Coenzyme-A
General
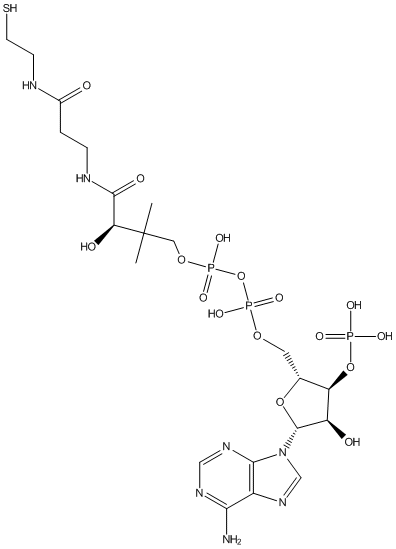
Type : CoA || Aminopurin
Chemical_Nomenclature : [[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-phosphonooxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] [(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxo-4-[[3-oxo-3-(2-sulfanylethylamino)propyl]amino]butyl] hydrogen phosphate
Canonical SMILES : CC(C)(COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OCC1C(C(C(O1)N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3N)O)OP(=O)(O)O)C(C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCS)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C21H36N7O16P3S\/c1-21(2,16(31)19(32)24-4-3-12(29)23-5-6-48)8-41-47(38,39)44-46(36,37)40-7-11-15(43-45(33,34)35)14(30)20(42-11)28-10-27-13-17(22)25-9-26-18(13)28\/h9-11,14-16,20,30-31,48H,3-8H2,1-2H3,(H,23,29)(H,24,32)(H,36,37)(H,38,39)(H2,22,25,26)(H2,33,34,35)\/t11-,14-,15-,16+,20-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : RGJOEKWQDUBAIZ-IBOSZNHHSA-N
Other name(s) : Coenzyme A, Coenzym A, Co-enzyme-A, HSCoA, CoASH, CoA
MW : 767.53
Formula : C21H36N7O16P3S
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
References (3)
| Title : Functional Annotation of ABHD14B, an Orphan Serine Hydrolase Enzyme - Rajendran_2020_Biochemistry_59_183 |
| Author(s) : Rajendran A , Vaidya K , Mendoza J , Bridwell-Rabb J , Kamat SS |
| Ref : Biochemistry , 59 :183 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Rajendran_2020_Biochemistry_59_183 |
| ESTHER : Rajendran_2020_Biochemistry_59_183 |
| PubMedSearch : Rajendran_2020_Biochemistry_59_183 |
| PubMedID: 31478652 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CIB |
| Title : Crystal structure and biochemical characterization of O-acetylhomoserine acetyltransferase from Mycobacterium smegmatis ATCC 19420 - Sagong_2019_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_517_399 |
| Author(s) : Sagong HY , Hong J , Kim KJ |
| Ref : Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications , 517 :399 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Sagong_2019_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_517_399 |
| ESTHER : Sagong_2019_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_517_399 |
| PubMedSearch : Sagong_2019_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_517_399 |
| PubMedID: 31378370 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: mycs2-metx |
| Title : Structural and biochemical characterisation of Archaeoglobus fulgidus esterase reveals a bound CoA molecule in the vicinity of the active site - Sayer_2016_Sci.Rep_6_25542 |
| Author(s) : Sayer C , Finnigan W , Isupov MN , Levisson M , Kengen SW , Van der Oost J , Harmer NJ , Littlechild JA |
| Ref : Sci Rep , 6 :25542 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Sayer_2016_Sci.Rep_6_25542 |
| ESTHER : Sayer_2016_Sci.Rep_6_25542 |
| PubMedSearch : Sayer_2016_Sci.Rep_6_25542 |
| PubMedID: 27160974 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: arcfu-est2 |