Phosmet
Trade names for products containing the compound include Appa, Decemthion,Decemtione, Imidan, Kemolate, Fesdan, Prolate, PMC and Safidon. It is also found in combination with other insecticides such as carbophenothion in russian phthalophos
General
Type : Organophosphate,Insecticide,Sulfur Compound,Organothiophosphate,Isoindole,Indole
Chemical_Nomenclature : phosphorodithioic acid S-[(1,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl)methyl] O,O-dimethylester
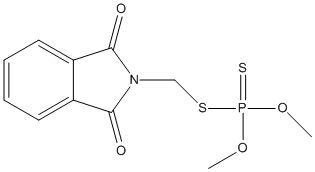
Canonical SMILES : COP(=S)(OC)SCN1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C1=O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C11H12NO4PS2\/c1-15-17(18,16-2)19-7-12-10(13)8-5-3-4-6-9(8)11(12)14\/h3-6H,7H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : LMNZTLDVJIUSHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : imidan
MW : 317.33
Formula : C11H12NO4PS2
CAS_number : 732-11-6
PubChem : 12901
UniChem : LMNZTLDVJIUSHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Phosmet
Target
References (23)
| Title : High-dose exposure to systemic phosmet insecticide modifies the phosphatidylinositol anchor on the prion protein: the origins of new variant transmissible spongiform encephalopathies? - Purdey_1998_Med.Hypotheses_50_91 |
| Author(s) : Purdey M |
| Ref : Med Hypotheses , 50 :91 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Purdey_1998_Med.Hypotheses_50_91 |
| ESTHER : Purdey_1998_Med.Hypotheses_50_91 |
| PubMedSearch : Purdey_1998_Med.Hypotheses_50_91 |
| PubMedID: 9572563 |
| Title : Phosmet induces up-regulation of surface levels of the cellular prion protein - Gordon_1998_Neuroreport_9_1391 |
| Author(s) : Gordon I , Abdulla EM , Campbell IC , Whatley SA |
| Ref : Neuroreport , 9 :1391 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Gordon_1998_Neuroreport_9_1391 |
| ESTHER : Gordon_1998_Neuroreport_9_1391 |
| PubMedSearch : Gordon_1998_Neuroreport_9_1391 |
| PubMedID: 9631435 |
| Title : Evaluation of organophosphorus pesticide residues in citrus fruits from the Valencian community (Spain) - Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| Author(s) : Torres CM , Pico Y , Marin R , Manes J |
| Ref : Journal of AOAC International , 80 :1122 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| ESTHER : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| PubMedSearch : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| PubMedID: 9325585 |
| Title : Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction procedure for multiresidue pesticide analysis in oranges - Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| Author(s) : Torres CM , Pico Y , Redondo MJ , Manes J |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 719 :95 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| ESTHER : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedSearch : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedID: 8589838 |
| Title : Pathophysiological studies of neuromuscular function in subacute organophosphate poisoning induced by phosmet - Good_1993_J.Neurol.Neurosurg.Psychiatry_56_290 |
| Author(s) : Good JL , Khurana RK , Mayer RF , Cintra WM , Albuquerque EX |
| Ref : Journal of Neurology Neurosurg Psychiatry , 56 :290 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Good_1993_J.Neurol.Neurosurg.Psychiatry_56_290 |
| ESTHER : Good_1993_J.Neurol.Neurosurg.Psychiatry_56_290 |
| PubMedSearch : Good_1993_J.Neurol.Neurosurg.Psychiatry_56_290 |
| PubMedID: 8384655 |
| Title : Mutagenic activity of phosmet, the active component of the organophosphorus insecticide Decemtione EK 20 in Salmonella and Saccharomyces assays - Vlckova_1993_Mutat.Res_302_153 |
