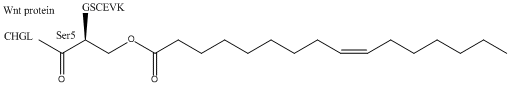
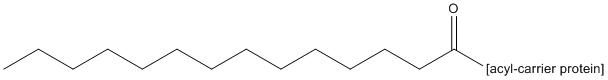
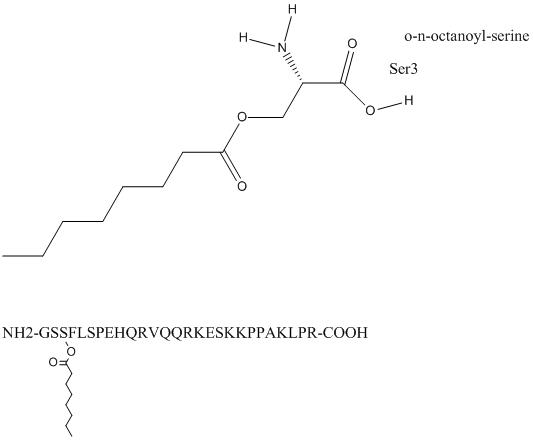
Acyl peptide
Fatty acylation, a post-translational modification that comprises the addition of fatty acids onto proteins, regulates protein function, stability, and membrane association. Myristoylation and palmitoylation, two distinct forms of fatty acylation of proteins, have been shown to promote membrane targeting and binding of proteins. They also could influence protein structure, as well as direct protein interactions. Palmitoylation has also been observed to regulate other posttranslational modifications including phosphorylation or ubiquitination at nearby sites. Many fatty acylated proteins play a key role in physiology and disease.