Triazophos
General
Type : Insecticide,Organophosphate,Triazol,Sulfur Compound
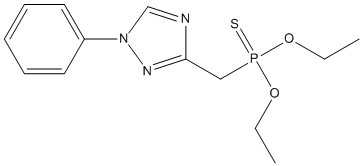
Chemical_Nomenclature : diethoxy-[(1-phenyl-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)oxy]-sulfanylidene-$l^{5}-phosphane
Canonical SMILES : CCOP(=S)(OCC)OC1=NN(C=N1)C2=CC=CC=C2
InChI : InChI=1S\/C12H16N3O3PS\/c1-3-16-19(20,17-4-2)18-12-13-10-15(14-12)11-8-6-5-7-9-11\/h5-10H,3-4H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : AMFGTOFWMRQMEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Hostathion,Triazofos,O,O-diethyl O-(1-phenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl) phosphorothioate,Diethyl O-(1-phenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl) phosphorothioate,Phenyl-1,2,4-triazolyl-3-(O,O-diethyl thionophosphate),Phenyl-3-(O,O-diethylthionophosphoryl)-1,2,4-triazol,Phosphorothioic acid O,O-diethyl O-(1-phenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl) ester
MW : 313.3
Formula : C12H16N3O3PS
CAS_number : 24017-47-8
PubChem : 32184
UniChem : AMFGTOFWMRQMEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (12)
| Title : Impact of triazophos insecticide on paddy soil environment - Liao_2002_J.Environ.Sci.(China)_14_309 |
| Author(s) : Liao M , Abid S , Huang CY , Xie ZM |
| Ref : J Environ Sci (China) , 14 :309 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Liao_2002_J.Environ.Sci.(China)_14_309 |
| ESTHER : Liao_2002_J.Environ.Sci.(China)_14_309 |
| PubMedSearch : Liao_2002_J.Environ.Sci.(China)_14_309 |
| PubMedID: 12211979 |
| Title : Persistence and dissipation behavior of triazophos in canal water under Indian climatic conditions - Rani_2001_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_50_82 |
| Author(s) : Rani S , Madan VK , Kathpal TS |
| Ref : Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety , 50 :82 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Rani_2001_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_50_82 |
| ESTHER : Rani_2001_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_50_82 |
| PubMedSearch : Rani_2001_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_50_82 |
| PubMedID: 11534957 |
| Title : Thermal stability of organophosphorus pesticide triazophos and its relevance in the assessment of risk to the consumer of triazophos residues in food - Holden_2001_J.Agric.Food.Chem_49_103 |
| Author(s) : Holden AJ , Chen L , Shaw IC |
| Ref : Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry , 49 :103 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Holden_2001_J.Agric.Food.Chem_49_103 |
| ESTHER : Holden_2001_J.Agric.Food.Chem_49_103 |
| PubMedSearch : Holden_2001_J.Agric.Food.Chem_49_103 |
| PubMedID: 11170565 |
| Title : How the variability issue was uncovered: the history of the UK residue variability findings - Harris_2000_Food.Addit.Contam_17_491 |
| Author(s) : Harris CA |
| Ref : Food Additives & Contaminants , 17 :491 , 2000 |
| Abstract : Harris_2000_Food.Addit.Contam_17_491 |
| ESTHER : Harris_2000_Food.Addit.Contam_17_491 |
| PubMedSearch : Harris_2000_Food.Addit.Contam_17_491 |
| PubMedID: 10983570 |
| Title : Hepatic injury and disturbed amino acid metabolism in mice following prolonged exposure to organophosphorus pesticides - Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| Author(s) : Gomes J , Dawodu AH , Lloyd O , Revitt DM , Anilal SV |
| Ref : Hum Exp Toxicol , 18 :33 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| ESTHER : Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| PubMedSearch : Gomes_1999_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_18_33 |
| PubMedID: 10025366 |
| Title : The variation of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables and the associated assessment of risk - Hamey_1999_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_30_S34 |
| Author(s) : Hamey PY , Harris CA |
| Ref : Regul Toxicol Pharmacol , 30 :S34 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Hamey_1999_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_30_S34 |
| ESTHER : Hamey_1999_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_30_S34 |
| PubMedSearch : Hamey_1999_Regul.Toxicol.Pharmacol_30_S34 |
| PubMedID: 10597612 |
| Title : Evaluation of multiwavelength chromatograms for the quantification of mixtures of pesticides by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection with multivariate calibration - Martinez_1997_J.Chromatogr.A_778_139 |
| Author(s) : Martinez Galera M , Martinez Vidal JL , Garrido Frenich A , Gil Garcia MD |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 778 :139 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Martinez_1997_J.Chromatogr.A_778_139 |
| ESTHER : Martinez_1997_J.Chromatogr.A_778_139 |
| PubMedSearch : Martinez_1997_J.Chromatogr.A_778_139 |
| PubMedID: 9299731 |
| Title : Selective, solid-matrix dispersion extraction of organophosphate pesticide residues from milk - Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| Author(s) : Di Muccio A , Pelosi P , Camoni I , Attard Barbini D , Dommarco R , Generali T , Ausili A |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 754 :497 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| ESTHER : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedSearch : Di Muccio_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_754_497 |
| PubMedID: 8997741 |
| Title : Mutagenic evaluation of the organophosphorus insecticides methyl parathion and triazophos in Drosophila melanogaster - Velazquez_1990_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_31_313 |
| Author(s) : Velazquez A , Xamena N , Creus A , Marcos R |
| Ref : J Toxicol Environ Health , 31 :313 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Velazquez_1990_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_31_313 |
| ESTHER : Velazquez_1990_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_31_313 |
| PubMedSearch : Velazquez_1990_J.Toxicol.Environ.Health_31_313 |
| PubMedID: 2123939 |
| Title : The study of heptenophos and triazophos residues in vegetables treated with the organophosphorus insecticides Hostaquick and Hostathion - Horbowicz_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_465 |
| Author(s) : Horbowicz M , Czapski J , Bakowski J |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health B , 18 :465 , 1983 |
| Abstract : Horbowicz_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_465 |
| ESTHER : Horbowicz_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_465 |
| PubMedSearch : Horbowicz_1983_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_18_465 |
| PubMedID: 6630896 |
| Title : Triazophos (active substance in the sales product Hostathion) environmental impact (degradation on\/in plants, in soil and in warm-blooded animals) - |
| Author(s) : Bock KD , Bock R , Fischer H , Gorbach S , Thier WG |
| Ref : Environmental Quality Safety Supplement , 3 :833 , 1975 |
| PubMedID: 1063719 |