Spermidine
Spermidine is a polyamine formed from putrescine. It is found in almost all tissues in association with nucleic acids. It is found as a cation at all pH values, and is thought to help stabilize some membranes and nucleic acid structures. It is a precursor of spermine. Inhibits some lipases CarbLipBact_2 or moderately activates others
General
Type : Natural
Chemical_Nomenclature : N'-(3-aminopropyl)butane-1,4-diamine
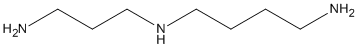
Canonical SMILES : C(CCNCCCN)CN
InChI : InChI=1S\/C7H19N3\/c8-4-1-2-6-10-7-3-5-9\/h10H,1-9H2
InChIKey : ATHGHQPFGPMSJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 1,5,10-Triazadecane,4-Azaoctamethylenediamine,Spermidin,4-Azaoctane-1,8-diamine
MW : 145.25
Formula : C7H19N3
CAS_number : 124-20-9
PubChem : 1102
UniChem : ATHGHQPFGPMSJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : Spermidine ligand of proteins in family: CarbLipBact_2
Stucture : 4FBL LipS and LipT, two metagenome-derived lipolytic enzymes increase the diversity of known lipase and esterase families 1. This is LipS
Protein : symth-q67mr3
References (3)
| Title : CGI-58, a key regulator of lipid homeostasis and signaling in plants, also regulates polyamine metabolism - Park_2014_Plant.Signal.Behav_9_e27723 |
| Author(s) : Park S , Keereetaweep J , James CN , Gidda SK , Chapman KD , Mullen RT , Dyer JM |
| Ref : Plant Signal Behav , 9 :e27723 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Park_2014_Plant.Signal.Behav_9_e27723 |
| ESTHER : Park_2014_Plant.Signal.Behav_9_e27723 |
| PubMedSearch : Park_2014_Plant.Signal.Behav_9_e27723 |
| PubMedID: 24492485 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: arath-LPAAT |
| Title : The metagenome-derived enzymes LipS and LipT increase the diversity of known lipases - Chow_2012_PLoS.One_7_e47665 |
| Author(s) : Chow J , Kovacic F , Dall Antonia Y , Krauss U , Fersini F , Schmeisser C , Lauinger B , Bongen P , Pietruszka J , Schmidt M , Menyes I , Bornscheuer UT , Eckstein M , Thum O , Liese A , Mueller-Dieckmann J , Jaeger KE , Streit WR |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 7 :e47665 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Chow_2012_PLoS.One_7_e47665 |
| ESTHER : Chow_2012_PLoS.One_7_e47665 |
| PubMedSearch : Chow_2012_PLoS.One_7_e47665 |
| PubMedID: 23112831 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: symth-q67mr3 , 9bact-k7qe48 |
| Title : Cloning, expression, purification and preliminary X-ray analysis of a putative metagenome-derived lipase - Fersini_2012_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_68_923 |
| Author(s) : Fersini F , Dall'Antonia Y , Chow J , Streit WR , Mueller-Dieckmann J |
| Ref : Acta Crystallographica Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun , 68 :923 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Fersini_2012_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_68_923 |
| ESTHER : Fersini_2012_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_68_923 |
| PubMedSearch : Fersini_2012_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_68_923 |
| PubMedID: 22869123 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: symth-q67mr3 |