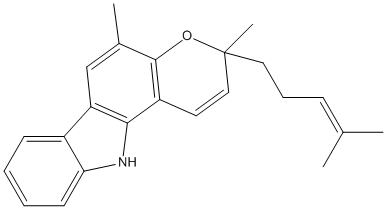
Mahanimbine
Mahanimbine is a natural product found in Murraya euchrestifolia, Murraya siamensis. Found together with Galanthamine
General
Type : Natural,Alkaloid
Chemical_Nomenclature : 3,5-dimethyl-3-(4-methylpent-3-enyl)-11H-pyrano[3,2-a]carbazole
Canonical SMILES : CC1=CC2=C(C3=C1OC(C=C3)(C)CCC=C(C)C)NC4=CC=CC=C42
InChI : InChI=1S\/C23H25NO\/c1-15(2)8-7-12-23(4)13-11-18-21-19(14-16(3)22(18)25-23)17-9-5-6-10-20(17)24-21\/h5-6,8-11,13-14,24H,7,12H2,1-4H3
InChIKey : HTNVFUBCWIYPJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : (+)-Mahanimbine,CHEBI:6646,Rel-(+)-Mahanimbine,CHEMBL495873
MW : 331.4
Formula : C23H25NO
CAS_number : 21104-28-9
PubChem : 167963
UniChem : HTNVFUBCWIYPJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Target
References (3)
| Title : Mahanimbine Improved Aging-Related Memory Deficits in Mice through Enhanced Cholinergic Transmission and Suppressed Oxidative Stress, Amyloid Levels, and Neuroinflammation - Mani_2021_Brain.Sci_12_12 |
| Author(s) : Mani V , Mohd Azahan NS , Ramasamy K , Lim SM , Abdul Majeed AB |
| Ref : Brain Sci , 12 :12 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Mani_2021_Brain.Sci_12_12 |
| ESTHER : Mani_2021_Brain.Sci_12_12 |
| PubMedSearch : Mani_2021_Brain.Sci_12_12 |
| PubMedID: 35053756 |
| Title : Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potential of a carbazole alkaloid, mahanimbine, from Murraya koenigii - Kumar_2010_Phytother.Res_24_629 |
| Author(s) : Kumar NS , Mukherjee PK , Bhadra S , Saha BP , Pal BC |
| Ref : Phytother Res , 24 :629 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Kumar_2010_Phytother.Res_24_629 |
| ESTHER : Kumar_2010_Phytother.Res_24_629 |
| PubMedSearch : Kumar_2010_Phytother.Res_24_629 |
| PubMedID: 19943242 |
| Title : Pancreatic lipase inhibitory alkaloids of Murraya koenigii leaves - Birari_2009_Nat.Prod.Commun_4_1089 |
| Author(s) : Birari R , Roy SK , Singh A , Bhutani KK |
| Ref : Nat Prod Commun , 4 :1089 , 2009 |
| Abstract : Birari_2009_Nat.Prod.Commun_4_1089 |
| ESTHER : Birari_2009_Nat.Prod.Commun_4_1089 |
| PubMedSearch : Birari_2009_Nat.Prod.Commun_4_1089 |
| PubMedID: 19768989 |