| Author(s) : Vlckova V , Miadokova E , Podstavkova S , Vlcek D |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 302 :153 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Vlckova_1993_Mutat.Res_302_153 |
| ESTHER : Vlckova_1993_Mutat.Res_302_153 |
| PubMedSearch : Vlckova_1993_Mutat.Res_302_153 |
| PubMedID: 7686624 |
| Title : Evaluation of an in vitro method for acaricidal effect. Activity of parathion, phosmet and phoxim against Sarcoptes scabiei - Brimer_1993_Vet.Parasitol_51_123 |
| Author(s) : Brimer L , Henriksen SA , Gyrd-Hansen N , Rasmussen F |
| Ref : Vet Parasitol , 51 :123 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Brimer_1993_Vet.Parasitol_51_123 |
| ESTHER : Brimer_1993_Vet.Parasitol_51_123 |
| PubMedSearch : Brimer_1993_Vet.Parasitol_51_123 |
| PubMedID: 8128575 |
| Title : Decemtione (Imidan)-induced single-strand breaks to human DNA, mutations at the hgprt locus of V79 cells, and morphological transformations of embryo cells - Slamenova_1992_Environ.Mol.Mutagen_20_73 |
| Author(s) : Slamenova D , Dusinska M , Gabelova A , Bohusova T , Ruppova K |
| Ref : Environmental & Molecular Mutagenesis , 20 :73 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Slamenova_1992_Environ.Mol.Mutagen_20_73 |
| ESTHER : Slamenova_1992_Environ.Mol.Mutagen_20_73 |
| PubMedSearch : Slamenova_1992_Environ.Mol.Mutagen_20_73 |
| PubMedID: 1639085 |
| Title : Treatment and control of sarcoptic mange: evaluation of treatment of both the pigs and environment - Kambarage_1991_Trop.Anim.Health.Prod_23_59 |
| Author(s) : Kambarage DM |
| Ref : Trop Anim Health Prod , 23 :59 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Kambarage_1991_Trop.Anim.Health.Prod_23_59 |
| ESTHER : Kambarage_1991_Trop.Anim.Health.Prod_23_59 |
| PubMedSearch : Kambarage_1991_Trop.Anim.Health.Prod_23_59 |
| PubMedID: 1903897 |
| Title : A rapid in vivo bioassay for the carcinogenicity of pesticides - Cabral_1991_Tumori_77_185 |
| Author(s) : Cabral R , Hoshiya T , Hakoi K , Hasegawa R , Fukushima S , Ito N |
| Ref : Tumori , 77 :185 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Cabral_1991_Tumori_77_185 |
| ESTHER : Cabral_1991_Tumori_77_185 |
| PubMedSearch : Cabral_1991_Tumori_77_185 |
| PubMedID: 1862543 |
| Title : Monitoring Ontario-grown apples for pest control chemicals used in their production, 1978-86 - Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| Author(s) : Frank R , Braun HE , Ripley BD |
| Ref : Food Additives & Contaminants , 6 :227 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| ESTHER : Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| PubMedSearch : Frank_1989_Food.Addit.Contam_6_227 |
| PubMedID: 2924979 |
| Title : Effect of DNOC, Ferbam and Imidan exposure on mouse sperm morphology - Quinto_1989_Mutat.Res_224_405 |
| Author(s) : Quinto I , De Marinis E , Mallardo M , Arcucci A , Della Morte R , Staiano N |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 224 :405 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Quinto_1989_Mutat.Res_224_405 |
| ESTHER : Quinto_1989_Mutat.Res_224_405 |
| PubMedSearch : Quinto_1989_Mutat.Res_224_405 |
| PubMedID: 2555709 |
| Title : [The effect of silymarin on gluconeogenesis in the liver of rats after damage due to phosmet] - |
| Author(s) : Ulicna O , Batora I , Kubalova V , Brixova E |
| Ref : Bratislavske Lekarske Listy , 89 :678 , 1988 |
| PubMedID: 3208172 |
| Title : Phosmet for the systemic control of pig mange in growing pigs - Hewett_1985_Vet.Parasitol_18_265 |
| Author(s) : Hewett GR |
| Ref : Vet Parasitol , 18 :265 , 1985 |
| Abstract : Hewett_1985_Vet.Parasitol_18_265 |
