MSF
An enzyme inhibitor that inactivates cholinesterases, esterases, lipases, and many other serine hydrolases unrelated to alpha/beta hydrolases
General
Type : Sulfur Compound,Sulfonyl
Chemical_Nomenclature : methanesulfonyl fluoride
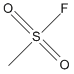
Canonical SMILES : CS(=O)(=O)F
InChI : InChI=1S\/CH3FO2S\/c1-5(2,3)4\/h1H3
InChIKey : KNWQLFOXPQZGPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Fumette,Mesyl fluoride,Methanesulphonyl fluoride,Fluoro methyl sulfone,Methanesulfonyl fluoride,HSDB 6397,NISTC558258,EINECS 209-192-2,BRN 1740836,4-04-00-00027
MW : 98.09
Formula : CH3FO2S
CAS_number : 558-25-8
PubChem : 11207
UniChem : KNWQLFOXPQZGPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Wikipedia : Methanesulfonyl_fluoride
Target
Families : MSF ligand of proteins in family
ACHE
Protein :
torca-ACHE
References (10)
| Title : A randomized phase I study of methanesulfonyl fluoride, an irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor, for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease - Moss_2013_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_75_1231 |
| Author(s) : Moss DE , Fariello RG , Sahlmann J , Sumaya I , Pericle F , Braglia E |
| Ref : British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology , 75 :1231 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Moss_2013_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_75_1231 |
| ESTHER : Moss_2013_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_75_1231 |
| PubMedSearch : Moss_2013_Br.J.Clin.Pharmacol_75_1231 |
| PubMedID: 23116458 |
| Title : Effect of a CNS-Sensitive Anticholinesterase Methane Sulfonyl Fluoride on Hippocampal Acetylcholine Release in Freely Moving Rats - Imanishi_2012_Adv.Pharmacol.Sci_2012_708178 |
| Author(s) : Imanishi T , Hossain MM , Suzuki T , Xu P , Sato I , Kobayashi H |
| Ref : Advances in Pharmacology Sci , 2012 :708178 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Imanishi_2012_Adv.Pharmacol.Sci_2012_708178 |
| ESTHER : Imanishi_2012_Adv.Pharmacol.Sci_2012_708178 |
| PubMedSearch : Imanishi_2012_Adv.Pharmacol.Sci_2012_708178 |
| PubMedID: 22319525 |
| Title : In utero methanesulfonyl fluoride differentially affects learning and maze performance in the absence of long-lasting cholinergic changes in the adult rat - Carcoba_2008_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_88_374 |
| Author(s) : Carcoba LM , Santiago M , Moss DE , Cabeza R |
| Ref : Pharmacol Biochem Behav , 88 :374 , 2008 |
| Abstract : Carcoba_2008_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_88_374 |
| ESTHER : Carcoba_2008_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_88_374 |
| PubMedSearch : Carcoba_2008_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_88_374 |
| PubMedID: 17920111 |
| Title : Methanesulfonyl fluoride, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, attenuates simple learning and memory deficits in ischemic rats - Borlongan_2005_Brain.Res_1038_50 |
| Author(s) : Borlongan CV , Sumaya IC , Moss DE |
| Ref : Brain Research , 1038 :50 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Borlongan_2005_Brain.Res_1038_50 |
| ESTHER : Borlongan_2005_Brain.Res_1038_50 |
| PubMedSearch : Borlongan_2005_Brain.Res_1038_50 |
| PubMedID: 15748872 |
| Title : Prenatal exposure to the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor methanesulfonyl fluoride alters forebrain morphology and gene expression - Byers_2005_Brain.Res.Dev.Brain.Res_158_13 |
| Author(s) : Byers DM , Irwin LN , Moss DE , Sumaya IC , Hohmann CF |
| Ref : Brain Research Developmental Brain Research , 158 :13 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Byers_2005_Brain.Res.Dev.Brain.Res_158_13 |
| ESTHER : Byers_2005_Brain.Res.Dev.Brain.Res_158_13 |
| PubMedSearch : Byers_2005_Brain.Res.Dev.Brain.Res_158_13 |
| PubMedID: 15964079 |
| Title : Acceleration of Drosophila melanogaster acetylcholinesterase methanesulfonylation: peripheral ligand D-tubocurarine enhances the affinity for small methanesulfonylfluoride - Golicnik_2002_Chem.Biol.Interact_139_145 |
| Author(s) : Golicnik M , Fournier D , Stojan J |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 139 :145 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Golicnik_2002_Chem.Biol.Interact_139_145 |
| ESTHER : Golicnik_2002_Chem.Biol.Interact_139_145 |
| PubMedSearch : Golicnik_2002_Chem.Biol.Interact_139_145 |
| PubMedID: 11823003 |
| Title : Methanesulfonyl fluoride (MSF): a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy in the treatment of senile dementia of the Alzheimer type - Moss_1999_Alzheimer.Dis.Assoc.Disord_13_20 |
| Author(s) : Moss DE , Berlanga P , Hagan MM , Sandoval H , Ishida C |
| Ref : Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders , 13 :20 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Moss_1999_Alzheimer.Dis.Assoc.Disord_13_20 |
| ESTHER : Moss_1999_Alzheimer.Dis.Assoc.Disord_13_20 |
| PubMedSearch : Moss_1999_Alzheimer.Dis.Assoc.Disord_13_20 |
| PubMedID: 10192638 |
| Title : Cholinesterase inhibitors proposed for treating dementia in Alzheimer's disease: selectivity toward human brain acetylcholinesterase compared with butyrylcholinesterase - Pacheco_1995_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_274_767 |
| Author(s) : Pacheco G , Palacios-Esquivel R , Moss DE |
| Ref : Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics , 274 :767 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Pacheco_1995_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_274_767 |
| ESTHER : Pacheco_1995_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_274_767 |
| PubMedSearch : Pacheco_1995_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_274_767 |
| PubMedID: 7636741 |
| Title : Methanesulfonyl fluoride (MSF) blocks scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats - Palacios-Esquivel_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_93 |
| Author(s) : Palacios-Esquivel RL , Pacheco G , Moss DE |
| Ref : Neurobiology of Aging , 14 :93 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Palacios-Esquivel_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_93 |
| ESTHER : Palacios-Esquivel_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_93 |
| PubMedSearch : Palacios-Esquivel_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_93 |
| PubMedID: 8450938 |
| Title : Chronic methanesulfonyl fluoride enhances one-trial per day reward learning in aged rats - Malin_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_393 |
| Author(s) : Malin DH , Plotner RE , Radulescu SJ , Ferebee RN , Lake JR , Negrete PG , Schaefer PJ , Crothers MK , Moss DE |
| Ref : Neurobiology of Aging , 14 :393 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Malin_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_393 |
| ESTHER : Malin_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_393 |
| PubMedSearch : Malin_1993_Neurobiol.Aging_14_393 |
| PubMedID: 8367021 |