Pirimiphos-methyl
General
Type : Organophosphate,Insecticide,Pyrimidine,Sulfur Compound
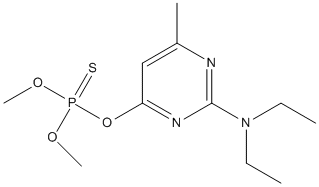
Chemical_Nomenclature : O-(2-(Diethylamino)-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl)-O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate
Canonical SMILES : CCN(CC)C1=NC(=CC(=N1)OP(=S)(OC)OC)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C11H20N3O3PS\/c1-6-14(7-2)11-12-9(3)8-10(13-11)17-18(19,15-4)16-5\/h8H,6-7H2,1-5H3
InChIKey : QHOQHJPRIBSPCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : PP511,Actellic,Actellifog,Blex,Silosan,Pirimiphos-Me
MW : 277.28
Formula : C9H16N3O3PS
CAS_number : 29232-93-7
PubChem : 34526
UniChem : QHOQHJPRIBSPCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Pirimiphos-methyl
Target
References (77)
| Title : Copy number variants underlie the major selective sweeps in insecticide resistance genes in Anopheles arabiensis from Tanzania - Lucas_2024_bioRxiv__ |
| Author(s) : Lucas ER , Nagi SC , Kabula B , Batengana B , Kisinza W , Egyir-Yawson A , Essandoh J , Dadzie S , Chabi J , Van't Hof AE , Rippon EJ , Pipini D , Harding NJ , Dyer NA , Clarkson CS , Miles A , Weetman D , Donnelly MJ |
| Ref : Biorxiv , : , 2024 |
| Abstract : Lucas_2024_bioRxiv__ |
| ESTHER : Lucas_2024_bioRxiv__ |
| PubMedSearch : Lucas_2024_bioRxiv__ |
| PubMedID: 38559088 |
| Title : A case report of severe pirimiphos-methyl intoxication: Clinical findings and cholinesterase status - Zellner_2022_Front.Pharmacol_13_1102160 |
| Author(s) : Zellner T , Rabe C , von der Wellen-Pawlowski J , Hansen D , John H , Worek F , Eyer F |
| Ref : Front Pharmacol , 13 :1102160 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Zellner_2022_Front.Pharmacol_13_1102160 |
| ESTHER : Zellner_2022_Front.Pharmacol_13_1102160 |
| PubMedSearch : Zellner_2022_Front.Pharmacol_13_1102160 |
| PubMedID: 36618943 |
| Title : Hepatic injury and disturbed amino acid metabolism in mice following prolonged exposure to organophosphorus pesticides - Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| Author(s) : Gomes J , Dawodu AH , Lloyd O , Revitt DM , Anilal SV |
| Ref : Hum Exp Toxicol , 18 :33 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| ESTHER : Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| PubMedSearch : Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| PubMedID: 10025366 |
| Title : Susceptibility of Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae) to selected insecticides in an endemic focus of visceral leishmaniasis in Venezuela - Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| Author(s) : Mazzarri MB , Feliciangeli MD , Maroli M , Hernandez A , Bravo A |
| Ref : J Am Mosq Control Assoc , 13 :335 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| ESTHER : Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| PubMedSearch : Mazzarri_1997_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_13_335 |
| PubMedID: 9474559 |
| Title : Effect of pirimiphos-methyl on proteolytic enzyme activities in rat heart, kidney, brain and liver tissues in vivo - Mantle_1997_Clin.Chim.Acta_262_89 |
| Author(s) : Mantle D , Saleem MA , Williams FM , Wilkins RM , Shakoori AR |
| Ref : Clinica Chimica Acta , 262 :89 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Mantle_1997_Clin.Chim.Acta_262_89 |
| ESTHER : Mantle_1997_Clin.Chim.Acta_262_89 |
| PubMedSearch : Mantle_1997_Clin.Chim.Acta_262_89 |
| PubMedID: 9204212 |
| Title : Oxidative liver DNA damage in rats treated with pesticide mixtures - Lodovici_1997_Toxicology_117_55 |
| Author(s) : Lodovici M , Casalini C , Briani C , Dolara P |
| Ref : Toxicology , 117 :55 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Lodovici_1997_Toxicology_117_55 |
| ESTHER : Lodovici_1997_Toxicology_117_55 |
| PubMedSearch : Lodovici_1997_Toxicology_117_55 |
| PubMedID: 9020199 |
| Title : Yellowfever mosquito (Diptera:Culicidae) introduced into Landi Kotal, Pakistan, by tire importation - Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| Author(s) : Suleman M , Arshad M , Khan K |
| Ref : Journal of Medical Entomology , 33 :689 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| ESTHER : Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| PubMedSearch : Suleman_1996_J.Med.Entomol_33_689 |
| PubMedID: 8699469 |
