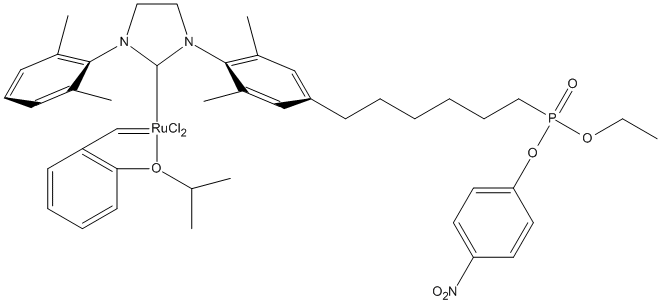
Ru-NHC-3
The incorporation of a synthetic, catalytically competent metallo cofactor into a protein scaffold to generate an artificial metalloenzyme (ArM) lead to new activities specific of the cofactor. Here NHC= N-heterocyclic carbenes Grubs-type catalyst with organophosphate function, inhibits cutinase and forms an artificial metalloenzyme for olefin metathesis
General
Type : Organophosphate,Pincer-Metal-cofactor,pNP
Chemical_Nomenclature :
Canonical SMILES :
InChI :
InChIKey :
Other name(s) :
MW : 912,86
Formula : C43H55Cl2N3O6PRu
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (1)
| Title : Ring-Closing and Cross-Metathesis with Artificial Metalloenzymes Created by Covalent Active Site-Directed Hybridization of a Lipase - Basauri-Molina_2015_Chemistry_21_15676 |
| Author(s) : Basauri-Molina M , Verhoeven DG , van Schaik AJ , Kleijn H , Klein Gebbink RJ |
| Ref : Chemistry , 21 :15676 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Basauri-Molina_2015_Chemistry_21_15676 |
| ESTHER : Basauri-Molina_2015_Chemistry_21_15676 |
| PubMedSearch : Basauri-Molina_2015_Chemistry_21_15676 |
| PubMedID: 26346291 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: fusso-cutas |