Carbachol
Parasympathomimetic, Cholinergic receptor agonist, as a carbamate it is a slowly hydrolyzed substrate of acetylcholinesterase. This drug is administered ocularly to induce miosis to reduce intraocular pressure in the treatment of glaucoma. Carbachol is also used to stimulate micturition by contraction of detrusor muscle. This drug may cause hypotension, bradycardia, nausea, vomiting, bronchospasm, and abdominal cramps.
General
Type : Drug, Not AlphaBeta Hydrolase target, Carbamate, Trimethylammonium, Ammonium, Choline ester, Analogue of substrate, Muscarinic agonist, Nicotinic agonist
Chemical_Nomenclature : 2-[(Aminocarbonyl)oxy]-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride\; (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium chloride carbamate \; 2-carbamoyloxyethyl-trimethyl-ammonium
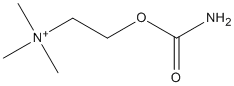
Canonical SMILES : C[N+](C)(C)CCOC(=O)N.[Cl-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C6H14N2O2.ClH\/c1-8(2,3)4-5-10-6(7)9\;\/h4-5H2,1-3H3,(H-,7,9)\;1H
InChIKey : AIXAANGOTKPUOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Carbamylcholine || Carbacholin || Carbacholine || Carbacolina || Carbamiotin || Carbocholin || Carbocholine || Carbochol || Carcholin || Miostat || Carbacholinum || Karbachol || carbamylcholine chloride
MW : 147.196
Formula : C6H15N2O2
CAS_number : 51-83-2
PubChem : 5831
UniChem : AIXAANGOTKPUOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR : 298
Wikipedia : Carbachol
Target
Structures : No structure
Families : ACHE
References (9)
| Title : Molecular basis of inhibition of substrate hydrolysis by a ligand bound to the peripheral site of acetylcholinesterase - Auletta_2010_Chem.Biol.Interact_187_135 |
| Author(s) : Auletta JT , Johnson JL , Rosenberry TL |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 187 :135 , 2010 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Auletta_2010_Chem.Biol.Interact_187_135 |
| PubMedID: 20493829 |
| Title : Molecular basis of inhibition of substrate hydrolysis by a ligand bound to the peripheral site of acetylcholinesterase - Auletta_2010_Chem.Biol.Interact_187_135 |
| Author(s) : Auletta JT , Johnson JL , Rosenberry TL |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 187 :135 , 2010 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Auletta_2010_Chem.Biol.Interact_187_135 |
| PubMedID: 20493829 |
| Title : Molecular basis of inhibition of substrate hydrolysis by a ligand bound to the peripheral site of acetylcholinesterase - Auletta_2010_Chem.Biol.Interact_187_135 |
| Author(s) : Auletta JT , Johnson JL , Rosenberry TL |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 187 :135 , 2010 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Auletta_2010_Chem.Biol.Interact_187_135 |
| PubMedID: 20493829 |
| Title : Analysis of the reaction of carbachol with acetylcholinesterase using thioflavin T as a coupled fluorescence reporter - Rosenberry_2008_Biochemistry_47_13056 |
| Author(s) : Rosenberry TL , Sonoda LK , Dekat SE , Cusack B , Johnson JL |
| Ref : Biochemistry , 47 :13056 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rosenberry_2008_Biochemistry_47_13056 |
| PubMedID: 19006330 |
| Title : Monitoring the reaction of carbachol with acetylcholinesterase by thioflavin T fluorescence and acetylthiocholine hydrolysis - Rosenberry_2008_Chem.Biol.Interact_175_235 |
| Author(s) : Rosenberry TL , Sonoda LK , Dekat SE , Cusack B , Johnson JL |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 175 :235 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rosenberry_2008_Chem.Biol.Interact_175_235 |
| PubMedID: 18602908 |
| Title : Analysis of the reaction of carbachol with acetylcholinesterase using thioflavin T as a coupled fluorescence reporter - Rosenberry_2008_Biochemistry_47_13056 |
| Author(s) : Rosenberry TL , Sonoda LK , Dekat SE , Cusack B , Johnson JL |
| Ref : Biochemistry , 47 :13056 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rosenberry_2008_Biochemistry_47_13056 |
| PubMedID: 19006330 |
| Title : Monitoring the reaction of carbachol with acetylcholinesterase by thioflavin T fluorescence and acetylthiocholine hydrolysis - Rosenberry_2008_Chem.Biol.Interact_175_235 |
| Author(s) : Rosenberry TL , Sonoda LK , Dekat SE , Cusack B , Johnson JL |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 175 :235 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rosenberry_2008_Chem.Biol.Interact_175_235 |
| PubMedID: 18602908 |
| Title : Analysis of the reaction of carbachol with acetylcholinesterase using thioflavin T as a coupled fluorescence reporter - Rosenberry_2008_Biochemistry_47_13056 |
| Author(s) : Rosenberry TL , Sonoda LK , Dekat SE , Cusack B , Johnson JL |
| Ref : Biochemistry , 47 :13056 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rosenberry_2008_Biochemistry_47_13056 |
| PubMedID: 19006330 |
| Title : Monitoring the reaction of carbachol with acetylcholinesterase by thioflavin T fluorescence and acetylthiocholine hydrolysis - Rosenberry_2008_Chem.Biol.Interact_175_235 |
| Author(s) : Rosenberry TL , Sonoda LK , Dekat SE , Cusack B , Johnson JL |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 175 :235 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rosenberry_2008_Chem.Biol.Interact_175_235 |
| PubMedID: 18602908 |