NEMP-F
General
Type : Organophosphate,Surrogate OP,Nerve Agent V-series,Derivative of VX,pNP
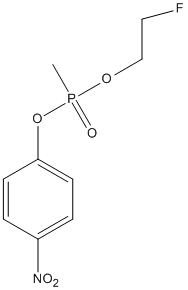
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1-[2-fluoroethoxy(methyl)phosphoryl]oxy-4-nitrobenzene
Canonical SMILES : CP(=O)(OCCF)OC1=CC=C(C=C1)[N+](=O)[O-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C9H11FNO5P\/c1-17(14,15-7-6-10)16-9-4-2-8(3-5-9)11(12)13\/h2-5H,6-7H2,1H3
InChIKey : BBDQLOUKNUVPFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : CHEMBL2348365,2-Fluoroethyl 4-Nitrophenyl Methylphosphonate,SCHEMBL19106914,BDBM50490822
MW : 263.16
Formula : C9H11FNO5P
CAS_number :
PubChem : 71579905
UniChem : BBDQLOUKNUVPFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (1)
| Title : The inhibition, reactivation and mechanism of VX-, sarin-, fluoro-VX and fluoro-sarin surrogates following their interaction with HuAChE and HuBuChE - Chao_2018_Chem.Biol.Interact_291_220 |
| Author(s) : Chao CK , Balasubramanian N , Gerdes JM , Thompson CM |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 291 :220 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Chao_2018_Chem.Biol.Interact_291_220 |
| ESTHER : Chao_2018_Chem.Biol.Interact_291_220 |
| PubMedSearch : Chao_2018_Chem.Biol.Interact_291_220 |
| PubMedID: 29920286 |