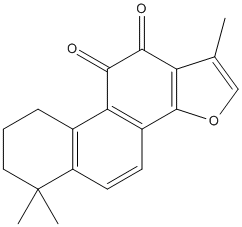
Tanshinone-IIA
Tanshinone IIA, extracted from a Chinese herb Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen), has been clinically used to treat diverse disorders such as inflammation, myocardial ischemia, and atherosclerosis. Potent, irreversible inhibition of human carboxylesterases Tanshinone Anhydride hCE1 Ki 1.9nm hiCE Ki 1.4nM
General
Type : Natural,Benzofuran
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1,6,6-trimethyl-8,9-dihydro-7H-naphtho[1,2-g][1]benzofuran-10,11-dione
Canonical SMILES : CC1=COC2=C1C(=O)C(=O)C3=C2C=CC4=C3CCCC4(C)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C19H18O3\/c1-10-9-22-18-12-6-7-13-11(5-4-8-19(13,2)3)15(12)17(21)16(20)14(10)18\/h6-7,9H,4-5,8H2,1-3H3
InChIKey : HYXITZLLTYIPOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Tanshinone IIA,568-72-9,Tanshinone II,Tanshinone B,Dan Shen Ketone,Tanshinon II,Tanshinone Anhydride
MW : 294.35
Formula : C19H18O3
CAS_number :
PubChem : 164676
UniChem : HYXITZLLTYIPOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : Tanshinone-IIA ligand of proteins in family: Carb_B_Chordata
Stucture :
Protein : human-ACHE || human-CES1 || human-CES2
References (7)
| Title : Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate improves cognitive impairment via regulating Abeta transportation in AD transgenic mouse model - Ma_2022_Metab.Brain.Dis__ |
| Author(s) : Ma HH , Wan C , Zhang LD , Zhang RR , Peng D , Qiao LJ , Zhang SJ , Cai YF , Huang HQ |
| Ref : Metabolic Brain Disease , : , 2022 |
| Abstract : Ma_2022_Metab.Brain.Dis__ |
| ESTHER : Ma_2022_Metab.Brain.Dis__ |
| PubMedSearch : Ma_2022_Metab.Brain.Dis__ |
| PubMedID: 35080687 |
| Title : Tanshinone IIA regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-related signaling pathway and ameliorates memory impairment in APP\/PS1 transgenic mice - Peng_2022_Eur.J.Pharmacol__174772 |
| Author(s) : Peng X , Chen L , Wang Z , He Y , Ruganzu JB , Guo H , Zhang X , Ji S , Zheng L , Yang W |
| Ref : European Journal of Pharmacology , :174772 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Peng_2022_Eur.J.Pharmacol__174772 |
| ESTHER : Peng_2022_Eur.J.Pharmacol__174772 |
| PubMedSearch : Peng_2022_Eur.J.Pharmacol__174772 |
| PubMedID: 35090935 |
| Title : Potent, Irreversible Inhibition of Human Carboxylesterases by Tanshinone Anhydrides Isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) - Hatfield_2018_J.Nat.Prod_81_2410 |
| Author(s) : Hatfield MJ , Binder RJ , Gannon R , Fratt EM , Bowling J , Potter PM |
| Ref : Journal of Natural Products , 81 :2410 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Hatfield_2018_J.Nat.Prod_81_2410 |
| ESTHER : Hatfield_2018_J.Nat.Prod_81_2410 |
| PubMedSearch : Hatfield_2018_J.Nat.Prod_81_2410 |
| PubMedID: 30351923 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES1 , human-CES2 |
| Title : Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel tanshinone IIA derivatives for treating pain - Li_2018_Chin.J.Nat.Med_16_113 |
| Author(s) : Li QN , Huang ZP , Gu QL , Zhi ZE , Yang YH , He L , Chen KL , Wang JX |
| Ref : Chin J Nat Med , 16 :113 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Li_2018_Chin.J.Nat.Med_16_113 |
| ESTHER : Li_2018_Chin.J.Nat.Med_16_113 |
| PubMedSearch : Li_2018_Chin.J.Nat.Med_16_113 |
| PubMedID: 29455726 |
| Title : Treatment effects of tanshinone IIA against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced memory deficits in mice - Liu_2016_Brain.Res_1631_137 |
| Author(s) : Liu C , Wu Y , Zha S , Liu M , Wang Y , Yang G , Ma K , Fei Y , Zhang Y , Hu X , Yang W , Qian Y |
| Ref : Brain Research , 1631 :137 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Liu_2016_Brain.Res_1631_137 |
| ESTHER : Liu_2016_Brain.Res_1631_137 |
| PubMedSearch : Liu_2016_Brain.Res_1631_137 |
| PubMedID: 26656068 |
| Title : Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Attenuates Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Dysfunctions via Improving Cholinergic System - Xu_2016_Biomed.Res.Int_2016_9852536 |
| Author(s) : Xu QQ , Xu YJ , Yang C , Tang Y , Li L , Cai HB , Hou BN , Chen HF , Wang Q , Shi XG , Zhang SJ |
| Ref : Biomed Res Int , 2016 :9852536 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Xu_2016_Biomed.Res.Int_2016_9852536 |
| ESTHER : Xu_2016_Biomed.Res.Int_2016_9852536 |
| PubMedSearch : Xu_2016_Biomed.Res.Int_2016_9852536 |
| PubMedID: 27556046 |
| Title : Identification of tanshinone IIA as a natural monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor by combined in silico and in vitro approach - Yang_2014_Med.Chem.Commun_5_1528 |
| Author(s) : Yang R , Lu Y , Liu J |
| Ref : Med Chem Commun , 5 :1528 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Yang_2014_Med.Chem.Commun_5_1528 |
| ESTHER : Yang_2014_Med.Chem.Commun_5_1528 |
| PubMedSearch : Yang_2014_Med.Chem.Commun_5_1528 |
| PubMedID: |