Malathion
insecticide, lipid soluble. Oxidises to Malaoxon which is more toxic
General
Type : Insecticide,Acaricide,Organophosphate,Sulfur Compound,Organothiophosphate
Chemical_Nomenclature : diethyl 2-dimethoxyphosphinothioylsulfanylbutanedioate
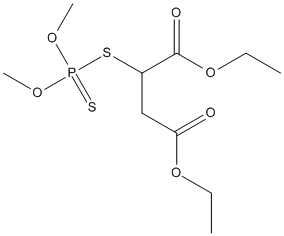
Canonical SMILES : CCOC(=O)CC(C(=O)OCC)SP(=S)(OC)OC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C10H19O6PS2\/c1-5-15-9(11)7-8(10(12)16-6-2)19-17(18,13-3)14-4\/h8H,5-7H2,1-4H3
InChIKey : JXSJBGJIGXNWCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : O,O'-dimethyl S-(1,2-dicarboxyethoxyethyl) phosphorothiolothionate or phosphorodithioate,s-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) O,O'-dimethyldithiophosphate,O,O'-dimethyl S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) thiothionophosphate,Malothon,Phosphoton,Cythion,calmathion,carbetox,carbethoxy malathion,arbetovur,celthion,cimexan,compound 4049,detmol ma,Malaspray,Ethiolacar,Etiol,Cleensheen,Lice Rid,Carbophos,Maldison,Mercaptothion
MW : 330.36
Formula : C10H19O6PS2
CAS_number : 121-75-5
PubChem : 4004
UniChem : JXSJBGJIGXNWCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Malathion
Target
References (62)
| Title : Evaluation of insecticide resistance and biochemical mechanisms in a population of culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Sao Paulo, Brazil - Bracco_1999_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_94_115 |
| Author(s) : Bracco JE , Barata JM , Marinotti O |
| Ref : Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz , 94 :115 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Bracco_1999_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_94_115 |
| ESTHER : Bracco_1999_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_94_115 |
| PubMedSearch : Bracco_1999_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_94_115 |
| PubMedID: 10029921 |
| Title : Dimethylphosphorus metabolites in serum and urine of persons poisoned by malathion or thiometon - Vasilic_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_479 |
| Author(s) : Vasilic Z , Stengl B , Drevenkar V |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 119-120 :479 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Vasilic_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_479 |
| ESTHER : Vasilic_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_479 |
| PubMedSearch : Vasilic_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_479 |
| PubMedID: 10421486 |
| Title : The use of biomarkers to measure the interactive effects of chemicals - Walker_1998_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_40_65 |
| Author(s) : Walker CH |
| Ref : Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety , 40 :65 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Walker_1998_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_40_65 |
| ESTHER : Walker_1998_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_40_65 |
| PubMedSearch : Walker_1998_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_40_65 |
| PubMedID: 98289839 |
| Title : Evaluation of organophosphorus pesticide residues in citrus fruits from the Valencian community (Spain) - Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| Author(s) : Torres CM , Pico Y , Marin R , Manes J |
| Ref : Journal of AOAC International , 80 :1122 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| ESTHER : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| PubMedSearch : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| PubMedID: 9325585 |
| Title : Effect of administration of malathion for 14 days on macrophage function and mast cell degranulation - Rodgers_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_37_95 |
| Author(s) : Rodgers K , Xiong S |
| Ref : Fundamental & Applied Toxicology , 37 :95 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Rodgers_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_37_95 |
| ESTHER : Rodgers_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_37_95 |
| PubMedSearch : Rodgers_1997_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_37_95 |
| PubMedID: 9193927 |
| Title : Effects of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides on acetylcholinesterase and choline acetyltransferase activities of the polychaete Nereis diversicolor - Scaps_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_203 |
| Author(s) : Scaps P , Demuynck S , Descamps M , Dhainaut A |