| ESTHER : Hewett_1985_Vet.Parasitol_18_265 |
| PubMedSearch : Hewett_1985_Vet.Parasitol_18_265 |
| PubMedID: 4082451 |
| Title : Systemic activity of coumaphos, famphur, crufomate, ronnel, and phosmet given orally to hens for control of the northern fowl mite, Ornitbonyssus sulviarum (Canestrini and Fanzago) - DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| Author(s) : DeVaney JA , Ivie GW |
| Ref : Poult Sci , 59 :1208 , 1980 |
| Abstract : DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| ESTHER : DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| PubMedSearch : DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| PubMedID: 6157151 |
| Title : [Embryotoxicity and teratogenicity of phosmet in mice] - Bleyl_1980_Arch.Exp.Veterinarmed_34_791 |
| Author(s) : Bleyl DW |
| Ref : Archiv Exp Veterinarmed , 34 :791 , 1980 |
| Abstract : Bleyl_1980_Arch.Exp.Veterinarmed_34_791 |
| ESTHER : Bleyl_1980_Arch.Exp.Veterinarmed_34_791 |
| PubMedSearch : Bleyl_1980_Arch.Exp.Veterinarmed_34_791 |
| PubMedID: 7458565 |
| Title : Isolation and concentration of organophosphorus pesticides from drinking water at the ng\/L level, using macroreticular resin - LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| Author(s) : LeBel GL , Williams DT , Griffith G , Benoit FM |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 62 :241 , 1979 |
| Abstract : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| ESTHER : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| PubMedSearch : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| PubMedID: 447594 |
| Title : Evaluation of phosmet for the control of the common scabies mite on cattle - Roberts_1978_J.Am.Vet.Med.Assoc_173_840 |
| Author(s) : Roberts IH , Wilson GI , Meleney WP |
| Ref : J Am Vet Med Assoc , 173 :840 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Roberts_1978_J.Am.Vet.Med.Assoc_173_840 |
| ESTHER : Roberts_1978_J.Am.Vet.Med.Assoc_173_840 |
| PubMedSearch : Roberts_1978_J.Am.Vet.Med.Assoc_173_840 |
| PubMedID: 711605 |
| Title : Experimental study of the effect of a series of phosphoroorganic pesticides (Dipterex and Imidan) on embryogenesis - Martson_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_121 |
| Author(s) : Martson LV , Voronina VM |
| Ref : Environmental Health Perspectives , 13 :121 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Martson_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_121 |
| ESTHER : Martson_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_121 |
| PubMedSearch : Martson_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_121 |
| PubMedID: 1269499 |
| Title : Developmental toxicity in the rat after ingestion or gavage of organophosphate pesticides (Dipterex, Imidan) during pregnancy - Staples_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_133 |
| Author(s) : Staples RE , Kellam RG , Haseman JK |
| Ref : Environmental Health Perspectives , 13 :133 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Staples_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_133 |
| ESTHER : Staples_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_133 |
| PubMedSearch : Staples_1976_Environ.Health.Perspect_13_133 |
| PubMedID: 944629 |
| Title : Metabolic and toxic behavior of phthalimide derivates. I. Fate of imidan in the fetus - Ackermann_1976_Arch.Toxicol_36_127 |
| Author(s) : Ackermann H , Seidler H , Kagan YS , Voronina VM |
| Ref : Archives of Toxicology , 36 :127 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Ackermann_1976_Arch.Toxicol_36_127 |
| ESTHER : Ackermann_1976_Arch.Toxicol_36_127 |
| PubMedSearch : Ackermann_1976_Arch.Toxicol_36_127 |
| PubMedID: 1036887 |