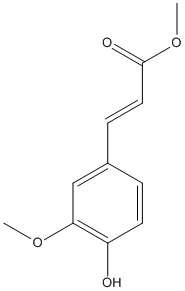
Methyl-ferulate
General
Type : Aryl ester || Acrylate || Feruloyl || Hydroxycinnamic-ester
Chemical_Nomenclature : methyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate
Canonical SMILES : COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C=CC(=O)OC)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C11H12O4\/c1-14-10-7-8(3-5-9(10)12)4-6-11(13)15-2\/h3-7,12H,1-2H3\/b6-4+
InChIKey : AUJXJFHANFIVKH-GQCTYLIASA-N
Other name(s) : MFA, Methyl ferulate, Methyl 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylate, Ferulic acid methyl ester, Ferulic acid methylester, CHEBI:67379
Target
Families : A85-Feruloyl-Esterase, FaeC, Lipase_3, Tannase, FAE-Bacterial-promiscuous
References (12)
| Title : Structural insights into the oligomeric effects on catalytic activity of a decameric feruloyl esterase and its application in ferulic acid production - Du_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__126540 |
| Author(s) : Du G , Wang Y , Zhang Y , Yu H , Liu S , Ma X , Cao H , Wei X , Wen B , Li Z , Fan S , Zhou H , Xin F |
| Ref : Int J Biol Macromol , :126540 , 2023 |
| Abstract : Du_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__126540 |
| ESTHER : Du_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__126540 |
| PubMedSearch : Du_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__126540 |
| PubMedID: 37634773 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: bactn-BT4077 |
| Title : Fungal feruloyl esterases can catalyze release of diferulic acids from complex arabinoxylan - Lin_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__123365 |
| Author(s) : Lin S , Hunt CJ , Holck J , Brask J , Krogh K , Meyer AS , Wilkens C , Agger JW |
| Ref : Int J Biol Macromol , :123365 , 2023 |
| Abstract : Lin_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__123365 |
| ESTHER : Lin_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__123365 |
| PubMedSearch : Lin_2023_Int.J.Biol.Macromol__123365 |
| PubMedID: 36690236 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: humin-HiFae1 , malci-McFae1 , 9zzzz-CE1.6RZN , 9zzzz-DAC80243 , 9pezi-a0a481sy08 , aspni-FAEA , aspor-q2uh24 , aspor-q2umx6 , aspor-q2unw5 , aspor-q2up89 , neucr-faeb , magoy-l7ic25 |
| Title : Crystal structure of the feruloyl esterase from Lentilactobacillus buchneri reveals a novel homodimeric state - Kasmaei_2022_Front.Microbiol_13_1050160 |
| Author(s) : Kasmaei KM , Kalyani DC , Reichenbach T , Jimenez-Quero A , Vilaplana F , Divne C |
| Ref : Front Microbiol , 13 :1050160 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Kasmaei_2022_Front.Microbiol_13_1050160 |
| ESTHER : Kasmaei_2022_Front.Microbiol_13_1050160 |
| PubMedSearch : Kasmaei_2022_Front.Microbiol_13_1050160 |
| PubMedID: 36569051 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: lenbu-d7ru28 |
| Title : Structure-guided rational design of the Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius feruloyl esterase GthFAE to improve its thermostability - Yang_2022_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_600_117 |
| Author(s) : Yang W , Sun L , Dong P , Chen Y , Zhang H , Huang X , Wu L , Chen L , Jing D , Wu Y |
| Ref : Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications , 600 :117 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Yang_2022_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_600_117 |
| ESTHER : Yang_2022_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_600_117 |
| PubMedSearch : Yang_2022_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_600_117 |
| PubMedID: 35219099 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: partm-GthFAE |
| Title : A polysaccharide utilization locus from the gut bacterium Dysgonomonas mossii encodes functionally distinct carbohydrate esterases - Kmezik_2021_J.Biol.Chem__100500 |
| Author(s) : Kmezik C , Mazurkewich S , Meents T , McKee LS , Idstrom A , Armeni M , Savolainen O , Branden G , Larsbrink J |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , :100500 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Kmezik_2021_J.Biol.Chem__100500 |
| ESTHER : Kmezik_2021_J.Biol.Chem__100500 |
| PubMedSearch : Kmezik_2021_J.Biol.Chem__100500 |
| PubMedID: 33667545 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9bact-f8x1n1.1 , 9bact-f8x1n1.2 |