| Ref : Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 33 :203 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Scaps_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_203 |
| ESTHER : Scaps_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_203 |
| PubMedSearch : Scaps_1997_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_33_203 |
| PubMedID: 9294250 |
| Title : Renal effects of chronic exposure to malathion in Octodon degus - Bosco_1997_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_118_247 |
| Author(s) : Bosco C , Rodrigo R , Diaz S , Borax J |
| Ref : Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology C Pharmacology Toxicology & Endocrinology , 118 :247 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Bosco_1997_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_118_247 |
| ESTHER : Bosco_1997_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_118_247 |
| PubMedSearch : Bosco_1997_Comp.Biochem.Physiol.C.Pharmacol.Toxicol.Endocrinol_118_247 |
| PubMedID: 9440252 |
| Title : Susceptibility of Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae) to selected insecticides in an endemic focus of visceral leishmaniasis in Venezuela - Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| Author(s) : Mazzarri MB , Feliciangeli MD , Maroli M , Hernandez A , Bravo A |
| Ref : J Am Mosq Control Assoc , 13 :335 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| ESTHER : Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| PubMedSearch : Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| PubMedID: 9474559 |
| Title : Human mortality in organophosphate poisonings - Yamashita_1997_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_39_84 |
| Author(s) : Yamashita M , Tanaka J , Ando Y |
| Ref : Vet Hum Toxicol , 39 :84 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Yamashita_1997_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_39_84 |
| ESTHER : Yamashita_1997_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_39_84 |
| PubMedSearch : Yamashita_1997_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_39_84 |
| PubMedID: 9080632 |
| Title : [Determination of insecticide resistance and its biochemical mechanisms in 2 strains of Culex quinquefasciatus from Santiago de Cuba] - Rodriguez_1997_Rev.Cubana.Med.Trop_49_209 |
| Author(s) : Rodriguez MM , Bisset J , Rodriguez I , Diaz C |
| Ref : Rev Cubana Med Trop , 49 :209 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Rodriguez_1997_Rev.Cubana.Med.Trop_49_209 |
| ESTHER : Rodriguez_1997_Rev.Cubana.Med.Trop_49_209 |
| PubMedSearch : Rodriguez_1997_Rev.Cubana.Med.Trop_49_209 |
| PubMedID: 9685989 |
| Title : Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction procedure for multiresidue pesticide analysis in oranges - Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| Author(s) : Torres CM , Pico Y , Redondo MJ , Manes J |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 719 :95 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| ESTHER : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedSearch : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedID: 8589838 |
| Title : Yellowfever mosquito (Diptera:Culicidae) introduced into Landi Kotal, Pakistan, by tire importation - Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| Author(s) : Suleman M , Arshad M , Khan K |
| Ref : Journal of Medical Entomology , 33 :689 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| ESTHER : Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| PubMedSearch : Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| PubMedID: 8699469 |
| Title : Efficiency of some technological processes on reducing the residues of malathion and pirimiphos methyl in mature broad bean seeds - Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| Author(s) : Kamil ME , Abou-Zahw MM , Hegazy NA |
| Ref : Nahrung , 40 :277 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| ESTHER : Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| PubMedSearch : Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| PubMedID: 8921619 |
| Title : Organophosphate resistance in Culex pipiens from Cyprus - Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| Author(s) : Wirth MC , Georghiou GP |
| Ref : J Am Mosq Control Assoc , 12 :112 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| ESTHER : Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| PubMedSearch : Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| PubMedID: 8723267 |