| Title : Efficiency of some technological processes on reducing the residues of malathion and pirimiphos methyl in mature broad bean seeds - Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| Author(s) : Kamil ME , Abou-Zahw MM , Hegazy NA |
| Ref : Nahrung , 40 :277 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| ESTHER : Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| PubMedSearch : Kamil_1996_Nahrung_40_277 |
| PubMedID: 8921619 |
| Title : Effect of pesticide mixtures on in vitro nervous cells: comparison with single pesticides - Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| Author(s) : Marinovich M , Ghilardi F , Galli CL |
| Ref : Toxicology , 108 :201 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| ESTHER : Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| PubMedSearch : Marinovich_1996_Toxicology_108_201 |
| PubMedID: 8658539 |
| Title : Organophosphate resistance in Culex pipiens from Cyprus - Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| Author(s) : Wirth MC , Georghiou GP |
| Ref : J Am Mosq Control Assoc , 12 :112 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| ESTHER : Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| PubMedSearch : Wirth_1996_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_12_112 |
| PubMedID: 8723267 |
| Title : Organohalogen and organophosphorus pesticides in mixed feed rations: findings from FDA's domestic surveillance during fiscal years 1989-1994 - Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| Author(s) : Lovell RA , McChesney DG , Price WD |
| Ref : Journal of AOAC International , 79 :544 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| ESTHER : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| PubMedSearch : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| PubMedID: 8920144 |
| Title : Selective, solid-matrix dispersion extraction of organophosphate pesticide residues from milk - Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| Author(s) : Di Muccio A , Pelosi P , Camoni I , Attard Barbini D , Dommarco R , Generali T , Ausili A |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 754 :497 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| ESTHER : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedSearch : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedID: 8997741 |
| Title : Anopheles culicifacies in Baluchistan, Iran - Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| Author(s) : Zaim M , Manouchehri AV , Motabar M , Emadi AM , Nazari M , Pakdad K , Kayedi MH , Mowlaii G |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 9 :181 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| ESTHER : Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| PubMedSearch : Zaim_1995_Med.Vet.Entomol_9_181 |
| PubMedID: 7787227 |
| Title : A resistance of head lice (Pediculus capitis) to permethrin in Czech Republic - Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| Author(s) : Rupes V , Moravec J , Chmela J , Ledvinka J , Zelenkova J |
| Ref : Central European Journal of Public Health , 3 :30 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| ESTHER : Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| PubMedSearch : Rupes_1995_Cent.Eur.J.Public.Health_3_30 |
| PubMedID: 7787823 |
| Title : Effects of three organophosphorus insecticides in the reproductive potential of Culex quinquefasciatus - Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| Author(s) : Aguilera L , Marquetti MC , Navarro A , Bisset J |
| Ref : Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz , 90 :411 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| ESTHER : Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| PubMedSearch : Aguilera_1995_Mem.Inst.Oswaldo.Cruz_90_411 |
| PubMedID: 8544743 |
| Title : Characterization of resistance to organophosphate, carbamate, and pyrethroid insecticides in field populations of Aedes aegypti from Venezuela - Mazzarri_1995_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_11_315 |
| Author(s) : Mazzarri MB , Georghiou GP |
| Ref : J Am Mosq Control Assoc , 11 :315 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Mazzarri_1995_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_11_315 |
| ESTHER : Mazzarri_1995_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_11_315 |
| PubMedSearch : Mazzarri_1995_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_11_315 |
