CHEMBL3585776
compound 18 in Akincioglu et al. 2015. Ki 4.5 +/- 0.61 pM inhibits also carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes I and II
General
Type : Carbamate,Sulfur Compound,Sulfonamide
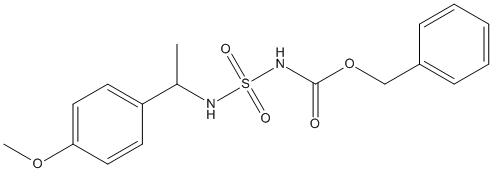
Chemical_Nomenclature : benzyl N-[1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylsulfamoyl]carbamate
Canonical SMILES : CC(C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)NS(=O)(=O)NC(=O)OCC2=CC=CC=C2
InChI : InChI=1S\/C17H20N2O5S\/c1-13(15-8-10-16(23-2)11-9-15)18-25(21,22)19-17(20)24-12-14-6-4-3-5-7-14\/h3-11,13,18H,12H2,1-2H3,(H,19,20)
InChIKey : GIRLQTWFPQINCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : BDBM50093588,N-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)ethyl]sulfamoylcarbamic acid benzyl ester
MW : 364.4
Formula : C17H20N2O5S
CAS_number :
PubChem : 122179857
UniChem : GIRLQTWFPQINCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (1)
| Title : Discovery of potent carbonic anhydrase and acetylcholine esterase inhibitors: novel sulfamoylcarbamates and sulfamides derived from acetophenones - Akincioglu_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_3592 |
| Author(s) : Akincioglu A , Akincioglu H , Gulcin I , Durdagi S , Supuran CT , Goksu S |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry , 23 :3592 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Akincioglu_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_3592 |
| ESTHER : Akincioglu_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_3592 |
| PubMedSearch : Akincioglu_2015_Bioorg.Med.Chem_23_3592 |
| PubMedID: 25921269 |