Methomyl
General
Type : Insecticide,Carbamate,Sulfur Compound
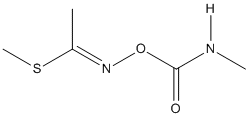
Chemical_Nomenclature : N-[[(Methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]ethan-imidothioicacidmethyl ester
Canonical SMILES : CC(=NOC(=O)NC)SC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C5H10N2O2S\/c1-4(10-3)7-9-5(8)6-2\/h1-3H3,(H,6,8)\/b7-4+
InChIKey : UHXUZOCRWCRNSJ-QPJJXVBHSA-N
Other name(s) : Nudrin,Lannate,Methomyl 5G,Lannabait,Nu-bait II,Thiobutan-2-one, O-(methylcarbamoyl)oxime
MW : 162.21
Formula : C6H12N2O3S
CAS_number : 16752-77-5
PubChem : 5353758
UniChem : UHXUZOCRWCRNSJ-QPJJXVBHSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Methomyl
Target
References (10)
| Title : Time course of cholinesterase inhibition in adult rats treated acutely with carbaryl, carbofuran, formetanate, methomyl, methiocarb, oxamyl or propoxur - Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| Author(s) : Padilla S , Marshall RS , Hunter DL , Lowit A |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 219 :202 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| ESTHER : Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| PubMedSearch : Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| PubMedID: 17197007 |
| Title : Kinetic constants for the inhibition of camel retinal acetylcholinesterase by the carbamate insecticide lannate - Kamal_1999_J.Biochem.Mol.Toxicol_13_41 |
| Author(s) : Kamal MA , Al-Jafari AA |
| Ref : J Biochem Mol Toxicol , 13 :41 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Kamal_1999_J.Biochem.Mol.Toxicol_13_41 |
| ESTHER : Kamal_1999_J.Biochem.Mol.Toxicol_13_41 |
| PubMedSearch : Kamal_1999_J.Biochem.Mol.Toxicol_13_41 |
| PubMedID: 9890446 |
| Title : Pesticide deposition in hair: preliminary results of a model study of methomyl incorporation into rabbit hair - Tsatsakis_1998_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_40_200 |
| Author(s) : Tsatsakis AM , Tutudaki MI , Tzatzarakis MN , Psaroudakis K , Dolapsakis GP , Michalodimitrakis MN |
| Ref : Vet Hum Toxicol , 40 :200 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Tsatsakis_1998_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_40_200 |
| ESTHER : Tsatsakis_1998_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_40_200 |
| PubMedSearch : Tsatsakis_1998_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_40_200 |
| PubMedID: 9682403 |
| Title : Inhibition of 17 beta-estradiol and progesterone activity in human breast and endometrial cancer cells by carbamate insecticides - Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| Author(s) : Klotz DM , Arnold SF , McLachlan JA |
| Ref : Life Sciences , 60 :1467 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| ESTHER : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| PubMedSearch : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| PubMedID: 9126867 |
| Title : Solid-phase extraction of polar pesticides from environmental water samples on graphitized carbon and Empore-activated carbon disks and on- line coupling to octadecyl-bonded silica analytical columns - Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| Author(s) : Slobodnik J , Oztezkizan O , Lingeman H , Brinkman UA |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 750 :227 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| ESTHER : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| PubMedSearch : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| PubMedID: 8938388 |
| Title : Energy related metabolic alterations in diaphragm muscle resulting from acute methomyl toxicity - Gupta_1994_Neurotoxicol_15_321 |
| Author(s) : Gupta RC , Goad JT , Kadel WL |
| Ref : Neurotoxicology , 15 :321 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Gupta_1994_Neurotoxicol_15_321 |
| ESTHER : Gupta_1994_Neurotoxicol_15_321 |
| PubMedSearch : Gupta_1994_Neurotoxicol_15_321 |
| PubMedID: 7991221 |
| Title : Carbamate poisoning and oxime treatment in children: a clinical and laboratory study - Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| Author(s) : Lifshitz M , Rotenberg M , Sofer S , Tamiri T , Shahak E , Almog S |
| Ref : Pediatrics , 93 :652 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| ESTHER : Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| PubMedSearch : Lifshitz_1994_Pediatrics_93_652 |
| PubMedID: 8134223 |
| Title : Determination of residues of methomyl and oxamyl and their oximes in crops by gas-liquid chromatography of oxime trimethylsilyl ethers - Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| Author(s) : Chapman RA , Harris CR |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography , 171 :249 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| ESTHER : Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| PubMedSearch : Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| PubMedID: 546852 |
| Title : High pressure liquid chromatographic determination of methomyl and oxamyl on vegetable crops - Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| Author(s) : Thean JE , Fong WG , Lorenz DR , Stephens TL |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 61 :15 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| ESTHER : Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| PubMedSearch : Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| PubMedID: 621190 |
| Title : [Radiometric determination of 11 carbamate pesticides in the nanogram and subnanongram ranges by means of cholinesterase inhibition] - Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| Author(s) : Schmid ER , Damboritz W , Markl P |
| Ref : Nahrung , 21 :311 , 1977 |
| Abstract : Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| ESTHER : Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| PubMedSearch : Schmid_1977_Nahrung_21_311 |
| PubMedID: 406567 |