| PubMedID: 8551300 |
| Title : Influence of insecticidal plant materials used during storage on sensory attributes and instrumental hardness of dry edible beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) - Dunkel_1995_Plant.Foods.Hum.Nutr_48_1 |
| Author(s) : Dunkel FV , Serugendo A , Breene WM , Sriharan S |
| Ref : Plant Foods Hum Nutr , 48 :1 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Dunkel_1995_Plant.Foods.Hum.Nutr_48_1 |
| ESTHER : Dunkel_1995_Plant.Foods.Hum.Nutr_48_1 |
| PubMedSearch : Dunkel_1995_Plant.Foods.Hum.Nutr_48_1 |
| PubMedID: 8719734 |
| Title : Benomyl affects the microtubule cytoskeleton and the glutathione level of mammalian primary cultured hepatocytes - Urani_1995_Toxicol.Lett_76_135 |
| Author(s) : Urani C , Chiesara E , Galvani P , Marabini L , Santagostino A , Camatini M |
| Ref : Toxicol Lett , 76 :135 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Urani_1995_Toxicol.Lett_76_135 |
| ESTHER : Urani_1995_Toxicol.Lett_76_135 |
| PubMedSearch : Urani_1995_Toxicol.Lett_76_135 |
| PubMedID: 7725345 |
| Title : Genotoxicity assay of five pesticides and their mixtures in Saccharomyces cerevisiae D7 - Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| Author(s) : Bianchi L , Zannoli A , Pizzala R , Stivala LA , Chiesara E |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 321 :203 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| ESTHER : Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| PubMedSearch : Bianchi_1994_Mutat.Res_321_203 |
| PubMedID: 7515158 |
| Title : Mixtures of benomyl, pirimiphos-methyl, dimethoate, diazinon and azinphos-methyl affect protein synthesis in HL-60 cells differently - Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| Author(s) : Marinovich M , Guizzetti M , Galli CL |
| Ref : Toxicology , 94 :173 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| ESTHER : Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| PubMedSearch : Marinovich_1994_Toxicology_94_173 |
| PubMedID: 7801320 |
| Title : Cytogenetic effects on human lymphocytes of a mixture of fifteen pesticides commonly used in Italy - Dolara_1994_Mutat.Res_325_47 |
| Author(s) : Dolara P , Torricelli F , Antonelli N |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 325 :47 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Dolara_1994_Mutat.Res_325_47 |
| ESTHER : Dolara_1994_Mutat.Res_325_47 |
| PubMedSearch : Dolara_1994_Mutat.Res_325_47 |
| PubMedID: 7521012 |
| Title : Behavioral response of host-seeking mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) to insecticide-impregnated bed netting: a new approach to insecticide bioassays - Miller_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_114 |
| Author(s) : Miller JE , Gibson G |
| Ref : Journal of Medical Entomology , 31 :114 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Miller_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_114 |
| ESTHER : Miller_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_114 |
| PubMedSearch : Miller_1994_J.Med.Entomol_31_114 |
| PubMedID: 7908985 |
| Title : [The isolation and detection of actellic by thin-layer chromatography in the forensic chemical study of cadaveric organs] - Gorbacheva_1994_Sud.Med.Ekspert_37_28 |
| Author(s) : Gorbacheva NA |
| Ref : Sud Med Ekspert , 37 :28 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Gorbacheva_1994_Sud.Med.Ekspert_37_28 |
| ESTHER : Gorbacheva_1994_Sud.Med.Ekspert_37_28 |
| PubMedSearch : Gorbacheva_1994_Sud.Med.Ekspert_37_28 |
| PubMedID: 8184454 |
| Title : Increase of micronucleus frequency in cultured rat hepatocytes treated in vitro with benomyl and pirimiphos-methyl separately and in mixture - Piatti_1994_Mutat.Res_324_59 |
| Author(s) : Piatti E , Marabini L , Chiesara E |
| Ref : Mutat Res , 324 :59 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Piatti_1994_Mutat.Res_324_59 |
| ESTHER : Piatti_1994_Mutat.Res_324_59 |
| PubMedSearch : Piatti_1994_Mutat.Res_324_59 |
| PubMedID: 7515471 |
| Title : Effect of a mixture of 15 commonly used pesticides on DNA levels of 8- hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine and xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in rat liver - Lodovici_1994_J.Environ.Pathol.Toxicol.Oncol_13_163 |
| Author(s) : Lodovici M , Aiolli S , Monserrat C , Dolara P , Medica A , Di Simplicio P |
