PFAc
N-Acyloxymethyl-phthalimides are esterase-sensitive chemical tools that enable controllable delivery of formaldehyde to human cells. N-acyloxymethyl-phthalimides can increase intracellular HCHO concentrations, can affect cancer cell metabolism, can induce DPCs, and can kill gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells
General
Type : Phthalimido, Acetate
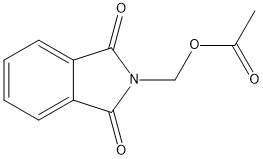
Chemical_Nomenclature : (1,3-dioxoisoindol-2-yl)methyl acetate
Canonical SMILES : CC(=O)OCN1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C1=O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C11H9NO4\/c1-7(13)16-6-12-10(14)8-4-2-3-5-9(8)11(12)15\/h2-5H,6H2,1H3
InChIKey : TUKNTJVUVGIEQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : (1,3-dioxoisoindol-2-yl)methyl Acetate || N-(acetoxymethyl)phthalimide || 1H-Isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, 2-[(acetyloxy)methyl]- || SCHEMBL2701523
MW : 219.19
Formula : C11H9NO4
CAS_number : 5493-24-3
PubChem : 4737795
UniChem : TUKNTJVUVGIEQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Target
Structures : No structure
Families : No family
References (3)
| Title : N-Acyloxymethyl-phthalimides deliver genotoxic formaldehyde to human cells - Emms_2023_Chem.Sci_14_12498 |
| Author(s) : Emms VL , Lewis LA , Beja L , Bulman NFA , Pires E , Muskett FW , McCullagh JSO , Swift LP , McHugh PJ , Hopkinson RJ |
| Ref : Chem Sci , 14 :12498 , 2023 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Emms_2023_Chem.Sci_14_12498 |
| PubMedID: 38020377 |
| Title : N-Acyloxymethyl-phthalimides deliver genotoxic formaldehyde to human cells - Emms_2023_Chem.Sci_14_12498 |
| Author(s) : Emms VL , Lewis LA , Beja L , Bulman NFA , Pires E , Muskett FW , McCullagh JSO , Swift LP , McHugh PJ , Hopkinson RJ |
| Ref : Chem Sci , 14 :12498 , 2023 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Emms_2023_Chem.Sci_14_12498 |
| PubMedID: 38020377 |
| Title : N-Acyloxymethyl-phthalimides deliver genotoxic formaldehyde to human cells - Emms_2023_Chem.Sci_14_12498 |
| Author(s) : Emms VL , Lewis LA , Beja L , Bulman NFA , Pires E , Muskett FW , McCullagh JSO , Swift LP , McHugh PJ , Hopkinson RJ |
| Ref : Chem Sci , 14 :12498 , 2023 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Emms_2023_Chem.Sci_14_12498 |
| PubMedID: 38020377 |