Lalistat-2
Apart from Lysosomal acid lipase human-LIPA, Lalistat-1 and -2 also inhibit major cytosolic lipid hydrolases responsible for lipid degradation in primary cells at neutral pH through off-target effects (ATGL not alpha/beta hydrolas; HSL hormone sensitive lipase); MGL Monoglyceride lipase). Lalistat also impairs Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by targeting hydolases LipR Rv3084 Rv1984c Rv0183
General
Type : Piperidine,Lipase inhibitor,Sulfur Compound,Thiadiazol
Chemical_Nomenclature : (4-piperidin-1-yl-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl) piperidine-1-carboxylate
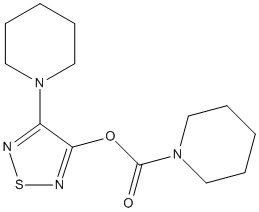
Canonical SMILES : C1CCN(CC1)C2=NSN=C2OC(=O)N3CCCCC3
InChI : InChI=1S\/C13H20N4O2S\/c18-13(17-9-5-2-6-10-17)19-12-11(14-20-15-12)16-7-3-1-4-8-16\/h1-10H2
InChIKey : PNYYVHOTXOEBEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : CHEMBL1085857,4-(Piperidin-1-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl piperidine-1-carboxylate,Lalistat 2,SCHEMBL17078239,BDBM50318691,Lalistat2,La-0
MW : 296.38
Formula : C13H20N4O2S
CAS_number : 1234569-09-5
PubChem : 46867138
UniChem : PNYYVHOTXOEBEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : Lalistat-2 ligand of proteins in family: Acidic_Lipase || Hormone-sensitive_lipase_like || Monoglyceridelipase_lysophospholip || Cutinase || 6_AlphaBeta_hydrolase
Stucture :
Protein : human-LIPA || myctu-Rv3084 || myctu-rv0183 || myctu-cutas1 || myctu-RV0045C
References (12)
| Title : Off-target effects of the lysosomal acid lipase inhibitors Lalistat-1 and Lalistat-2 on neutral lipid hydrolases - Bradic_2022_Mol.Metab__101510 |
| Author(s) : Bradic I , Kuentzel KB , Honeder S , Grabner GF , Vujic N , Zimmermann R , Birner-Gruenberger R , Kratky D |
| Ref : Mol Metab , :101510 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Bradic_2022_Mol.Metab__101510 |
| ESTHER : Bradic_2022_Mol.Metab__101510 |
| PubMedSearch : Bradic_2022_Mol.Metab__101510 |
| PubMedID: 35504532 |
| Title : Low levels of Lysosomal Acid Lipase (LAL) activity increases necroinflammation in adult patients with biopsy-proven metabolic associated fatty liver disease - Thoen_2021_Clin.Res.Hepatol.Gastroenterol_45_101638 |
| Author(s) : Thoen RU , Longo L , Neto SC , Alvares-da-Silva MR |
| Ref : Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol , 45 :101638 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Thoen_2021_Clin.Res.Hepatol.Gastroenterol_45_101638 |
| ESTHER : Thoen_2021_Clin.Res.Hepatol.Gastroenterol_45_101638 |
| PubMedSearch : Thoen_2021_Clin.Res.Hepatol.Gastroenterol_45_101638 |
| PubMedID: 33662773 |
| Title : Loss of Function of Lysosomal Acid Lipase (LAL) Profoundly Impacts Osteoblastogenesis and Increases Fracture Risk in Humans - Helderman_2021_Bone__115946 |
| Author(s) : Helderman RC , Whitney DG , Duta-Mare M , Akhmetshina A , Vujic N , Jayapalan S , Nyman JS , Misra BB , Rosen CJ , Czech MP , Kratky D , Rendina-Ruedy E |
| Ref : Bone , :115946 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Helderman_2021_Bone__115946 |
| ESTHER : Helderman_2021_Bone__115946 |
| PubMedSearch : Helderman_2021_Bone__115946 |
| PubMedID: 33838322 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA , mouse-1llip |
| Title : Deacetylation of LAMP1 drives lipophagy-dependent generation of free fatty acids by Abrus agglutinin to promote senescence in prostate cancer - Panda_2020_J.Cell.Physiol_235_2776 |
| Author(s) : Panda PK , Patra S , Naik PP , Praharaj PP , Mukhopadhyay S , Meher BR , Gupta PK , Verma RS , Maiti TK , Bhutia SK |
| Ref : Journal of Cellular Physiology , 235 :2776 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Panda_2020_J.Cell.Physiol_235_2776 |
| ESTHER : Panda_2020_J.Cell.Physiol_235_2776 |
| PubMedSearch : Panda_2020_J.Cell.Physiol_235_2776 |
| PubMedID: 31544977 |
| Title : Lysosomal acid lipase is the major acid retinyl ester hydrolase in cultured human hepatic stellate cells but not essential for retinyl ester degradation - Wagner_2020_Biochim.Biophys.Acta.Mol.Cell.Biol.Lipids_1865_158730 |
| Author(s) : Wagner C , Hois V , Pajed L , Pusch LM , Wolinski H , Trauner M , Zimmermann R , Taschler U , Lass A |
| Ref : Biochimica & Biophysica Acta Molecular & Cellular Biology Lipids , 1865 :158730 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Wagner_2020_Biochim.Biophys.Acta.Mol.Cell.Biol.Lipids_1865_158730 |