| Title : Organohalogen and organophosphorus pesticides in mixed feed rations: findings from FDA's domestic surveillance during fiscal years 1989-1994 - Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| Author(s) : Lovell RA , McChesney DG , Price WD |
| Ref : Journal of AOAC International , 79 :544 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| ESTHER : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| PubMedSearch : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| PubMedID: 8920144 |
| Title : Selective, solid-matrix dispersion extraction of organophosphate pesticide residues from milk - Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| Author(s) : Di Muccio A , Pelosi P , Camoni I , Attard Barbini D , Dommarco R , Generali T , Ausili A |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 754 :497 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| ESTHER : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedSearch : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedID: 8997741 |
| Title : Anopheles culicifacies in Baluchistan, Iran - Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| Author(s) : Zaim M , Manouchehri AV , Motabar M , Emadi AM , Nazari M , Pakdad K , Kayedi MH , Mowlaii G |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 9 :181 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| ESTHER : Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| PubMedSearch : Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| PubMedID: 7787227 |
| Title : A resistance of head lice (Pediculus capitis) to permethrin in Czech Republic - Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| Author(s) : Rupes V , Moravec J , Chmela J , Ledvinka J , Zelenkova J |
| Ref : Central European Journal of Public Health , 3 :30 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| ESTHER : Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| PubMedSearch : Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| PubMedID: 7787823 |
| Title : The study of interactive effects of pollutants: a biomarker approach. - Johnston_1995_Sci.Tot.Environ_171_205 |
| Author(s) : Johnston G |
| Ref : Sci Tot Environ , 171 :205 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Johnston_1995_Sci.Tot.Environ_171_205 |
| ESTHER : Johnston_1995_Sci.Tot.Environ_171_205 |
| PubMedSearch : Johnston_1995_Sci.Tot.Environ_171_205 |
| PubMedID: 7481747 |
| Title : Fenitrothion intoxication during spraying operations in the malaria programme for Afghan refugees in North West Frontier Province of Pakistan - Bouma_1995_Trop.Geog.Med_47_12 |
| Author(s) : Bouma MJ , Nesbit R |
| Ref : Tropical & Geographical Medicine , 47 :12 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Bouma_1995_Trop.Geog.Med_47_12 |
| ESTHER : Bouma_1995_Trop.Geog.Med_47_12 |
| PubMedSearch : Bouma_1995_Trop.Geog.Med_47_12 |
| PubMedID: 7747323 |
| Title : Effects of three organophosphorus insecticides in the reproductive potential of Culex quinquefasciatus - Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| Author(s) : Aguilera L , Marquetti MC , Navarro A , Bisset J |
| Ref : Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz , 90 :411 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| ESTHER : Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| PubMedSearch : Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| PubMedID: 8544743 |
| Title : Insecticide susceptibility in mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) from French Polynesia - Failloux_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_639 |
| Author(s) : Failloux AB , Ung A , Raymond M , Pasteur N |
| Ref : Journal of Medical Entomology , 31 :639 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Failloux_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_639 |
| ESTHER : Failloux_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_639 |
| PubMedSearch : Failloux_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_639 |
| PubMedID: 7966164 |
| Title : Isolation of an esterase conferring insecticide resistance in the mosquito Culex tarsalis - Whyard_1994_Insect.Biochem.Mol.Biol_24_819 |
| Author(s) : Whyard S , Downe AE , Walker VK |
| Ref : Insect Biochemistry & Molecular Biology , 24 :819 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Whyard_1994_Insect.Biochem.Mol.Biol_24_819 |
| ESTHER : Whyard_1994_Insect.Biochem.Mol.Biol_24_819 |
| PubMedSearch : Whyard_1994_Insect.Biochem.Mol.Biol_24_819 |
| PubMedID: 7981729 |
| Title : Insecticide resistance and malathion carboxylesterase in the sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina - Whyard_1994_Biochem.Genet_32_9 |