| Ref : J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol , 13 :163 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Lodovici_1994_J.Environ.Pathol.Toxicol.Oncol_13_163 |
| ESTHER : Lodovici_1994_J.Environ.Pathol.Toxicol.Oncol_13_163 |
| PubMedSearch : Lodovici_1994_J.Environ.Pathol.Toxicol.Oncol_13_163 |
| PubMedID: 7722883 |
| Title : Residues and half-lives of acephate, methamidophos, and pirimiphos- methyl in leaves and fruit of greenhouse-grown tomatoes - |
| Author(s) : Antonious GF , Snyder JC |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 52 :141 , 1994 |
| PubMedID: 8130409 |
| Title : Dermal toxicity of hexachlorocyclohexane and pirimiphos-methyl in female rats - Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| Author(s) : Raizada RB , Srivastava MK , Kaushal RA , Singh RP , Gupta KP , Dikshith TS |
| Ref : Vet Hum Toxicol , 36 :128 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| ESTHER : Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| PubMedSearch : Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| PubMedID: 7515208 |
| Title : Genetic toxicity of a mixture of fifteen pesticides commonly found in the Italian diet - Dolara_1993_Cell.Biol.Toxicol_9_333 |
| Author(s) : Dolara P , Vezzani A , Caderni G , Coppi C , Torricelli F |
| Ref : Cell Biol Toxicol , 9 :333 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Dolara_1993_Cell.Biol.Toxicol_9_333 |
| ESTHER : Dolara_1993_Cell.Biol.Toxicol_9_333 |
| PubMedSearch : Dolara_1993_Cell.Biol.Toxicol_9_333 |
| PubMedID: 8039010 |
| Title : Effect of four pesticides on aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus IMI 89717 - el-Kady_1993_Zentralbl.Mikrobiol_148_549 |
| Author(s) : el-Kady IA , el-Maraghy SS , Abdel-Mallek AY , Hasan HA |
| Ref : Zentralbl Mikrobiol , 148 :549 , 1993 |
| Abstract : el-Kady_1993_Zentralbl.Mikrobiol_148_549 |
| ESTHER : el-Kady_1993_Zentralbl.Mikrobiol_148_549 |
| PubMedSearch : el-Kady_1993_Zentralbl.Mikrobiol_148_549 |
| PubMedID: 8303955 |
| Title : Influence of different means of washing and processing on removing of Actellic residue from spinach and eggplant and its in-vivo action on mice hepatic biochemical targets - Awad_1993_J.Egypt.Public.Health.Assoc_68_671 |
| Author(s) : Awad OM , el-Shimi NM |
| Ref : J Egypt Public Health Assoc , 68 :671 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Awad_1993_J.Egypt.Public.Health.Assoc_68_671 |
| ESTHER : Awad_1993_J.Egypt.Public.Health.Assoc_68_671 |
| PubMedSearch : Awad_1993_J.Egypt.Public.Health.Assoc_68_671 |
| PubMedID: 7775887 |
| Title : Susceptibility of the bedbug, Cimex lectularius, to selected insecticides and various treated surfaces - Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| Author(s) : Fletcher MG , Axtell RC |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 7 :69 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| ESTHER : Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| PubMedSearch : Fletcher_1993_Med.Vet.Entomol_7_69 |
| PubMedID: 8435492 |
| Title : Insecticide resistance gene frequencies in Anopheles sacharovi populations of the Cukurova plain, Adana Province, Turkey - Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| Author(s) : Hemingway J , Small GJ , Monro A , Sawyer BV , Kasap H |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 6 :342 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| ESTHER : Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| PubMedSearch : Hemingway_1992_Med.Vet.Entomol_6_342 |
| PubMedID: 1463899 |
| Title : Residual efficacy of pirimiphos methyl (Actellic) on Anopheles sacharovi in Cukurova, Turkey - Kasap_1992_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_8_47 |
| Author(s) : Kasap H , Kasap M , Akbaba M , Alptekin D , Demirhan O , Luleyap U , Pazarbasi A , Akdur R , Wade J |
| Ref : J Am Mosq Control Assoc , 8 :47 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Kasap_1992_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_8_47 |
| ESTHER : Kasap_1992_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_8_47 |
| PubMedSearch : Kasap_1992_J.Am.Mosq.Control.Assoc_8_47 |
| PubMedID: 1583488 |
| Title : Bioavailability and toxicological potential of wheat-bound pirimiphos- methyl residues in rats - Akay_1992_Xenobiotica_22_293 |
| Author(s) : Akay MT , Yilmazoglu G , Yasacan S , Turk H , Kolanyaka D |
