Dioxathion
General
Type : Organophosphate,Sulfur Compound
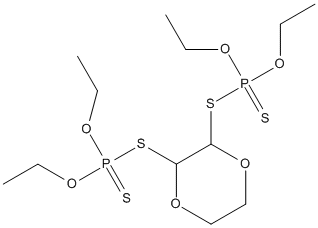
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1,4-Dioxan-2,3-diyl-bis(O,O-diethyl phosphorothiolothionate)
Canonical SMILES : CCOP(=S)(OCC)SC1C(OCCO1)SP(=S)(OCC)OCC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C12H26O6P2S4\/c1-5-15-19(21,16-6-2)23-11-12(14-10-9-13-11)24-20(22,17-7-3)18-8-4\/h11-12H,5-10H2,1-4H3
InChIKey : VBKKVDGJXVOLNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Hercules AC528,Ruphos,Navadel,Delnatex,Delnav
MW : 456.5
Formula : C12H26O6P2S4
CAS_number : 78-34-2
PubChem : 6531
UniChem : VBKKVDGJXVOLNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Dioxathion
Target
References (7)
| Title : Putative M2 muscarinic receptors of rat heart have high affinity for organophosphorus anticholinesterases - Silveira_1990_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_103_474 |
| Author(s) : Silveira CL , Eldefrawi AT , Eldefrawi ME |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 103 :474 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Silveira_1990_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_103_474 |
| ESTHER : Silveira_1990_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_103_474 |
| PubMedSearch : Silveira_1990_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_103_474 |
| PubMedID: 2339420 |
| Title : The resistance spectrum shown by a fenvalerate-resistant strain of blue tick (Boophilus decoloratus) to a range of ixodicides - Coetzee_1987_Onderstepoort.J.Vet.Res_54_79 |
| Author(s) : Coetzee BB , Stanford GD , Davis DA |
| Ref : Onderstepoort J Vet Res , 54 :79 , 1987 |
| Abstract : Coetzee_1987_Onderstepoort.J.Vet.Res_54_79 |
| ESTHER : Coetzee_1987_Onderstepoort.J.Vet.Res_54_79 |
| PubMedSearch : Coetzee_1987_Onderstepoort.J.Vet.Res_54_79 |
| PubMedID: 3587932 |
| Title : Inhibition of oviposition in the cattle tick Boophilus microplus by certain acaricides - Mansingh_1979_Pest.Sci_10_485 |
| Author(s) : Mansingh A , Rawlins SC |
| Ref : Pest Sci , 10 :485 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Mansingh_1979_Pest.Sci_10_485 |
| ESTHER : Mansingh_1979_Pest.Sci_10_485 |
| PubMedSearch : Mansingh_1979_Pest.Sci_10_485 |
| PubMedID: |
| Title : Ixodicidal resistance in Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) in the Republic of South Africa and Transkei - Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| Author(s) : Baker JA , Jordaan JO , Robertson WD |
| Ref : J S Afr Vet Assoc , 50 :296 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| ESTHER : Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| PubMedSearch : Baker_1979_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_50_296 |
| PubMedID: 553968 |
| Title : Resistance to certain organophosphorus ixodicides in the bont tick, Amblyomma hebraeum Koch, in the Republic of South Africa and Swaziland - Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_337 |
| Author(s) : Baker JA , Miles JO , Robertson WD |
| Ref : J S Afr Vet Assoc , 49 :337 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_337 |
| ESTHER : Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_337 |
| PubMedSearch : Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_337 |
| PubMedID: 752082 |
| Title : The current status of resistance to organophosphorus ixodicides by the blue tick, Boophilus Decoloratus (Koch) in the Republic of South Africa and Transkei - Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_327 |
| Author(s) : Baker JA , Miles JO , Robertson WD , Stanford GD , Taylor RJ |
| Ref : J S Afr Vet Assoc , 49 :327 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_327 |
| ESTHER : Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_327 |
| PubMedSearch : Baker_1978_J.S.Afr.Vet.Assoc_49_327 |
| PubMedID: 752081 |