| Author(s) : Whyard S , Russell RJ , Walker VK |
| Ref : Biochemical Genetics , 32 :9 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Whyard_1994_Biochem.Genet_32_9 |
| ESTHER : Whyard_1994_Biochem.Genet_32_9 |
| PubMedSearch : Whyard_1994_Biochem.Genet_32_9 |
| PubMedID: 8031296 |
| Title : Correlation of the anticholinesterase activity of a series of organophosphates with their ability to compete with agonist binding to muscarinic receptors - Ward_1993_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_122_300 |
| Author(s) : Ward TR , Ferris DJ , Tilson HA , Mundy WR |
| Ref : Toxicology & Applied Pharmacology , 122 :300 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Ward_1993_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_122_300 |
| ESTHER : Ward_1993_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_122_300 |
| PubMedSearch : Ward_1993_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_122_300 |
| PubMedID: 8212012 |
| Title : Changes in malathion and pyrethroid resistance after cypermethrin selection of Culex quinquefasciatus field populations of Cuba - Rodriguez_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_117 |
| Author(s) : Rodriguez M , Ortiz E , Bisset JA , Hemingway J , Saledo E |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 7 :117 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Rodriguez_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_117 |
| ESTHER : Rodriguez_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_117 |
| PubMedSearch : Rodriguez_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_117 |
| PubMedID: 8481527 |
| Title : Control of Mansonia mosquitos, vectors of brugian filariasis in Sarawak, Malaysia - Chang_1993_Southeast.Asian.J.Trop.Med.Public.Health_2_93 |
| Author(s) : Chang MS , Chan KL , Ho BC |
| Ref : Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health , 2 :93 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Chang_1993_Southeast.Asian.J.Trop.Med.Public.Health_2_93 |
| ESTHER : Chang_1993_Southeast.Asian.J.Trop.Med.Public.Health_2_93 |
| PubMedSearch : Chang_1993_Southeast.Asian.J.Trop.Med.Public.Health_2_93 |
| PubMedID: 7973956 |
| Title : Insecticide susceptibility status & enzyme profile of Aedes albopictus populations from different localities of Maharashtra state - Chakraborti_1993_Indian.J.Med.Res_97_37 |
| Author(s) : Chakraborti S , Mourya DT , Gokhale MD , Banerjee K |
| Ref : Indian J Med Res , 97 :37 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Chakraborti_1993_Indian.J.Med.Res_97_37 |
| ESTHER : Chakraborti_1993_Indian.J.Med.Res_97_37 |
| PubMedSearch : Chakraborti_1993_Indian.J.Med.Res_97_37 |
| PubMedID: 8486408 |
| Title : Susceptibility of the bedbug, Cimex lectularius, to selected insecticides and various treated surfaces - Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| Author(s) : Fletcher MG , Axtell RC |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 7 :69 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| ESTHER : Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| PubMedSearch : Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| PubMedID: 8435492 |
| Title : Synthesis, absolute configuration, and analysis of malathion, malaoxon, and isomalathion enantiomers [published erratum appears in Chem Res Toxicol 1994 Mar-Apr\;7(2):275] - Berkman_1993_Chem.Res.Toxicol_6_718 |
| Author(s) : Berkman CE , Thompson CM , Perrin SR |
| Ref : Chemical Research in Toxicology , 6 :718 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Berkman_1993_Chem.Res.Toxicol_6_718 |
| ESTHER : Berkman_1993_Chem.Res.Toxicol_6_718 |
| PubMedSearch : Berkman_1993_Chem.Res.Toxicol_6_718 |
| PubMedID: 8292751 |
| Title : [A study on acute organophosphorus poisoning--changes in the activity and isoenzyme patterns of serum cholinesterase in human poisoning]. [Japanese] - Yamanaka_1993_Japanese.J.Hyg_48_955 |
| Author(s) : Yamanaka S , Yoshida M , Yamamura Y , Nishimura M , Takaesu Y |
| Ref : Nippon Eiseigaku Zasshi Japanese Journal of Hygiene , 48 :955 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Yamanaka_1993_Japanese.J.Hyg_48_955 |
| ESTHER : Yamanaka_1993_Japanese.J.Hyg_48_955 |
| PubMedSearch : Yamanaka_1993_Japanese.J.Hyg_48_955 |
| PubMedID: 8107298 |
| Title : Determination of organophosphorous and carbamate insecticides by flow injection analysis - Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| Author(s) : Kumaran S , Tran-Minh C |
