PAF
Extracellular signaling lipid; ligand for G protein-coupled platelet activating factor (PAF) receptors. Induces inflammation by increasing vascular permeability; activates MAP kinase (MAPK) and MAP kinase kinase (MAPKK) in CHO cells. PAF is a substrate for lysophospholipase II and for PAF-Acetyl hydrolase
General
Type : Natural, Trimethylammonium, Ammonium, Water-insoluble medium and long chain ester, Choline ester, Not AlphaBeta Hydrolase target, Phosphatidylcholine
Chemical_Nomenclature : [(2R)-2-acetyloxy-3-hexadecoxypropyl] 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphate
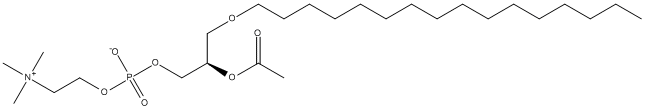
Canonical SMILES : CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCOCC(COP(=O)([O-])OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C26H54NO7P\/c1-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-21-31-23-26(34-25(2)28)24-33-35(29,30)32-22-20-27(3,4)5\/h26H,6-24H2,1-5H3\/t26-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : HVAUUPRFYPCOCA-AREMUKBSSA-N
Other name(s) : Platelet activating factor || Platelet-activating factor || C16-PAF || 1-O-Hexadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine || Hag-PC || APRL || (1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
MW : 523.68
Formula : C26H54NO7P
CAS_number : 74389-68-7
PubChem : 108156
UniChem : HVAUUPRFYPCOCA-AREMUKBSSA-N
Target
Structures : No structure
Families : PAF-Acetylhydrolase, LYsophospholipase_carboxylesterase
References (3)
| Title : Catabolism of platelet-activating factor and its acyl analog. Differentiation of the activities of lysophospholipase and platelet- activating-factor acetylhydrolase - Aarsman_1991_Eur.J.Biochem_200_187 |
| Author(s) : Aarsman AJ , Neys FW , Van den Bosch H |
| Ref : European Journal of Biochemistry , 200 :187 , 1991 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Aarsman_1991_Eur.J.Biochem_200_187 |
| PubMedID: 1879423 |
| Title : Catabolism of platelet-activating factor and its acyl analog. Differentiation of the activities of lysophospholipase and platelet- activating-factor acetylhydrolase - Aarsman_1991_Eur.J.Biochem_200_187 |
| Author(s) : Aarsman AJ , Neys FW , Van den Bosch H |
| Ref : European Journal of Biochemistry , 200 :187 , 1991 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Aarsman_1991_Eur.J.Biochem_200_187 |
| PubMedID: 1879423 |
| Title : Catabolism of platelet-activating factor and its acyl analog. Differentiation of the activities of lysophospholipase and platelet- activating-factor acetylhydrolase - Aarsman_1991_Eur.J.Biochem_200_187 |
| Author(s) : Aarsman AJ , Neys FW , Van den Bosch H |
| Ref : European Journal of Biochemistry , 200 :187 , 1991 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Aarsman_1991_Eur.J.Biochem_200_187 |
| PubMedID: 1879423 |