| Ref : Xenobiotica , 22 :293 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Akay_1992_Xenobiotica_22_293 |
| ESTHER : Akay_1992_Xenobiotica_22_293 |
| PubMedSearch : Akay_1992_Xenobiotica_22_293 |
| PubMedID: 1496821 |
| Title : Bioavailability to rats of bound [14C] pirimiphos-methyl in stored wheat - Khan_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_355 |
| Author(s) : Khan SU , Kacew S , Matthews W |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 27 :355 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Khan_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_355 |
| ESTHER : Khan_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_355 |
| PubMedSearch : Khan_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_355 |
| PubMedID: 1527359 |
| Title : Bioavailability and toxicity to rats of bound residues of 14C- pirimiphos-methyl in stored wheat - Qureshi_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_369 |
| Author(s) : Qureshi MJ , Jamil FF , Haq A , Naqvi SH |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 27 :369 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Qureshi_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_369 |
| ESTHER : Qureshi_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_369 |
| PubMedSearch : Qureshi_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_369 |
| PubMedID: 1527360 |
| Title : Bioavailability and biological activity of bound residues of radiolabelled pirimiphos-methyl in maize grains - Yeboah_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_377 |
| Author(s) : Yeboah PO , Semanhyia CB , Melfah PT |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 27 :377 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Yeboah_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_377 |
| ESTHER : Yeboah_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_377 |
| PubMedSearch : Yeboah_1992_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_27_377 |
| PubMedID: 1527361 |
| Title : Malaria transmission during post-spray period of pirimiphos-methyl in Arunachal Pradesh - Biswas_1992_J.Commun.Dis_24_219 |
| Author(s) : Biswas H , Yadava RL , Rao CK , Thapar BR , Narasimham MV |
| Ref : J Commun Dis , 24 :219 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Biswas_1992_J.Commun.Dis_24_219 |
| ESTHER : Biswas_1992_J.Commun.Dis_24_219 |
| PubMedSearch : Biswas_1992_J.Commun.Dis_24_219 |
| PubMedID: 1344956 |
| Title : Efficacy of diethylcarbamazine and pirimiphos-methyl residual spraying in controlling brugian filariasis - Chang_1991_Trop.Med.Parasitol_42_95 |
| Author(s) : Chang MS , Ho BC , Chan KL |
| Ref : Trop Med Parasitol , 42 :95 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Chang_1991_Trop.Med.Parasitol_42_95 |
| ESTHER : Chang_1991_Trop.Med.Parasitol_42_95 |
| PubMedSearch : Chang_1991_Trop.Med.Parasitol_42_95 |
| PubMedID: 1680246 |
| Title : Malathion and pyrethroid resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus from Cuba: efficacy of pirimiphos-methyl in the presence of at least three resistance mechanisms - Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| Author(s) : Bisset JA , Rodriguez MM , Hemingway J , Diaz C , Small GJ , Ortiz E |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 5 :223 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| ESTHER : Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| PubMedSearch : Bisset_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_223 |
| PubMedID: 1768912 |
| Title : Horn fly (Diptera: Muscidae) insecticide resistance in Kentucky and Arkansas - Cilek_1991_J.Econ.Entomol_84_756 |
| Author(s) : Cilek JE , Steelman CD , Knapp FW |
| Ref : J Econ Entomol , 84 :756 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Cilek_1991_J.Econ.Entomol_84_756 |
| ESTHER : Cilek_1991_J.Econ.Entomol_84_756 |
| PubMedSearch : Cilek_1991_J.Econ.Entomol_84_756 |
| PubMedID: 1885841 |
| Title : Experimental hut trials of bednets impregnated with synthetic pyrethroid or organophosphate insecticide for mosquito control in The Gambia - Miller_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_465 |
| Author(s) : Miller JE , Lindsay SW , Armstrong JR |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 5 :465 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Miller_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_465 |