| Ref : Analytical Biochemistry , 200 :187 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| ESTHER : Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| PubMedSearch : Kumaran_1992_Anal.Biochem_200_187 |
| PubMedID: 1595894 |
| Title : Insecticide resistance gene frequencies in Anopheles sacharovi populations of the Cukurova plain, Adana Province, Turkey - Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| Author(s) : Hemingway J , Small GJ , Monro A , Sawyer BV , Kasap H |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 6 :342 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| ESTHER : Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| PubMedSearch : Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| PubMedID: 1463899 |
| Title : The effect of malathion, an organophosphate, on the plasma FSH, 17 beta-estradiol and progesterone concentrations and acetylcholinesterase activity and conception in dairy cattle - Prakash_1992_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_34_116 |
| Author(s) : Prakash N , Narayana K , Murthy GS , Moudgal NR , Honnegowda |
| Ref : Vet Hum Toxicol , 34 :116 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Prakash_1992_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_34_116 |
| ESTHER : Prakash_1992_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_34_116 |
| PubMedSearch : Prakash_1992_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_34_116 |
| PubMedID: 1509669 |
| Title : Malathion and pyrethroid resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus from Cuba: efficacy of pirimiphos-methyl in the presence of at least three resistance mechanisms - Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| Author(s) : Bisset JA , Rodriguez MM , Hemingway J , Diaz C , Small GJ , Ortiz E |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 5 :223 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| ESTHER : Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| PubMedSearch : Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| PubMedID: 1768912 |
| Title : Susceptibilities of northern fowl mite, Ornithonyssus sylviarum (Acarina: Macronyssidae), and chicken mite, Dermanyssus gallinae (Acarina: Dermanyssidae), to selected acaricides - Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| Author(s) : Fletcher MG , Axtell RC |
| Ref : Exp Appl Acarol , 13 :137 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| ESTHER : Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| PubMedSearch : Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| PubMedID: 1786744 |
| Title : Effectiveness of certain drugs in acute malathion intoxication in rats - Husain_1990_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_19_271 |
| Author(s) : Husain K , Ansari RA |
| Ref : Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety , 19 :271 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Husain_1990_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_19_271 |
| ESTHER : Husain_1990_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_19_271 |
| PubMedSearch : Husain_1990_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_19_271 |
| PubMedID: 2364909 |
| Title : Simple analytical method for organophosphorus pesticide residues in milk - Toyoda_1990_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_73_770 |
| Author(s) : Toyoda M , Adachi K , Ida T , Noda K , Minagawa N |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 73 :770 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Toyoda_1990_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_73_770 |
| ESTHER : Toyoda_1990_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_73_770 |
| PubMedSearch : Toyoda_1990_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_73_770 |
| PubMedID: 2273003 |
| Title : Simultaneous determination of some organophosphorus pesticides by high performance liquid chromatography - Kumar_1989_Biomed.Chromatogr_3_272 |
| Author(s) : Kumar R |
| Ref : Biomedical Chromatography , 3 :272 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Kumar_1989_Biomed.Chromatogr_3_272 |
| ESTHER : Kumar_1989_Biomed.Chromatogr_3_272 |
| PubMedSearch : Kumar_1989_Biomed.Chromatogr_3_272 |
| PubMedID: 2620148 |
| Title : Cytotoxicity of certain organic solvents and organophosphorus insecticides to the ciliated protozoan Paramecium caudatum - Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| Author(s) : Rajini PS , Krishnakumari MK , Majumder SK |
