Polyaspartic-acid
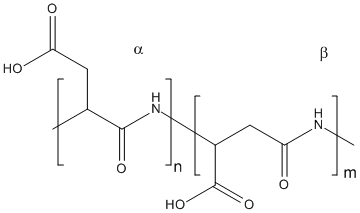
Polyaspartic acid (PASA) is a biodegradable, water-soluble polyaminoacid with potential to replace many non-biodegradable polymers. It is used also as copolymers (eg with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)). It is also a natural polymer as fragment of larger proteins with length up to 50 amino acids. Synthetic tPAA(thermally synthesized PAA) consists of beta-amide (70%) and alpha-amide,(30%) D- and L-aspartate units; the alpha- and beta-amide units are randomly distributed. PASA has ability to inhibit deposition of calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate, barium sulfate, and calcium phosphate and can be used as an antiscaling agent in cooling water systems Its high affinity with calcium has been exploited for targeting various forms of drug-containing carriers to the bone. Polyaspartate is a potential green alternative in disposable diapers and agriculture. It can act as a super-swelling material in diapers. The level of water uptake which is inversely related to the mechanical properties of the hydrogel can be tuned by changing the crosslinking density
General
Chemical_Nomenclature : poly-L-aspartic acid
Canonical SMILES :
InChI :
InChIKey :
Other name(s) : Polyaspartic acid || Polyaspartate || PASA || PAA || tPAA || poly-L-aspartic acid
Target
Structures : No structure
Families : PolyAspartate-hydrolase
References (9)
| Title : Poly(aspartate) hydrolases: biochemical properties and applications - Hiraishi_2011_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_91_895 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Maeda M |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 91 :895 , 2011 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2011_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_91_895 |
| PubMedID: 21713512 |
| Title : Poly(aspartate) hydrolases: biochemical properties and applications - Hiraishi_2011_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_91_895 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Maeda M |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 91 :895 , 2011 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2011_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_91_895 |
| PubMedID: 21713512 |
| Title : Poly(aspartate) hydrolases: biochemical properties and applications - Hiraishi_2011_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_91_895 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Maeda M |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 91 :895 , 2011 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2011_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_91_895 |
| PubMedID: 21713512 |
| Title : Cloning of poly(aspartic acid) (PAA) hydrolase-1 gene from Pedobacter sp. KP-2 and hydrolysis of thermally synthesized PAA by its gene product - Hiraishi_2009_Macromol.Biosci_9_10 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Masuda E , Kanayama N , Nagata M , Doi Y , Abe H , Maeda M |
| Ref : Macromol Biosci , 9 :10 , 2009 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2009_Macromol.Biosci_9_10 |
| PubMedID: 18756460 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphi-b6vqa9 |
| Title : Cloning of poly(aspartic acid) (PAA) hydrolase-1 gene from Pedobacter sp. KP-2 and hydrolysis of thermally synthesized PAA by its gene product - Hiraishi_2009_Macromol.Biosci_9_10 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Masuda E , Kanayama N , Nagata M , Doi Y , Abe H , Maeda M |
| Ref : Macromol Biosci , 9 :10 , 2009 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2009_Macromol.Biosci_9_10 |
| PubMedID: 18756460 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphi-b6vqa9 |
| Title : Cloning of poly(aspartic acid) (PAA) hydrolase-1 gene from Pedobacter sp. KP-2 and hydrolysis of thermally synthesized PAA by its gene product - Hiraishi_2009_Macromol.Biosci_9_10 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Masuda E , Kanayama N , Nagata M , Doi Y , Abe H , Maeda M |
| Ref : Macromol Biosci , 9 :10 , 2009 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2009_Macromol.Biosci_9_10 |
| PubMedID: 18756460 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphi-b6vqa9 |
| Title : Genetic Analysis and Characterization of Poly(aspartic acid) Hydrolase-1 from Sphingomonas sp. KT-1 - Hiraishi_2003_Biomacromolecules_4_80 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Kajiyama M , Tabata K , Yamato I , Doi Y |
| Ref : Biomacromolecules , 4 :80 , 2003 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2003_Biomacromolecules_4_80 |
| PubMedID: 12523851 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-q7wsc1 |
| Title : Genetic Analysis and Characterization of Poly(aspartic acid) Hydrolase-1 from Sphingomonas sp. KT-1 - Hiraishi_2003_Biomacromolecules_4_80 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Kajiyama M , Tabata K , Yamato I , Doi Y |
| Ref : Biomacromolecules , 4 :80 , 2003 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2003_Biomacromolecules_4_80 |
| PubMedID: 12523851 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-q7wsc1 |
| Title : Genetic Analysis and Characterization of Poly(aspartic acid) Hydrolase-1 from Sphingomonas sp. KT-1 - Hiraishi_2003_Biomacromolecules_4_80 |
| Author(s) : Hiraishi T , Kajiyama M , Tabata K , Yamato I , Doi Y |
| Ref : Biomacromolecules , 4 :80 , 2003 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hiraishi_2003_Biomacromolecules_4_80 |
| PubMedID: 12523851 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-q7wsc1 |