| ESTHER : Miller_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_465 |
| PubMedSearch : Miller_1991_Med.Vet.Entomol_5_465 |
| PubMedID: 1685337 |
| Title : Susceptibilities of northern fowl mite, Ornithonyssus sylviarum (Acarina: Macronyssidae), and chicken mite, Dermanyssus gallinae (Acarina: Dermanyssidae), to selected acaricides - Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| Author(s) : Fletcher MG , Axtell RC |
| Ref : Exp Appl Acarol , 13 :137 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| ESTHER : Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| PubMedSearch : Fletcher_1991_Exp.Appl.Acarol_13_137 |
| PubMedID: 1786744 |
| Title : Confirmation method for the identification and determination of some organophosphorus and organochlorine pesticides in cocoa beans by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry - Rodriguez_1991_J.Chromatogr_562_547 |
| Author(s) : Rodriguez P , Permanyer J , Grases JM , Gonzalez C |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography , 562 :547 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Rodriguez_1991_J.Chromatogr_562_547 |
| ESTHER : Rodriguez_1991_J.Chromatogr_562_547 |
| PubMedSearch : Rodriguez_1991_J.Chromatogr_562_547 |
| PubMedID: 2026717 |
| Title : Delayed neuropathy and acute toxicity studies with pirimiphos-methyl in the hen - Lock_1990_J.Appl.Toxicol_10_17 |
| Author(s) : Lock EA , Johnson MK |
| Ref : Journal of Applied Toxicology , 10 :17 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Lock_1990_J.Appl.Toxicol_10_17 |
| ESTHER : Lock_1990_J.Appl.Toxicol_10_17 |
| PubMedSearch : Lock_1990_J.Appl.Toxicol_10_17 |
| PubMedID: 2335708 |
| Title : Mechanisms of organophosphate and carbamate resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus from Saudi Arabia - Hemingway_1990_Med.Vet.Entomol_4_275 |
| Author(s) : Hemingway J , Callaghan A , Amin AM |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 4 :275 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Hemingway_1990_Med.Vet.Entomol_4_275 |
| ESTHER : Hemingway_1990_Med.Vet.Entomol_4_275 |
| PubMedSearch : Hemingway_1990_Med.Vet.Entomol_4_275 |
| PubMedID: 2132992 |
| Title : Cytotoxicity of certain organic solvents and organophosphorus insecticides to the ciliated protozoan Paramecium caudatum - Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| Author(s) : Rajini PS , Krishnakumari MK , Majumder SK |
| Ref : Microbios , 59 :157 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| ESTHER : Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| PubMedSearch : Rajini_1989_Microbios_59_157 |
| PubMedID: 2593868 |
| Title : [Exposure to residues on plant surfaces following the use of plant pesticides in the greenhouse] - Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| Author(s) : Goedicke HJ , Hermes H , Wagner R |
| Ref : Z Gesamte Hyg , 35 :531 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| ESTHER : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| PubMedSearch : Goedicke_1989_Z.Gesamte.Hyg_35_531 |
| PubMedID: 2588705 |
| Title : Toxic effects of pirimiphos-methyl residues on rats - Neskovic_1989_Biomed.Environ.Sci_2_115 |
| Author(s) : Neskovic NK , Karan VZ , Sabovljevic V , Vitorovic SL |
| Ref : Biomedical & Environmental Sciences , 2 :115 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Neskovic_1989_Biomed.Environ.Sci_2_115 |
| ESTHER : Neskovic_1989_Biomed.Environ.Sci_2_115 |
| PubMedSearch : Neskovic_1989_Biomed.Environ.Sci_2_115 |
| PubMedID: 2590497 |
| Title : Toxicity of pirimiphos-methyl: I. The acute and subacute oral toxicity in albino rats - Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_127 |
| Author(s) : Rajini PS , Krishnakumari MK |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 23 :127 , 1988 |
| Abstract : Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_127 |
| ESTHER : Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_127 |
| PubMedSearch : Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_127 |
| PubMedID: 3385133 |
| Title : Toxicity of pirimiphos-methyl: II. Effect of dietary feeding on blood and urine constituents in albino rats - Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_145 |
| Author(s) : Rajini PS , Krishnakumari MK |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 23 :145 , 1988 |