| Ref : Microbios , 59 :157 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| ESTHER : Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| PubMedSearch : Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| PubMedID: 2593868 |
| Title : [Exposure to residues on plant surfaces following the use of plant pesticides in the greenhouse] - Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| Author(s) : Goedicke HJ , Hermes H , Wagner R |
| Ref : Z Gesamte Hyg , 35 :531 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| ESTHER : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| PubMedSearch : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| PubMedID: 2588705 |
| Title : Profile of drug metabolizing enzymes in rats treated with parathion, malathion, and phosalone under various conditions of protein energy malnutrition - |
| Author(s) : Bulusu S , Chakravarty I |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 40 :110 , 1988 |
| PubMedID: 3125871 |
| Title : Evaluation of mutagenic activities of endosulfan, phosalone, malathion, and permethrin, before and after metabolic activation, in the Ames Salmonella test - |
| Author(s) : Pednekar MD , Gandhi SR , Netrawali MS |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 38 :925 , 1987 |
| PubMedID: 3555658 |
| Title : Effect of subacute administration of three organophosphorus pesticides on the hepatic phosphatases under various nutritional conditions - Bulusu_1987_Environ.Res_44_126 |
| Author(s) : Bulusu S , Chakravarty I |
| Ref : Environ Research , 44 :126 , 1987 |
| Abstract : Bulusu_1987_Environ.Res_44_126 |
| ESTHER : Bulusu_1987_Environ.Res_44_126 |
| PubMedSearch : Bulusu_1987_Environ.Res_44_126 |
| PubMedID: 2820707 |
| Title : An enzyme test for determining isomalathion impurities in water-dispersible powders of malathion - Reiner_1986_Bull.World.Health.Organ_64_397 |
| Author(s) : Reiner E , Radic Z |
| Ref : Bulletin of the World Health Organization , 64 :397 , 1986 |
| Abstract : Reiner_1986_Bull.World.Health.Organ_64_397 |
| ESTHER : Reiner_1986_Bull.World.Health.Organ_64_397 |
| PubMedSearch : Reiner_1986_Bull.World.Health.Organ_64_397 |
| PubMedID: 3490319 |
| Title : Mutagenic and alkylating activities of organophosphate impurities of commercial malathion - Imamura_1985_Mutat.Res_155_1 |
| Author(s) : Imamura T , Talcott RE |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 155 :1 , 1985 |
| Abstract : Imamura_1985_Mutat.Res_155_1 |
| ESTHER : Imamura_1985_Mutat.Res_155_1 |
| PubMedSearch : Imamura_1985_Mutat.Res_155_1 |
| PubMedID: 3881662 |
| Title : Toxicological properties of trialkyl phosphorothioate and dialkyl alkyl- and arylphosphonothioate esters - Fukuto_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_89 |
| Author(s) : Fukuto TR |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health B , 18 :89 , 1983 |
| Abstract : Fukuto_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_89 |
| ESTHER : Fukuto_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_89 |
| PubMedSearch : Fukuto_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_89 |
| PubMedID: 6833715 |
| Title : Effect of selected pesticides on alkaline and acid phosphatase in the rat - Saigal_1982_Toxicol.Lett_12_177 |
| Author(s) : Saigal S , Bhatnagar VK , Malviya AN |
| Ref : Toxicol Lett , 12 :177 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Saigal_1982_Toxicol.Lett_12_177 |
| ESTHER : Saigal_1982_Toxicol.Lett_12_177 |
| PubMedSearch : Saigal_1982_Toxicol.Lett_12_177 |
| PubMedID: 7112611 |
| Title : A large-scale evaluation of pirimiphos-methyl 25\% WP during 1980-1981 for malaria control in Pakistan - Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| Author(s) : Nasir SM , Ahmad N , Shah MA , Azam CM |
| Ref : J Trop Med Hyg , 85 :239 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| ESTHER : Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| PubMedSearch : Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| PubMedID: 7154146 |
| Title : Observations on the accidental poisoning of birds by organophosphate insecticides and other toxic substances - Reece_1982_Vet.Rec_111_453 |
| Author(s) : Reece RL , Handson P |
| Ref : Vet Rec , 111 :453 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Reece_1982_Vet.Rec_111_453 |
| ESTHER : Reece_1982_Vet.Rec_111_453 |
| PubMedSearch : Reece_1982_Vet.Rec_111_453 |
| PubMedID: 7179689 |
| Title : Electroretinographic study of the white mouse intoxicated by organo- phosphorus: mevinphos and malathion - Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| Author(s) : Carricaburu P , Lacroix R , Lacroix J |
