Carbophenothion
related to methyltrithion
General
Type : Organophosphate,Insecticide,Sulfur Compound
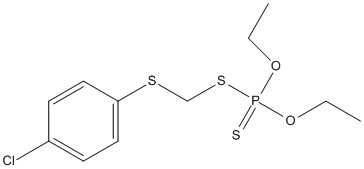
Chemical_Nomenclature : S-[[(p-chlorophenyl)thio] methyl] O,O-diethylphosphorodithioate
Canonical SMILES : CCOP(=S)(OCC)SCSC1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl
InChI : InChI=1S\/C11H16ClO2PS3\/c1-3-13-15(16,14-4-2)18-9-17-11-7-5-10(12)6-8-11\/h5-8H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : VEDTXTNSFWUXGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Akarithion,Hexathion,Oleoakarithion,Carbofenothion,Carbofenotion,Carbofenthion,Trade names for products containing carbophenothion include Trithion, Garrathion, Dagadip, R-1303, Endyl, Lethox, Nephocarp, Acarithion, and Hexathion ., Phthalophos
MW : 342.87
Formula : C11H16ClO2PS3
CAS_number : 789-19-6
PubChem : 13081
UniChem : VEDTXTNSFWUXGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Wikipedia : Carbophenothion
Target
Families : Carbophenothion ligand of proteins in family
ACHE
References (13)
| Title : Evaluation of organophosphorus pesticide residues in citrus fruits from the Valencian community (Spain) - Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| Author(s) : Torres CM , Pico Y , Marin R , Manes J |
| Ref : Journal of AOAC International , 80 :1122 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| ESTHER : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| PubMedSearch : Torres_1997_J.AOAC.Int_80_1122 |
| PubMedID: 9325585 |
| Title : Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction procedure for multiresidue pesticide analysis in oranges - Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| Author(s) : Torres CM , Pico Y , Redondo MJ , Manes J |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 719 :95 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| ESTHER : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedSearch : Torres_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_719_95 |
| PubMedID: 8589838 |
| Title : Determining organohalides in animal fats using gel permeation chromatographic cleanup: repeatability study - Goodspeed_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_388 |
| Author(s) : Goodspeed DP , Chestnut LI |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 74 :388 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Goodspeed_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_388 |
| ESTHER : Goodspeed_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_388 |
| PubMedSearch : Goodspeed_1991_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_74_388 |
| PubMedID: 2050618 |
| Title : [Influence of phthalophos on the permeability of artificial lipid membranes to water (letter)] - |
| Author(s) : Sergeev GB , Sergeev BM , Nekrasova GN |
| Ref : Biofizika , 27 :548 , 1982 |
| PubMedID: 7093347 |
| Title : [Effect of mixed function oxidases on phthalophos transformation in rat liver] - Voronina_1981_Ukr.Biokhim.Zh_53_26 |
| Author(s) : Voronina VM , Popov TA , Kagan Iu S , Pis'mennaia MV |
| Ref : Ukr Biokhim Zh , 53 :26 , 1981 |
| Abstract : Voronina_1981_Ukr.Biokhim.Zh_53_26 |
| ESTHER : Voronina_1981_Ukr.Biokhim.Zh_53_26 |
| PubMedSearch : Voronina_1981_Ukr.Biokhim.Zh_53_26 |
| PubMedID: 7210220 |
| Title : [Embryotoxic action of phthalophos] - |
| Author(s) : Abbasov TG , Karavaeva TM , Makhno PM |
| Ref : Veterinariia , 1 :62 , 1980 |
| PubMedID: 7376434 |
| Title : [Spectrophotometric analysis of sayphos, phosalone and phthalophos in study of the liver] - |
| Author(s) : Ikramov LT , Tashpulatov A , Mirkhaitov T |
| Ref : Sud Med Ekspert , 23 :33 , 1980 |
| PubMedID: 7404621 |
| Title : Ixodicidal resistance in Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) in the Republic of South Africa and Transkei - Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| Author(s) : Baker JA , Jordaan JO , Robertson WD |
| Ref : J S Afr Vet Assoc , 50 :296 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| ESTHER : Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| PubMedSearch : Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| PubMedID: 553968 |
| Title : [Mutagenic effect of several pesticides on durum spring wheat] - Logvinenko_1978_Tsitol.Genet_12_207 |
| Author(s) : Logvinenko VF , Morgun VV |
| Ref : Tsitol Genet , 12 :207 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Logvinenko_1978_Tsitol.Genet_12_207 |
| ESTHER : Logvinenko_1978_Tsitol.Genet_12_207 |
| PubMedSearch : Logvinenko_1978_Tsitol.Genet_12_207 |
| PubMedID: 684827 |
| Title : [Effect of phthalophos on embryogenesis and its metabolism in the body of white rats and their embryos] - |
| Author(s) : Kagan Iu S , Voronina VM , Ackermanm G |
| Ref : Gigiena i Sanitariia , 9 :28 , 1978 |
| PubMedID: 689400 |
| Title : [Method for the separate determination of phthalophos and phosalone in fish and water] - |
| Author(s) : Trondina GA |
| Ref : Veterinariia , 6 :96 , 1978 |
| PubMedID: 676068 |
| Title : [Cytogenetic activity of the pesticides phthalophos, chlorophos and gardona in a culture of human lymphocytes] - Kurinnyi_1977_Genetika_13_337 |
| Author(s) : Kurinnyi AI , Pilinskaia MA |
| Ref : Genetika , 13 :337 , 1977 |
| Abstract : Kurinnyi_1977_Genetika_13_337 |
| ESTHER : Kurinnyi_1977_Genetika_13_337 |
| PubMedSearch : Kurinnyi_1977_Genetika_13_337 |
| PubMedID: 892431 |
| Title : [Effect of ethanol preservation on the retention of phosalone and phthalophos in a corpse] - |
| Author(s) : Ikramov LT , Mirkhaitov T |
| Ref : Sud Med Ekspert , 16 :35 , 1973 |
| PubMedID: 4750156 |