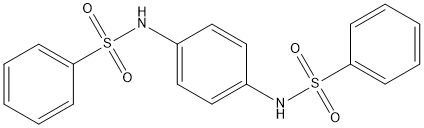
bis-benzene-sulfonamide
Prototype of a serie of compounds inhibiting hydrolysis of CPT11 by human intestinal carboxylesterase. Specificity in comparison with other carboxylesterases and cholinesterases was studied (Wadkins et al. 2004). Inhibition of less than 100nM was observed for p-chlorosubstituted benzene rings at both end of the molecule
General
Type : Lipase inhibitor,Sulfur Compound,Sulfonamide,Benzenesulfonamide
Chemical_Nomenclature : N-{4-[(Phenylsulfonyl)aminophenyl}benzenesulfonamide
Canonical SMILES : C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3
InChI : InChI=1S\/C18H16N2O4S2\/c21-25(22,17-7-3-1-4-8-17)19-15-11-13-16(14-12-15)20-26(23,24)18-9-5-2-6-10-18\/h1-14,19-20H
InChIKey : KOIVCFKRQUPPKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : CHEMBL2138676,MLS002919887,N,n'-1,4-phenylenedibenzenesulfonamide,NSC126446,AC1L5M6C,AC1Q6VV7,SCHEMBL810795
MW : 388.46
Formula : C18H164OS2N2
CAS_number :
PubChem : 277548
UniChem : KOIVCFKRQUPPKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : bis-benzene-sulfonamide ligand of proteins in family: Carboxylesterase || Carb_B_Chordata
Stucture :
Protein :
References (2)
| Title : Mammalian carboxylesterases: from drug targets to protein therapeutics - Redinbo_2005_Drug.Discov.Today_10_313 |
| Author(s) : Redinbo MR , Potter PM |
| Ref : Drug Discov Today , 10 :313 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Redinbo_2005_Drug.Discov.Today_10_313 |
| ESTHER : Redinbo_2005_Drug.Discov.Today_10_313 |
| PubMedSearch : Redinbo_2005_Drug.Discov.Today_10_313 |
| PubMedID: 15749280 |
| Title : Discovery of novel selective inhibitors of human intestinal carboxylesterase for the amelioration of irinotecan-induced diarrhea: synthesis, quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis, and biological activity - Wadkins_2004_Mol.Pharmacol_65_1336 |
| Author(s) : Wadkins RM , Hyatt JL , Yoon KJ , Morton CL , Lee RE , Damodaran K , Beroza P , Danks MK , Potter PM |
| Ref : Molecular Pharmacology , 65 :1336 , 2004 |
| Abstract : Wadkins_2004_Mol.Pharmacol_65_1336 |
| ESTHER : Wadkins_2004_Mol.Pharmacol_65_1336 |
| PubMedSearch : Wadkins_2004_Mol.Pharmacol_65_1336 |
| PubMedID: 15155827 |