| Title : Identification and characterization of ferulic acid esterase from Penicillium chrysogenum 31B: de-esterification of ferulic acid decorated with l-arabinofuranoses and d-galactopyranoses in sugar beet pectin - Phuengmaung_2019_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_131_109380 |
| Author(s) : Phuengmaung P , Sunagawa Y , Makino Y , Kusumoto T , Handa S , Sukhumsirichart W , Sakamoto T |
| Ref : Enzyme Microb Technol , 131 :109380 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Phuengmaung_2019_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_131_109380 |
| ESTHER : Phuengmaung_2019_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_131_109380 |
| PubMedSearch : Phuengmaung_2019_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_131_109380 |
| PubMedID: 31615673 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: pench-q3v6c9 |
| Title : Characterization of a feruloyl esterase from Aspergillus terreus facilitates the division of fungal enzymes from Carbohydrate Esterase family 1 of the carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZy) database - Makela_2018_Microb.Biotechnol_11_869 |
| Author(s) : Makela MR , Dilokpimol A , Koskela SM , Kuuskeri J , de Vries RP , Hilden K |
| Ref : Microb Biotechnol , 11 :869 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Makela_2018_Microb.Biotechnol_11_869 |
| ESTHER : Makela_2018_Microb.Biotechnol_11_869 |
| PubMedSearch : Makela_2018_Microb.Biotechnol_11_869 |
| PubMedID: 29697197 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: asptn-q0ci40 |
| Title : Biochemical and Structural Analyses of Two Cryptic Esterases in Bacteroides intestinalis and their Synergistic Activities with Cognate Xylanases - Wefers_2017_J.Mol.Biol_429_2509 |
| Author(s) : Wefers D , Cavalcante JJV , Schendel RR , Deveryshetty J , Wang K , Wawrzak Z , Mackie RI , Koropatkin NM , Cann I |
| Ref : Journal of Molecular Biology , 429 :2509 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Wefers_2017_J.Mol.Biol_429_2509 |
| ESTHER : Wefers_2017_J.Mol.Biol_429_2509 |
| PubMedSearch : Wefers_2017_J.Mol.Biol_429_2509 |
| PubMedID: 28669823 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9bace-b3c9d0.2 , 9bace-b3cet1 |
| Title : Overexpression of Aspergillus tubingensis faeA in protease-deficient Aspergillus niger enables ferulic acid production from plant material - Zwane_2014_J.Ind.Microbiol.Biotechnol_41_1027 |
| Author(s) : Zwane EN , Rose SH , van Zyl WH , Rumbold K , Viljoen-Bloom M |
| Ref : J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol , 41 :1027 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Zwane_2014_J.Ind.Microbiol.Biotechnol_41_1027 |
| ESTHER : Zwane_2014_J.Ind.Microbiol.Biotechnol_41_1027 |
| PubMedSearch : Zwane_2014_J.Ind.Microbiol.Biotechnol_41_1027 |
| PubMedID: 24664515 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: asptu-FAEA |
| Title : Development and application of a suite of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes for analyzing plant cell walls - Bauer_2006_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_103_11417 |
| Author(s) : Bauer S , Vasu P , Persson S , Mort AJ , Somerville CR |
| Ref : Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A , 103 :11417 , 2006 |
| Abstract : Bauer_2006_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_103_11417 |
| ESTHER : Bauer_2006_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_103_11417 |
| PubMedSearch : Bauer_2006_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_103_11417 |
| PubMedID: 16844780 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: emeni-axe1 , emeni-CUTI3 , emeni-faec |
| Title : Identification of a type-D feruloyl esterase from Neurospora crassa - Crepin_2004_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_63_567 |
| Author(s) : Crepin VF , Faulds CB , Connerton IF |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 63 :567 , 2004 |
| Abstract : Crepin_2004_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_63_567 |
| ESTHER : Crepin_2004_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_63_567 |
| PubMedSearch : Crepin_2004_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_63_567 |
| PubMedID: 14595525 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: neucr-FAED |