| Abstract : Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_145 |
| ESTHER : Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_145 |
| PubMedSearch : Rajini_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_145 |
| PubMedID: 3385134 |
| Title : A esterases and their role in regulating the toxicity of organophosphates - Walker_1987_Arch.Toxicol_60_30 |
| Author(s) : Walker CH , Mackness MI |
| Ref : Archives of Toxicology , 60 :30 , 1987 |
| Abstract : Walker_1987_Arch.Toxicol_60_30 |
| ESTHER : Walker_1987_Arch.Toxicol_60_30 |
| PubMedSearch : Walker_1987_Arch.Toxicol_60_30 |
| PubMedID: 3304214 |
| Title : Effect of pirimiphos-methyl, an organophosphorus insecticide on hematological parameters in albino rats - |
| Author(s) : Rajini PS , Viswanatha S , Krishnakumari MK |
| Ref : Indian J Exp Biol , 25 :190 , 1987 |
| PubMedID: 3666818 |
| Title : Field trial of the effectiveness of indoor-spraying with pirimiphos- methyl emulsion for malaria control in a tribal area of Phulbani district, Orissa State, India - Das_1987_Med.Vet.Entomol_1_289 |
| Author(s) : Das M , Srivastava BN , Rao CK , Thapar BR , Sharma GK |
| Ref : Med Vet Entomol , 1 :289 , 1987 |
| Abstract : Das_1987_Med.Vet.Entomol_1_289 |
| ESTHER : Das_1987_Med.Vet.Entomol_1_289 |
| PubMedSearch : Das_1987_Med.Vet.Entomol_1_289 |
| PubMedID: 2979544 |
| Title : Mutagenic properties of pirimiphos-methyl in male mice - |
| Author(s) : Rajini PS , Muralidhara , Krishnakumari MK , Majumder SK |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 36 :680 , 1986 |
| PubMedID: 3708170 |
| Title : Occupational exposure to organophosphorus insecticides and synthetic pyrethroid - Adamis_1985_Int.Arch.Occup.Environ.Health_56_299 |
| Author(s) : Adamis Z , Antal A , Fuzesi I , Molnar J , Nagy L , Susan M |
| Ref : Int Arch Occup Environ Health , 56 :299 , 1985 |
| Abstract : Adamis_1985_Int.Arch.Occup.Environ.Health_56_299 |
| ESTHER : Adamis_1985_Int.Arch.Occup.Environ.Health_56_299 |
| PubMedSearch : Adamis_1985_Int.Arch.Occup.Environ.Health_56_299 |
| PubMedID: 4066053 |
| Title : Reduction of house dust mite allergen levels in the home: use of the acaricide, pirimiphos methyl - Mitchell_1985_Clin.Allergy_15_235 |
| Author(s) : Mitchell EB , Wilkins S , Deighton JM , Platts-Mills TA |
| Ref : Clin Allergy , 15 :235 , 1985 |
| Abstract : Mitchell_1985_Clin.Allergy_15_235 |
| ESTHER : Mitchell_1985_Clin.Allergy_15_235 |
| PubMedSearch : Mitchell_1985_Clin.Allergy_15_235 |
| PubMedID: 4006173 |
| Title : Efficacy of pirimiphos methyl as a larvicide or adulticide against insecticide resistant and susceptible mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) - |
| Author(s) : Hemingway J , Rowland M , Kissoon KE |
| Ref : J Econ Entomol , 77 :868 , 1984 |
| PubMedID: 6501693 |
| Title : Partial purification and properties of sheep serum A'-esterases - Mackness_1983_Biochem.Pharmacol_32_2291 |
| Author(s) : Mackness MI , Walker CH |
| Ref : Biochemical Pharmacology , 32 :2291 , 1983 |
| Abstract : Mackness_1983_Biochem.Pharmacol_32_2291 |
| ESTHER : Mackness_1983_Biochem.Pharmacol_32_2291 |
| PubMedSearch : Mackness_1983_Biochem.Pharmacol_32_2291 |
| PubMedID: 6309189 |
| Title : [Combined toxicological and hygienic study of the organophosphate insecto-acaricide actellic] - |
| Author(s) : Kagan Iu S , Voitenko GA , Pan'shina TN , Voronina VM , Kokshareva NV |
| Ref : Gig Sanit , 6 :32 , 1983 |
| PubMedID: 6311688 |
| Title : [Cutaneous resorption of actellic (O,2-diethylamino-6-methyl pyrimidin- 4-yl-O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate) in the presence of high temperature and humidity] - Izmirova_1983_Probl.Khig_8_57 |
| Author(s) : Izmirova N , Kaloianova-Simeonova F |
| Ref : Probl Khig , 8 :57 , 1983 |
| Abstract : Izmirova_1983_Probl.Khig_8_57 |
| ESTHER : Izmirova_1983_Probl.Khig_8_57 |
| PubMedSearch : Izmirova_1983_Probl.Khig_8_57 |
| PubMedID: 6672828 |
| Title : [Effect of temephos on acetylcholinesterase activity in the brain of Tilapia guineensis. 3: Comparative effect of temephos and 3 substitute insecticides] - Pellissier_1983_Toxicol.Eur.Res_5_63 |
| Author(s) : Pellissier C , Leung Tack D , Gras G |
| Ref : Toxicol Eur Res , 5 :63 , 1983 |
| Abstract : Pellissier_1983_Toxicol.Eur.Res_5_63 |
| ESTHER : Pellissier_1983_Toxicol.Eur.Res_5_63 |
| PubMedSearch : Pellissier_1983_Toxicol.Eur.Res_5_63 |
