ZFR
The mycotoxin zearalenone has been contaminating maize and other grains. It can be hydrolyzed and inactivated by the lactonase ZHD. Zearalenone differs from other quorum-sensing lactones. ZFR is a ligand product of hydrolysis. Macrolides are organic compounds containing a lactone ring of at least twelve members.
General
Type : Natural,Toxin,Mycotoxin-metabolite
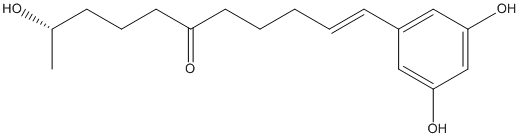
Chemical_Nomenclature : (E,10S)-1-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-10-hydroxyundec-1-en-6-one
Canonical SMILES : CC(CCCC(=O)CCCC=CC1=CC(=CC(=C1)O)O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C17H24O4\/c1-13(18)6-5-9-15(19)8-4-2-3-7-14-10-16(20)12-17(21)11-14\/h3,7,10-13,18,20-21H,2,4-6,8-9H2,1H3\/b7-3+\/t13-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : TVXRLKRGDWQGQV-MXPWBENCSA-N
Other name(s) : (1e,10s)-1-(3,5-Dihydroxyphenyl)-10-Hydroxyundec-1-En-6-One,SCHEMBL20975642,Q27467963,(2S,10E)-2-Hydroxy-11-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-10-undecene-6-one,DHZEN,(E)-1-(3,5-dihydroxy-phenyl)-10-hydroxy-1-undecen-6-one
MW : 292.4
Formula : C17H24O4
CAS_number :
PubChem : 101224147
UniChem : TVXRLKRGDWQGQV-MXPWBENCSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : ZFR ligand of proteins in family: Zearalenone-hydrolase
Stucture :
Protein : biooc-ZHD101
References (1)
| Title : The structure of a complex of the lactonohydrolase zearalenone hydrolase with the hydrolysis product of zearalenone at 1.60 A resolution - Qi_2017_Acta.Crystallogr.F.Struct.Biol.Commun_73_376 |
| Author(s) : Qi Q , Yang WJ , Zhou HJ , Ming DM , Sun KL , Xu TY , Hu XJ , Lv H |
| Ref : Acta Crystallographica F Struct Biol Commun , 73 :376 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Qi_2017_Acta.Crystallogr.F.Struct.Biol.Commun_73_376 |
| ESTHER : Qi_2017_Acta.Crystallogr.F.Struct.Biol.Commun_73_376 |
| PubMedSearch : Qi_2017_Acta.Crystallogr.F.Struct.Biol.Commun_73_376 |
| PubMedID: 28695844 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: biooc-ZHD101 |