Retinol-acetate
Retinyl Acetate is a naturally-occurring fatty acid ester form of retinol (vitamin A) with potential antineoplastic and chemopreventive activities. Retinyl acetate binds to and activates retinoid receptors, inducing cell differentiation and decreasing cell proliferation
General
Type : Retinol ester, Natural, Acetate
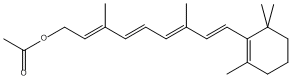
Chemical_Nomenclature : [(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenyl] acetate
Canonical SMILES : CC1=C(C(CCC1)(C)C)C=CC(=CC=CC(=CCOC(=O)C)C)Ce
InChI : InChI=1S\/C22H32O2\/c1-17(9-7-10-18(2)14-16-24-20(4)23)12-13-21-19(3)11-8-15-22(21,5)6\/h7,9-10,12-14H,8,11,15-16H2,1-6H3\/b10-7+,13-12+,17-9+,18-14+
InChIKey : QGNJRVVDBSJHIZ-QHLGVNSISA-N
Other name(s) : LMPR01090012 || Retinol Acetate || All-trans-retinyl Acetate || Retinyl acetate || Vitamin A acetate || Retinol, acetate
MW : 328.2
Formula : C22H32O2
CAS_number : 127-47-9
PubChem : 638034
UniChem : QGNJRVVDBSJHIZ-QHLGVNSISA-N
Target
Structures : No structure
Families : No family
References
No reference