| PubMedID: 6193610 |
| Title : A large-scale evaluation of pirimiphos-methyl 25\% WP during 1980-1981 for malaria control in Pakistan - Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| Author(s) : Nasir SM , Ahmad N , Shah MA , Azam CM |
| Ref : J Trop Med Hyg , 85 :239 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| ESTHER : Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| PubMedSearch : Nasir_1982_J.Trop.Med.Hyg_85_239 |
| PubMedID: 7154146 |
| Title : Gas-chromatographic analysis of residues of pirimiphos-methyl in water, fish, and snails - |
| Author(s) : Zakitis LH , McCray EM, Jr. |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 28 :334 , 1982 |
| PubMedID: 7082875 |
| Title : Use of granulated fertilizers with Actellic EC 50 insecticide in the control of mosquito larvae - Rettich_1981_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_25_6 |
| Author(s) : Rettich F |
| Ref : J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol , 25 :6 , 1981 |
| Abstract : Rettich_1981_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_25_6 |
| ESTHER : Rettich_1981_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_25_6 |
| PubMedSearch : Rettich_1981_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_25_6 |
| PubMedID: 6262402 |
| Title : GC-MS identification and analytical behavior of pirimiphos-methyl in imported foods - |
| Author(s) : Barry TL , Petzinger G , Gretch FM |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 27 :524 , 1981 |
| PubMedID: 7306717 |
| Title : Contact and vapour toxicity of bendiocarb and pirimiphosmethyl against Culex quinquefasciatus and Anopheles stephensi - |
| Author(s) : Das PK , Mariappan T , Somachary N |
| Ref : Indian J Med Res , 74 :380 , 1981 |
| PubMedID: 7319575 |
| Title : A comparison, on a village scale, of the effect of pirimiphos-methyl and DDT on Anopheles balabacensis - vectored malaria - |
| Author(s) : Pattanayak S , Samnotra KG , Seni A |
| Ref : J Trop Med Hyg , 83 :211 , 1980 |
| PubMedID: 7431465 |
| Title : Residual toxicity of wall-sprayed organophosphates, carbamates and pyrethroids to mosquito Culex pipiens molestus Forskal - Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| Author(s) : Rettich F |
| Ref : J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol , 24 :110 , 1980 |
| Abstract : Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| ESTHER : Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| PubMedSearch : Rettich_1980_J.Hyg.Epidemiol.Microbiol.Immunol_24_110 |
| PubMedID: 7190586 |
| Title : High-performance liquid chromatography of pirimiphos methyl and five metabolites - Brealey_1979_J.Chromatogr_168_461 |
| Author(s) : Brealey CJ , Lawrence DK |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography , 168 :461 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Brealey_1979_J.Chromatogr_168_461 |
| ESTHER : Brealey_1979_J.Chromatogr_168_461 |
| PubMedSearch : Brealey_1979_J.Chromatogr_168_461 |
| PubMedID: 762235 |
| Title : Insecticide residues in milled fractions of dry or tough wheat treated with malathion, bromophos, iodofenphos, and pirimiphos-methyl - |
| Author(s) : Mensah GW , Watters FL , Webster GR |
| Ref : J Econ Entomol , 72 :728 , 1979 |
| PubMedID: 544641 |
| Title : Determination of pirimiphos methyl in formulations by high performance liquid chromatography - Zehner_1977_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_60_14 |
| Author(s) : Zehner JM , Simonaitis RA |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 60 :14 , 1977 |
| Abstract : Zehner_1977_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_60_14 |
| ESTHER : Zehner_1977_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_60_14 |
| PubMedSearch : Zehner_1977_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_60_14 |
| PubMedID: 833089 |
| Title : [Determination of bromofos, diazinon and methylpyrimifos in fruit and vegetables] - |
| Author(s) : Zadrozinska J |
| Ref : Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig , 28 :69 , 1977 |
| PubMedID: 847332 |
| Title : Determination of the substituted pyrimidine pesticides ethirimol, dimethirimol, pirimiphos-methyl, pirimiphos-ethyl and pirimicarb in technical and formulated materials by gas chromatography - |
| Author(s) : Bagness JE , Sharples WG |
| Ref : Analyst , 99 :225 , 1974 |
| PubMedID: 4833650 |