| Ref : Toxicol Eur Res , 3 :87 , 1981 |
| Abstract : Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| ESTHER : Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| PubMedSearch : Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| PubMedID: 7245190 |
| Title : Properties and inhibition of rat malathion carboxylesterases - Mallipudi_1980_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_6_585 |
| Author(s) : Mallipudi NM , Talcott RE , Ketterman A , Fukuto TR |
| Ref : J Toxicol Environ Health , 6 :585 , 1980 |
| Abstract : Mallipudi_1980_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_6_585 |
| ESTHER : Mallipudi_1980_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_6_585 |
| PubMedSearch : Mallipudi_1980_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_6_585 |
| PubMedID: 7420466 |
| Title : Residual toxicity of wall-sprayed organophosphates, carbamates and pyrethroids to mosquito Culex pipiens molestus Forskal - Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| Author(s) : Rettich F |
| Ref : J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol , 24 :110 , 1980 |
| Abstract : Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| ESTHER : Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| PubMedSearch : Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| PubMedID: 7190586 |
| Title : Insecticide residues in milled fractions of dry or tough wheat treated with malathion, bromophos, iodofenphos, and pirimiphos-methyl - |
| Author(s) : Mensah GW , Watters FL , Webster GR |
| Ref : J Econ Entomol , 72 :728 , 1979 |
| PubMedID: 544641 |
| Title : Malathion carboxylesterase activity in human liver and its inactivation by isomalathion - |
| Author(s) : Talcott RE , Denk H , Mallipudi NM |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 49 :373 , 1979 |
| PubMedID: 494286 |
| Title : Isolation and concentration of organophosphorus pesticides from drinking water at the ng\/L level, using macroreticular resin - LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| Author(s) : LeBel GL , Williams DT , Griffith G , Benoit FM |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 62 :241 , 1979 |
| Abstract : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| ESTHER : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| PubMedSearch : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| PubMedID: 447594 |
| Title : The toxicological properties of impurities in malathion - Aldridge_1979_Arch.Toxicol_42_95 |
| Author(s) : Aldridge WN , Miles JW , Mount DL , Verschoyle RD |
| Ref : Archives of Toxicology , 42 :95 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Aldridge_1979_Arch.Toxicol_42_95 |
| ESTHER : Aldridge_1979_Arch.Toxicol_42_95 |
| PubMedSearch : Aldridge_1979_Arch.Toxicol_42_95 |
| PubMedID: 755464 |
| Title : Epidemic malathion poisoning in Pakistan malaria workers - Baker_1978_Lancet_1_31 |
| Author(s) : Baker EL, Jr. , Warren M , Zack M , Dobbin RD , Miles JW , Miller S , Alderman L , Teeters WR |
| Ref : Lancet , 1 :31 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Baker_1978_Lancet_1_31 |
| ESTHER : Baker_1978_Lancet_1_31 |
| PubMedSearch : Baker_1978_Lancet_1_31 |
| PubMedID: 74508 |
| Title : Evaluation of cytotoxic responses caused by selected organophosphorus esters in chick sympathetic ganglia cultures - Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| Author(s) : Obersteiner EJ , Sharma RP |
| Ref : Can J Comp Med , 42 :80 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| ESTHER : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| PubMedSearch : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| PubMedID: 565668 |
| Title : Correlation between organophosphate poisoning, acetylcholinesterase inhibition, and increased cyclic GMP levels in malathion-treated insects - Bodnaryk_1977_Can.J.Biochem_55_534 |
| Author(s) : Bodnaryk RP |
| Ref : Canadian Journal of Biochemistry , 55 :534 , 1977 |
| Abstract : Bodnaryk_1977_Can.J.Biochem_55_534 |
| ESTHER : Bodnaryk_1977_Can.J.Biochem_55_534 |
| PubMedSearch : Bodnaryk_1977_Can.J.Biochem_55_534 |
| PubMedID: 195684 |
| Title : Nonoxidative enzymes in the metabolism of insecticides - Ahmad_1976_Ann.Clin.Biochem_13_141 |
| Author(s) : Ahmad S , Forgash AJ |
| Ref : Annals of Clinical Biochemistry , 13 :141 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Ahmad_1976_Ann.Clin.Biochem_13_141 |
| ESTHER : Ahmad_1976_Ann.Clin.Biochem_13_141 |
| PubMedSearch : Ahmad_1976_Ann.Clin.Biochem_13_141 |
| PubMedID: 802086 |