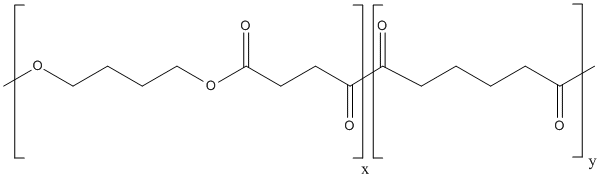
Polybutylene-succinate-co-adipate
General
Type : Polymer || Polyester || Aliphatic polyester || co-polyester
Chemical_Nomenclature :
Canonical SMILES :
InChI :
InChIKey :
Other name(s) : Poly(butylene succinate) co adipate, PBSA, poly-(butylene succinate-co-adipate), Polybutylene succinate co adipate, Bionolle 1001MD, Bionolle 1020MD
MW :
Formula :
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
References (10)
| Title : Co-Expression of ORFCma with PHB Depolymerase (PhaZCma ) in Escherichia coli Induces Efficient Whole-Cell Biodegradation of Polyesters - Lee_2018_Biotechnol.J_13_e1700560 |
| Author(s) : Lee MC , Liu EJ , Yang CH , Hsiao LJ , Wu TM , Li SY |
| Ref : Biotechnol J , 13 :e1700560 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Lee_2018_Biotechnol.J_13_e1700560 |
| ESTHER : Lee_2018_Biotechnol.J_13_e1700560 |
| PubMedSearch : Lee_2018_Biotechnol.J_13_e1700560 |
| PubMedID: 29337429 |
| Title : Asp30 of Aspergillus oryzae cutinase CutL1 is involved in the ionic interaction with fungal hydrophobin RolA - Terauchi_2017_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_81_1363 |
| Author(s) : Terauchi Y , Kim YK , Tanaka T , Nanatani K , Takahashi T , Abe K |
| Ref : Biosci Biotechnol Biochem , :1 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Terauchi_2017_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_81_1363 |
| ESTHER : Terauchi_2017_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_81_1363 |
| PubMedSearch : Terauchi_2017_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_81_1363 |
| PubMedID: 28475418 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: aspor-cutas |
| Title : Analysis of the ionic interaction between the hydrophobin RodA and two cutinases of Aspergillus nidulans obtained via an Aspergillus oryzae expression system - Tanaka_2017_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_101_2343 |
| Author(s) : Tanaka T , Nakayama M , Takahashi T , Nanatani K , Yamagata Y , Abe K |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 101 :2343 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Tanaka_2017_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_101_2343 |
| ESTHER : Tanaka_2017_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_101_2343 |
| PubMedSearch : Tanaka_2017_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_101_2343 |
| PubMedID: 27917435 |
| Title : Ionic interaction of positive amino acid residues of fungal hydrophobin RolA with acidic amino acid residues of cutinase CutL1 - Takahashi_2015_Mol.Microbiol_96_14 |
| Author(s) : Takahashi T , Tanaka T , Tsushima Y , Muragaki K , Uehara K , Takeuchi S , Maeda H , Yamagata Y , Nakayama M , Yoshimi A , Abe K |
| Ref : Molecular Microbiology , 96 :14 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Takahashi_2015_Mol.Microbiol_96_14 |
| ESTHER : Takahashi_2015_Mol.Microbiol_96_14 |
| PubMedSearch : Takahashi_2015_Mol.Microbiol_96_14 |
| PubMedID: 25588312 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: aspor-cutas |
| Title : A novel Ca-activated, thermostabilized polyesterase capable of hydrolyzing polyethylene terephthalate from Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190 - Kawai_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_10053 |
| Author(s) : Kawai F , Oda M , Tamashiro T , Waku T , Tanaka N , Yamamoto M , Mizushima H , Miyakawa T , Tanokura M |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 98 :10053 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Kawai_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_10053 |
| ESTHER : Kawai_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_10053 |
| PubMedSearch : Kawai_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_10053 |
| PubMedID: 24929560 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sacvd-c7mve8 |
| Title : Microbial degradation of aliphatic and aliphatic-aromatic co-polyesters - Shah_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_3437 |
| Author(s) : Shah AA , Kato S , Shintani N , Kamini NR , Nakajima-kambe T |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 98 :3437 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Shah_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_3437 |
| ESTHER : Shah_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_3437 |
| PubMedSearch : Shah_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_3437 |
| PubMedID: 24522729 |
| Title : Biodegradable plastic-degrading enzyme from Pseudozyma antarctica: cloning, sequencing, and characterization - Shinozaki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_2951 |
| Author(s) : Shinozaki Y , Morita T , Cao XH , Yoshida S , Koitabashi M , Watanabe T , Suzuki K , Sameshima-Yamashita Y , Nakajima-kambe T , Fujii T , Kitamoto HK |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 97 :2951 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Shinozaki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_2951 |
| ESTHER : Shinozaki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_2951 |
| PubMedSearch : Shinozaki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_2951 |
| PubMedID: 22678026 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psea2-s6bc01 |
| Title : Isolation of bacteria degrading poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate) and their lip A gene - Lee_2010_Int.Biodeterior.Biodegrad_64_184 |
| Author(s) : Crabbe JR , Campbell JR , Thompson L , Walz SL , Schultz WW |
| Ref : International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation , 64 :184 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Lee_2010_Int.Biodeterior.Biodegrad_64_184 |
| ESTHER : Lee_2010_Int.Biodeterior.Biodegrad_64_184 |
| PubMedSearch : Lee_2010_Int.Biodeterior.Biodegrad_64_184 |
| PubMedID: |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9burk-i3rta9 , burvg-a4jm54 |
| Title : Purification and characterization of a biodegradable plastic-degrading enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae - Maeda_2005_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_67_778 |
| Author(s) : Maeda H , Yamagata Y , Abe K , Hasegawa F , Machida M , Ishioka R , Gomi K , Nakajima T |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 67 :778 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Maeda_2005_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_67_778 |
| ESTHER : Maeda_2005_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_67_778 |
| PubMedSearch : Maeda_2005_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_67_778 |
| PubMedID: 15968570 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: aspor-cutas |
| Title : Biodegradation of poly(tetramethylene succinate-co-tetramethylene adipate) and poly(tetramethylene succinate) through water-soluble products - Kitakuni_2001_Environ.Toxicol.Chem_20_941 |
| Author(s) : Kitakuni E , Yoshikawa K , Nakano K , Sasuga J , Nobiki M , Naoi H , Yokota Y , Ishioka R , Yakabe Y |
| Ref : Environ Toxicol Chem , 20 :941 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Kitakuni_2001_Environ.Toxicol.Chem_20_941 |
| ESTHER : Kitakuni_2001_Environ.Toxicol.Chem_20_941 |
| PubMedSearch : Kitakuni_2001_Environ.Toxicol.Chem_20_941 |
| PubMedID: 11337881 |