Quinapril
General
Type : Isoquinoline || Not A\/B H target || Drug || Pro-Drug || Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor
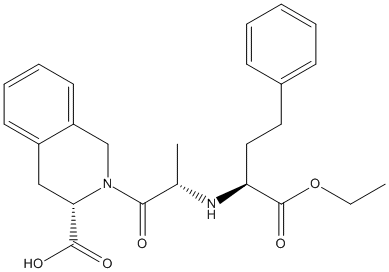
Chemical_Nomenclature : (3S)-2-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
Canonical SMILES : CCOC(=O)C(CCC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(C)C(=O)N2CC3=CC=CC=C3CC2C(=O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C25H30N2O5\/c1-3-32-25(31)21(14-13-18-9-5-4-6-10-18)26-17(2)23(28)27-16-20-12-8-7-11-19(20)15-22(27)24(29)30\/h4-12,17,21-22,26H,3,13-16H2,1-2H3,(H,29,30)\/t17-,21-,22-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : JSDRRTOADPPCHY-HSQYWUDLSA-N
Other name(s) : Quinaprilum, Quinaprilum [Latin], Quinazil, CHEBI:8713, CHEMBL1592
Target
Families : Carb_B_Chordata
References (1)
| Title : Effect of carboxylesterase 1 c.428G >\; A single nucleotide variation on the pharmacokinetics of quinapril and enalapril - Tarkiainen_2015_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_80_1131 |
| Author(s) : Tarkiainen EK , Tornio A , Holmberg MT , Launiainen T , Neuvonen PJ , Backman JT , Niemi M |
| Ref : British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology , 80 :1131 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Tarkiainen_2015_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_80_1131 |
| ESTHER : Tarkiainen_2015_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_80_1131 |
| PubMedSearch : Tarkiainen_2015_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_80_1131 |
| PubMedID: 25919042 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES1 |