Fluphenazine
antipsychotic agent which is no longer in common use. Fluphenazine can cause mild and transient serum enzyme elevations and has been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent cholestatic liver injury. blocking postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptors in the limbic, cortical system and basal ganglia. This prevents the actions of dopamine, thereby reducing the hallucinations and delusions that are associated with schizophrenia
General
Type : Phenothiazine,Sulfur Compound,Not A\/B H target,Trifluoro
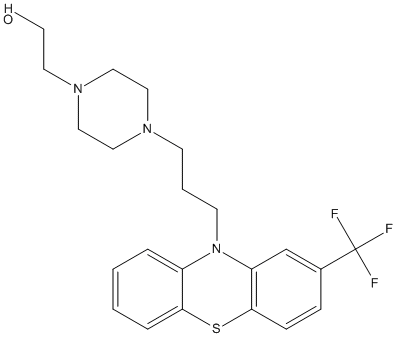
Chemical_Nomenclature : 2-[4-[3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazin-10-yl]propyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethanol
Canonical SMILES : C1CN(CCN1CCCN2C3=CC=CC=C3SC4=C2C=C(C=C4)C(F)(F)F)CCO
InChI : InChI=1S\/C22H26F3N3OS\/c23-22(24,25)17-6-7-21-19(16-17)28(18-4-1-2-5-20(18)30-21)9-3-8-26-10-12-27(13-11-26)14-15-29\/h1-2,4-7,16,29H,3,8-15H2
InChIKey : PLDUPXSUYLZYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Triflumethazine,Fluorophenazine,Fluorphenazine,CHEBI:5123,ZINC19203912,DB00623,CHEMBL726,SCHEMBL19221
MW : 437.5
Formula : C22H26F3N3OS
CAS_number : 69-23-8
PubChem : 3372
UniChem : PLDUPXSUYLZYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families :
Stucture :
Protein :
References (8)
| Title : Antiviral activity of chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, perphenazine, prochlorperazine, and thioridazine towards RNA-viruses. A review - Otreba_2020_Eur.J.Pharmacol_887_173553 |
| Author(s) : Otreba M , Kosmider L , Rzepecka-Stojko A |
| Ref : European Journal of Pharmacology , 887 :173553 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Otreba_2020_Eur.J.Pharmacol_887_173553 |
| ESTHER : Otreba_2020_Eur.J.Pharmacol_887_173553 |
| PubMedSearch : Otreba_2020_Eur.J.Pharmacol_887_173553 |
| PubMedID: 32949606 |
| Title : Treatment of psychotic symptoms in patients with Parkinson disease - Chen_2017_Ment.Health.Clin_7_262 |
| Author(s) : Chen JJ |
| Ref : Ment Health Clin , 7 :262 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Chen_2017_Ment.Health.Clin_7_262 |
| ESTHER : Chen_2017_Ment.Health.Clin_7_262 |
| PubMedSearch : Chen_2017_Ment.Health.Clin_7_262 |
| PubMedID: 29955532 |
| Title : In vitro human plasma leucine(5)-enkephalin degradation is inhibited by a select number of drugs with the phenothiazine molecule in their chemical structure - Mosnaim_2003_Pharmacology_67_6 |
| Author(s) : Mosnaim AD , Puente J , Saavedra R , Diamond S , Wolf ME |
| Ref : Pharmacology , 67 :6 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Mosnaim_2003_Pharmacology_67_6 |
| ESTHER : Mosnaim_2003_Pharmacology_67_6 |
| PubMedSearch : Mosnaim_2003_Pharmacology_67_6 |
| PubMedID: 12444298 |
| Title : A comparative study of the anticholinesterase activity of several antipsychotic agents - Nasello_2003_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_75_895 |
| Author(s) : Nasello AG , Gidali D , Felicio LF |
| Ref : Pharmacol Biochem Behav , 75 :895 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Nasello_2003_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_75_895 |
| ESTHER : Nasello_2003_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_75_895 |
| PubMedSearch : Nasello_2003_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_75_895 |
| PubMedID: 12957233 |
| Title : Inhibition of butyrylcholinesterase by phenothiazine derivatives - Debord_2002_J.Enzyme.Inhib.Med.Chem_17_197 |
| Author(s) : Debord J , Merle L , Bollinger JC , Dantoine T |
| Ref : J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem , 17 :197 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Debord_2002_J.Enzyme.Inhib.Med.Chem_17_197 |
| ESTHER : Debord_2002_J.Enzyme.Inhib.Med.Chem_17_197 |
| PubMedSearch : Debord_2002_J.Enzyme.Inhib.Med.Chem_17_197 |
| PubMedID: 12443046 |
| Title : A highly sensitive and specific radioimmunoassay for quantitation of plasma fluphenazine - Lo_1988_J.Pharm.Sci_77_255 |
| Author(s) : Lo ES , Fein M , Hunter C , Suckow RF , Cooper TB |
| Ref : J Pharm Sci , 77 :255 , 1988 |
| Abstract : Lo_1988_J.Pharm.Sci_77_255 |
| ESTHER : Lo_1988_J.Pharm.Sci_77_255 |
| PubMedSearch : Lo_1988_J.Pharm.Sci_77_255 |
| PubMedID: 3373431 |
| Title : Effects of the Combined Treatment of Rats with Fluphenazine and Choline or Lecithin on the Striatal Cholinergic and Dopaminergic System - |
| Author(s) : Flentge F , Arst D , Westerink BH , Zigmond MJ , Hanin I |
| Ref : Advances in Behavioral Biology , 30 :859 , 1986 |
| PubMedID: |
| Title : Fluphenazine-induced decline in striatal acetylcholine content is not abolished by exogenous choline - |
| Author(s) : Sherman KA , Zigmond MJ , Hanin I |
| Ref : Neuropharmacology , 20 :921 , 1981 |
| PubMedID: 7301054 |