Chelerythrine
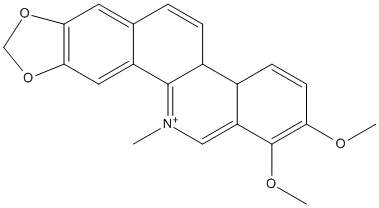
Chelerythrine is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid isolated from the root of Zanthoxylum simulans, Chelidonium majus L., and other Papaveraceae. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.13 (protein kinase C, PKC-alpha/-beta) inhibitor, an antibacterial agent and an antineoplastic agent. It is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid and an organic cation. || IC50 ACHE 1.45 muM (1.22-1.71) BChE 8.58 muM (5.34-12.1)
General
Type : Natural,Alkaloid,Not A\/B H target,Benzodioxo,Phenanthridinium
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1,2-dimethoxy-12-methyl-[1,3]benzodioxolo[5,6-c]phenanthridin-12-ium
Canonical SMILES : C[N+]1=C2C(=C3C=CC(=C(C3=C1)OC)OC)C=CC4=CC5=C(C=C42)OCO5
InChI : InChI=1S\/C21H18NO4\/c1-22-10-16-13(6-7-17(23-2)21(16)24-3)14-5-4-12-8-18-19(26-11-25-18)9-15(12)20(14)22\/h4-10H,11H2,1-3H3\/q+1
InChIKey : LLEJIEBFSOEYIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Toddalin,cheleritrine,broussonpapyrine
MW : 348.4
Formula : C21H18NO4+
CAS_number : 34316-15-9
PubChem : 2703
UniChem : LLEJIEBFSOEYIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (3)
| Title : Simple analogues of natural product chelerythrine: Discovery of a novel anticholinesterase 2-phenylisoquinolin-2-ium scaffold with excellent potency against acetylcholinesterase - Zhou_2020_Eur.J.Med.Chem_200_112415 |
| Author(s) : Zhou B , Li H , Cui Z , Li D , Geng H , Gao J , Zhou L |
| Ref : Eur Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 200 :112415 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Zhou_2020_Eur.J.Med.Chem_200_112415 |
| ESTHER : Zhou_2020_Eur.J.Med.Chem_200_112415 |
| PubMedSearch : Zhou_2020_Eur.J.Med.Chem_200_112415 |
| PubMedID: 32454229 |
| Title : Exploration of natural compounds as sources of new bifunctional scaffolds targeting cholinesterases and beta amyloid aggregation: The case of chelerythrine - Brunhofer_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_6669 |
| Author(s) : Brunhofer G , Fallarero A , Karlsson D , Batista-Gonzalez A , Shinde P , Gopi Mohan C , Vuorela P |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry , 20 :6669 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Brunhofer_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_6669 |
| ESTHER : Brunhofer_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_6669 |
| PubMedSearch : Brunhofer_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_6669 |
| PubMedID: 23062825 |
| Title : 8-hydroxydihydrochelerythrine and 8-hydroxydihydrosanguinarine with a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity from Chelidonium majus L - Cho_2006_Biol.Pharm.Bull_29_2317 |
| Author(s) : Cho KM , Yoo ID , Kim WG |
| Ref : Biol Pharm Bull , 29 :2317 , 2006 |
| Abstract : Cho_2006_Biol.Pharm.Bull_29_2317 |
| ESTHER : Cho_2006_Biol.Pharm.Bull_29_2317 |
| PubMedSearch : Cho_2006_Biol.Pharm.Bull_29_2317 |
| PubMedID: 17077538 |