MT-031
mild inhibitor of ACHE IC50 58.3 +/- 6.3 microM and BCHE 34.6 +/- 8.3 microM
General
Type : Monoamine-oxidase-inhibitor, Multitarget, Carbamate, prop-2-yn-1-yl
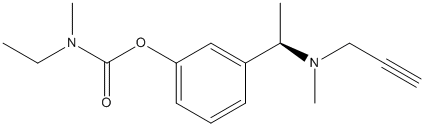
Chemical_Nomenclature : [3-[(1R)-1-[methyl(prop-2-ynyl)amino]ethyl]phenyl] N-ethyl-N-methylcarbamate
Canonical SMILES : CCN(C)C(=O)OC1=CC=CC(=C1)C(C)N(C)CC#C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C16H22N2O2\/c1-6-11-18(5)13(3)14-9-8-10-15(12-14)20-16(19)17(4)7-2\/h1,8-10,12-13H,7,11H2,2-5H3\/t13-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : ALHSEIIOFXOKLH-CYBMUJFWSA-N
Other name(s) : (S)-3-(1-(Methyl(prop-2-yn-1-yl)amino)ethyl)phenyl ethyl(methyl)carbamate || SCHEMBL16948183
MW : 274.36
Formula : C16H22N2O2
CAS_number : 1802158-63-9
PubChem : 118266847
UniChem : ALHSEIIOFXOKLH-CYBMUJFWSA-N
Target
Families : MT-031 ligand of proteins in family
ACHE
BCHE
Protein :
human-ACHE
human-BCHE
References (2)
| Title : A novel neuroprotective cholinesterase-monoamine oxidase inhibitor for treatment of dementia and depression in Parkinson's disease - Liu_2022_Ageing.Neurodegener.Dis__ |
| Author(s) : Liu W , Wang Y , Youdim MB |
| Ref : Ageing and Neurodegenerative Diseases , : , 2022 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Liu_2022_Ageing.Neurodegener.Dis__ |
| PubMedID: |
| Title : Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel dual monoamine-cholinesterase inhibitors as potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease - Liu_2016_Neuropharmacol_109_376 |
| Author(s) : Liu W , Lang M , Youdim MB , Amit T , Sun Y , Zhang Z , Wang Y , Weinreb O |
| Ref : Neuropharmacology , 109 :376 , 2016 |
| Abstract : |
| PubMedSearch : Liu_2016_Neuropharmacol_109_376 |
| PubMedID: 27318273 |