Naoi M |
| Ref : Neuroscience Letters , 341 :233 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Maruyama_2003_Neurosci.Lett_341_233 |
| ESTHER : Maruyama_2003_Neurosci.Lett_341_233 |
| PubMedSearch : Maruyama_2003_Neurosci.Lett_341_233 |
| PubMedID: 12697291 |
| Title : Attenuation of MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity by TV3326, a cholinesterase-monoamine oxidase inhibitor - Sagi_2003_J.Neurochem_86_290 |
| Author(s) : Sagi Y , Weinstock M , Youdim MB |
| Ref : Journal of Neurochemistry , 86 :290 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Sagi_2003_J.Neurochem_86_290 |
| ESTHER : Sagi_2003_J.Neurochem_86_290 |
| PubMedSearch : Sagi_2003_J.Neurochem_86_290 |
| PubMedID: 12871570 |
| Title : Novel neuroprotective anti-Alzheimer drugs with anti-depressant activity derived from the anti-Parkinson drug, rasagiline - Youdim_2002_Mech.Ageing.Dev_123_1081 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Weinstock M |
| Ref : Mech Ageing Dev , 123 :1081 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2002_Mech.Ageing.Dev_123_1081 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2002_Mech.Ageing.Dev_123_1081 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2002_Mech.Ageing.Dev_123_1081 |
| PubMedID: 12044957 |
| Title : Effect of TV3326, a novel monoamine-oxidase cholinesterase inhibitor, in rat models of anxiety and depression - Weinstock_2002_Psychopharmacology.(Berl)_160_318 |
| Author(s) : Weinstock M , Poltyrev T , Bejar C , Youdim MB |
| Ref : Psychopharmacology (Berl) , 160 :318 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Weinstock_2002_Psychopharmacology.(Berl)_160_318 |
| ESTHER : Weinstock_2002_Psychopharmacology.(Berl)_160_318 |
| PubMedSearch : Weinstock_2002_Psychopharmacology.(Berl)_160_318 |
| PubMedID: 11889501 |
| Title : The involvement of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in the regulation of amyloid precursor protein processing by novel cholinesterase inhibitors derived from rasagiline - Yogev-Falach_2002_Faseb.J_16_1674 |
| Author(s) : Yogev-Falach M , Amit T , Bar-Am O , Weinstock M , Youdim MB |
| Ref : FASEB Journal , 16 :1674 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Yogev-Falach_2002_Faseb.J_16_1674 |
| ESTHER : Yogev-Falach_2002_Faseb.J_16_1674 |
| PubMedSearch : Yogev-Falach_2002_Faseb.J_16_1674 |
| PubMedID: 12206996 |
| Title : Limited potentiation of blood pressure response to oral tyramine by brain-selective monoamine oxidase A-B inhibitor, TV-3326 in conscious rabbits(1) - Weinstock_2002_Neuropharmacol_43_999 |
| Author(s) : Weinstock M , Gorodetsky E , Wang RH , Gross A , Weinreb O , Youdim MB |
| Ref : Neuropharmacology , 43 :999 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Weinstock_2002_Neuropharmacol_43_999 |
| ESTHER : Weinstock_2002_Neuropharmacol_43_999 |
| PubMedSearch : Weinstock_2002_Neuropharmacol_43_999 |
| PubMedID: 12423669 |
| Title : Molecular basis of neuroprotective activities of rasagiline and the anti-Alzheimer drug TV3326 [(N-propargyl-(3R)aminoindan-5-YL)-ethyl methyl carbamate] - Youdim_2001_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_21_555 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Weinstock M |
| Ref : Cellular Molecular Neurobiology , 21 :555 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2001_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_21_555 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2001_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_21_555 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2001_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_21_555 |
| PubMedID: 12043833 |
| Title : Neuroprotective effects of novel cholinesterase inhibitors derived from rasagiline as potential anti-Alzheimer drugs - Weinstock_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_148 |
| Author(s) : Weinstock M , Kirschbaum-Slager N , Lazarovici P , Bejar C , Youdim MB , Shoham S |
| Ref : Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences , 939 :148 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Weinstock_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_148 |
| ESTHER : Weinstock_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_148 |
| PubMedSearch : Weinstock_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_148 |
| PubMedID: 11462767 |
| Title : The anti-Parkinson drug rasagiline and its cholinesterase inhibitor derivatives exert neuroprotection unrelated to MAO inhibition in cell culture and in vivo - Youdim_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_450 |
| Author(s) : Youdim MB , Wadia A , Tatton W , Weinstock M |
| Ref : Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences , 939 :450 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Youdim_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_450 |
| ESTHER : Youdim_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_450 |
| PubMedSearch : Youdim_2001_Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci_939_450 |
| PubMedID: 11462801 |
| Title : TV3326, a novel neuroprotective drug with cholinesterase and monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease - Weinstock_2000_J.Neural.Transm.Suppl__157 |
| Author(s) : Weinstock M , Bejar C , Wang RH , Poltyrev T , Gross A , Finberg JP , Youdim MB |
| Ref : J Neural Transm Suppl , :157 , 2000 |
| Abstract : Weinstock_2000_J.Neural.Transm.Suppl__157 |
| ESTHER : Weinstock_2000_J.Neural.Transm.Suppl__157 |
| PubMedSearch : Weinstock_2000_J.Neural.Transm.Suppl__157 |
| PubMedID: 11205137 |