Scopoletin
Scopoletin is highly fluorescent. It is found in the root of plants in the genus Scopolia such as Scopolia carniolica and Scopolia japonica, in chicory, in Artemisia scoparia, in the roots and leaves of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica). It is a low inhibitor of cholinesterase, and serves as fluorophore building block of probes of the strigolactone receptors of plants. When oxidized, its fluorescence is strongly suppressed.
General
Type : Coumarin, Natural, Chromen
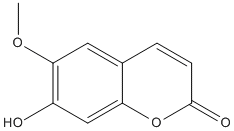
Chemical_Nomenclature : 7-hydroxy-6-methoxychromen-2-one
Canonical SMILES : COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C=CC(=O)O2)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C10H8O4\/c1-13-9-4-6-2-3-10(12)14-8(6)5-7(9)11\/h2-5,11H,1H3
InChIKey : RODXRVNMMDRFIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Gelseminic acid || 7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one || 6-Methylesculetin || CHEMBL71851 || SCHEMBL147702 || ZINC57733 || CHEBI:17488 || Murrayetin || Scopoletine || Scopoletol || Escopoletin
MW : 192.17
Formula : C10H8O4
CAS_number : 92-61-5
PubChem : 5280460
UniChem : RODXRVNMMDRFIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Wikipedia : Scopoletin
Target
References (13)
| Title : Expansion of the Strigolactone Profluorescent Probes Repertory: The Right Probe for the Right Application - de Saint Germain_2022_Front.Plant.Sci_13_887347 |
| Author(s) : de Saint Germain A , Clave G , Schouveiler P , Pillot JP , Singh AV , Chevalier A , Daignan Fornier S , Guillory A , Bonhomme S , Rameau C , Boyer FD |
| Ref : Front Plant Sci , 13 :887347 , 2022 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : de Saint Germain_2022_Front.Plant.Sci_13_887347 |
| PubMedID: 35720613 |
| Title : Scopoletin: Antiamyloidogenic, Anticholinesterase, and Neuroprotective Potential of a Natural Compound Present in Argyreia speciosa Roots by In Vitro and In Silico Study - Kashyap_2020_Neurosci.Insights_15_2633105520937693 |
| Author(s) : Kashyap P , Ram H , Shukla SD , Kumar S |
| Ref : Neurosci Insights , 15 :2633105520937693 , 2020 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Kashyap_2020_Neurosci.Insights_15_2633105520937693 |
| PubMedID: 32671342 |
| Title : Study of dynamics of genes involved in biosynthesis and accumulation of scopoletin at different growth stages of Convolvulus prostratus Forssk - Rutul_2020_Phytochemistry_182_112594 |
| Author(s) : Rutul VR , Amar AS , Mithil JP , K S , S TA , Parth JD , Ghanshyam BP , Jigar GM , N S |
| Ref : Phytochemistry , 182 :112594 , 2020 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rutul_2020_Phytochemistry_182_112594 |
| PubMedID: 33341029 |
| Title : Ratiometric fluorescence sensor for organophosphorus pesticide detection based on opposite responses of two fluorescence reagents to MnO2 nanosheets - Yao_2019_Biosens.Bioelectron_145_111705 |
| Author(s) : Yao T , Liu A , Liu Y , Wei M , Wei W , Liu S |
| Ref : Biosensors & Bioelectronics , 145 :111705 , 2019 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Yao_2019_Biosens.Bioelectron_145_111705 |
| PubMedID: 31550630 |
| Title : Combining in silico and in vitro approaches to evaluate the acetylcholinesterase inhibitory profile of some commercially available flavonoids in the management of Alzheimer's disease - Kuppusamy_2016_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_95_199 |
| Author(s) : Kuppusamy A , Arumugam M , George S |
| Ref : Int J Biol Macromol , 95 :199 , 2016 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Kuppusamy_2016_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_95_199 |
| PubMedID: 27871793 |
| Title : Synthesis and anti-acetylcholinesterase activity of scopoletin derivatives - Khunnawutmanotham_2015_Bioorg.Chem_65_137 |
| Author(s) : Khunnawutmanotham N , Chimnoi N , Saparpakorn P , Techasakul S |
| Ref : Bioorg Chem , 65 :137 , 2015 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Khunnawutmanotham_2015_Bioorg.Chem_65_137 |
| PubMedID: 26943478 |
| Title : Synthesis of aminoalkyl-substituted coumarin derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - Nam_2014_Bioorg.Med.Chem_22_1262 |
| Author(s) : Nam SO , Park DH , Lee YH , Ryu JH , Lee YS |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry , 22 :1262 , 2014 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Nam_2014_Bioorg.Med.Chem_22_1262 |
| PubMedID: 24485122 |
| Title : Anti-Inflammatory, Anticholinesterase, and Antioxidant Potential of Scopoletin Isolated from Canarium patentinervium Miq. (Burseraceae Kunth) - Mogana_2013_Evid.Based.Complement.Alternat.Med_2013_734824 |
| Author(s) : Mogana R , Teng-Jin K , Wiart C |
| Ref : Evid Based Complement Alternat Med , 2013 :734824 , 2013 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Mogana_2013_Evid.Based.Complement.Alternat.Med_2013_734824 |
| PubMedID: 23878606 |
| Title : The coumarin scopoletin potentiates acetylcholine release from synaptosomes, amplifies hippocampal long-term potentiation and ameliorates anticholinergic- and age-impaired memory - Hornick_2011_Neurosci_197_280 |
| Author(s) : Hornick A , Lieb A , Vo NP , Rollinger JM , Stuppner H , Prast H |
| Ref : Neuroscience , 197 :280 , 2011 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Hornick_2011_Neurosci_197_280 |
| PubMedID: 21945033 |
| Title : Effects of auxins on growth and scopoletin accumulation in cell suspension cultures of Angelica archangelica L - Siatka_2008_Ceska.Slov.Farm_57_17 |
| Author(s) : Siatka T , Kasparova M |
| Ref : Ceska a Slovenska Farmacie , 57 :17 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Siatka_2008_Ceska.Slov.Farm_57_17 |
| PubMedID: 18383919 |
| Title : Coumarin, anthroquinone and stilbene derivatives with anticholinesterase activity - Orhan_2008_Z.Naturforsch.C_63_366 |
| Author(s) : Orhan I , Tosun F , Sener B |
| Ref : Z Naturforsch C , 63 :366 , 2008 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Orhan_2008_Z.Naturforsch.C_63_366 |
| PubMedID: 18669022 |
| Title : Effect of scopoletin on lipoprotein lipase activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes - Yang_2007_Int.J.Mol.Med_20_527 |
| Author(s) : Yang JY , Koo JH , Yoon HY , Lee JH , Park BH , Kim JS , Chi MS , Park JW |
| Ref : Int J Mol Med , 20 :527 , 2007 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Yang_2007_Int.J.Mol.Med_20_527 |
| PubMedID: 17786283 |
| Title : Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of scopolin and scopoletin discovered by virtual screening of natural products - Rollinger_2004_J.Med.Chem_47_6248 |
| Author(s) : Rollinger JM , Hornick A , Langer T , Stuppner H , Prast H |
| Ref : Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 47 :6248 , 2004 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Rollinger_2004_J.Med.Chem_47_6248 |
| PubMedID: 15566295 |