| ESTHER : Wagner_2020_Biochim.Biophys.Acta.Mol.Cell.Biol.Lipids_1865_158730 |
| PubMedSearch : Wagner_2020_Biochim.Biophys.Acta.Mol.Cell.Biol.Lipids_1865_158730 |
| PubMedID: 32361002 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA |
| Title : A kinetic assay of total lipase activity for detecting lysosomal acid lipase deficiency (LAL-D) and the molecular characterization of 18 LAL-D patients from Russia - Mayanskiy_2019_JIMD.Rep_48_75 |
| Author(s) : Mayanskiy N , Brzhozovskaya E , Pushkov A , Strokova T , Vlasov N , Surkov A , Gundobina O , Savostianov K |
| Ref : JIMD Rep , 48 :75 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Mayanskiy_2019_JIMD.Rep_48_75 |
| ESTHER : Mayanskiy_2019_JIMD.Rep_48_75 |
| PubMedSearch : Mayanskiy_2019_JIMD.Rep_48_75 |
| PubMedID: 31392116 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA |
| Title : Specific Substrate for the Assay of Lysosomal Acid Lipase - Masi_2018_Clin.Chem_64_690 |
| Author(s) : Masi S , Chennamaneni N , Turecek F , Scott CR , Gelb MH |
| Ref : Clinical Chemistry , 64 :690 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Masi_2018_Clin.Chem_64_690 |
| ESTHER : Masi_2018_Clin.Chem_64_690 |
| PubMedSearch : Masi_2018_Clin.Chem_64_690 |
| PubMedID: 29339442 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA |
| Title : Best practice in the measurement and interpretation of lysosomal acid lipase in dried blood spots using the inhibitor Lalistat 2 - Lukacs_2017_Clin.Chim.Acta_471_201 |
| Author(s) : Lukacs Z , Barr M , Hamilton J |
| Ref : Clinica Chimica Acta , 471 :201 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Lukacs_2017_Clin.Chim.Acta_471_201 |
| ESTHER : Lukacs_2017_Clin.Chim.Acta_471_201 |
| PubMedSearch : Lukacs_2017_Clin.Chim.Acta_471_201 |
| PubMedID: 28532785 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA |
| Title : Human lysosomal acid lipase inhibitor lalistat impairs Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by targeting bacterial hydrolases - Lehmann_2016_Medchemcomm_7_1797 |
| Author(s) : Lehmann J , Vomacka J , Esser K , Nodwell M , Kolbe K , Ramer P , Protzer U , Reiling N , Sieber SA |
| Ref : Medchemcomm , 7 :1797 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Lehmann_2016_Medchemcomm_7_1797 |
| ESTHER : Lehmann_2016_Medchemcomm_7_1797 |
| PubMedSearch : Lehmann_2016_Medchemcomm_7_1797 |
| PubMedID: |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: myctu-cutas1 , myctu-lipG , myctu-RV0045C , myctu-rv0183 , myctu-RV0293C , myctu-RV0840C , myctu-Rv1191 , myctu-RV1192 , myctu-Rv1399c , myctu-Rv1400c , myctu-Rv1426c , myctu-Rv2045c , myctu-Rv2284 , myctu-Rv2970c , myctu-Rv3084 , myctu-YR15 , larcr-a0a0f7ir14 |
| Title : Extended use of a selective inhibitor of acid lipase for the diagnosis of Wolman disease and cholesteryl ester storage disease - Civallero_2014_Gene_539_154 |
| Author(s) : Civallero G , De Mari J , Bittar C , Burin M , Giugliani R |
| Ref : Gene , 539 :154 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Civallero_2014_Gene_539_154 |
| ESTHER : Civallero_2014_Gene_539_154 |
| PubMedSearch : Civallero_2014_Gene_539_154 |
| PubMedID: 24508470 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA |
| Title : A practical fluorometric assay method to measure lysosomal acid lipase activity in dried blood spots for the screening of cholesteryl ester storage disease and Wolman disease - Dairaku_2014_Mol.Genet.Metab_111_193 |
| Author(s) : Dairaku T , Iwamoto T , Nishimura M , Endo M , Ohashi T , Eto Y |
| Ref : Mol Genet Metab , 111 :193 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Dairaku_2014_Mol.Genet.Metab_111_193 |
| ESTHER : Dairaku_2014_Mol.Genet.Metab_111_193 |
| PubMedSearch : Dairaku_2014_Mol.Genet.Metab_111_193 |
| PubMedID: 24295952 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA |
| Title : A new method for the measurement of lysosomal acid lipase in dried blood spots using the inhibitor Lalistat 2 - Hamilton_2012_Clin.Chim.Acta_413_1207 |
| Author(s) : Hamilton J , Jones I , Srivastava R , Galloway P |
| Ref : Clinica Chimica Acta , 413 :1207 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Hamilton_2012_Clin.Chim.Acta_413_1207 |
| ESTHER : Hamilton_2012_Clin.Chim.Acta_413_1207 |
| PubMedSearch : Hamilton_2012_Clin.Chim.Acta_413_1207 |
| PubMedID: 22483793 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LIPA |