Pyraclofos
General
Type : Organophosphate,Insecticide,Sulfur Compound,Pyrazole
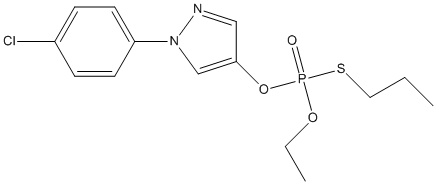
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-[ethoxy(propylsulfanyl)phosphoryl]oxypyrazole
Canonical SMILES : CCCSP(=O)(OCC)OC1=CN(N=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl
InChI : InChI=1S\/C14H18ClN2O3PS\/c1-3-9-22-21(18,19-4-2)20-14-10-16-17(11-14)13-7-5-12(15)6-8-13\/h5-8,10-11H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : QHGVXILFMXYDRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Boltage,Voltage,TIA 230,OMS 3040,(RS)-O-1-(4-Chlorophenyl)pyrazol-4-yl O-ethyl S-propyl phosphorothioate,O-(1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl) O-ethyl S-propyl phosphorothioate,(+-)-O-(1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl) O-ethyl S-propyl phosphorothioate,(RS)-(O-1-(4-Chlorophenyl)pyrazol-4-yl-O-ethyl-S-propylphosphorothioate) (IUPAC),Phosphorothioic acid, O-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl) O-ethyl S-propyl ester
MW : 360.8
Formula : C14H18ClN2O3PS
CAS_number : 77458-01-6
PubChem : 93460
UniChem : QHGVXILFMXYDRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (6)
| Title : Characterizing the potentially neuronal acetylcholinesterase reactivity toward chiral pyraclofos: Enantioselective insights from spectroscopy, in silico docking, molecular dynamics simulation and per-residue energy decomposition studies - Peng_2021_J.Mol.Graph.Model_110_108069 |
| Author(s) : Peng W , Wang T , Liang XR , Yang YS , Wang QZ , Cheng HF , Peng YK , Ding F |
| Ref : J Mol Graph Model , 110 :108069 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Peng_2021_J.Mol.Graph.Model_110_108069 |
| ESTHER : Peng_2021_J.Mol.Graph.Model_110_108069 |
| PubMedSearch : Peng_2021_J.Mol.Graph.Model_110_108069 |
| PubMedID: 34773872 |
| Title : [Multiresidue analysis of organophosphorus pesticides in vegetables and fruits using dual-column GC-FPD, -NPD] - Ueno_2001_Shokuhin.Eiseigaku.Zasshi_42_385 |
| Author(s) : Ueno E , Oshima H , Saito I , Matsumoto H |
| Ref : Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi , 42 :385 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Ueno_2001_Shokuhin.Eiseigaku.Zasshi_42_385 |
| ESTHER : Ueno_2001_Shokuhin.Eiseigaku.Zasshi_42_385 |
| PubMedSearch : Ueno_2001_Shokuhin.Eiseigaku.Zasshi_42_385 |
| PubMedID: 11875824 |
| Title : Risk assessment of etofenprox (Vectron) on non-target aquatic fauna compared with other pesticides used as Simulium larvicide in a tropical environment - Yameogo_2001_Chemosphere_42_965 |
| Author(s) : Yameogo L , Traore K , Back C , Hougard JM , Calamari D |
| Ref : Chemosphere , 42 :965 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Yameogo_2001_Chemosphere_42_965 |
| ESTHER : Yameogo_2001_Chemosphere_42_965 |
| PubMedSearch : Yameogo_2001_Chemosphere_42_965 |
| PubMedID: 11272920 |
| Title : Hut-scale trial of pyraclofos against malaria vectors in Malkangiri District of Orissa - Sahu_1996_Indian.J.Malariol_33_16 |
| Author(s) : Sahu SS |
| Ref : Indian J Malariol , 33 :16 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Sahu_1996_Indian.J.Malariol_33_16 |
| ESTHER : Sahu_1996_Indian.J.Malariol_33_16 |
| PubMedSearch : Sahu_1996_Indian.J.Malariol_33_16 |
| PubMedID: 8690128 |
| Title : Laboratory toxicity of potential blackfly larvicides on some African fish species in the Onchocerciasis Control Programme area - Yameogo_1991_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_21_248 |
| Author(s) : Yameogo L , Tapsoba JM , Calamari D |
| Ref : Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety , 21 :248 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Yameogo_1991_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_21_248 |
| ESTHER : Yameogo_1991_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_21_248 |
| PubMedSearch : Yameogo_1991_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_21_248 |
| PubMedID: 1868781 |
| Title : Insecticidal activity of carbosulfan (OMS 3022) and pyraclofos (OMS 3040) against mosquitoes - Velayudhan_1990_J.Commun.Dis_22_140 |
| Author(s) : Velayudhan R , Amalraj D , Arunachalam N , Das PK |
| Ref : J Commun Dis , 22 :140 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Velayudhan_1990_J.Commun.Dis_22_140 |
| ESTHER : Velayudhan_1990_J.Commun.Dis_22_140 |
| PubMedSearch : Velayudhan_1990_J.Commun.Dis_22_140 |
| PubMedID: 1983012 |