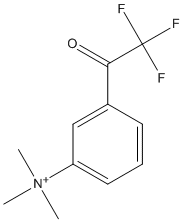
Transition state analogue
General
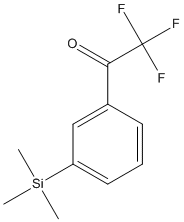
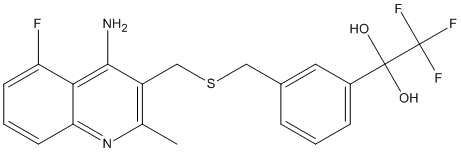
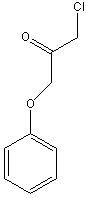
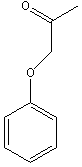
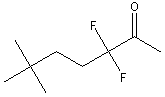
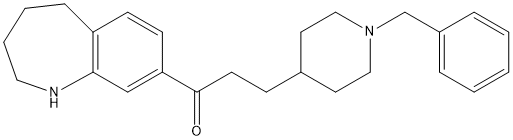
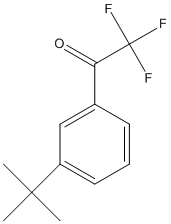
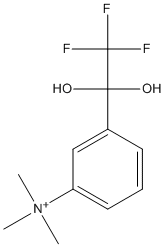
Transition state analogs, are chemical compounds with a chemical structure that resembles the transition state of a substrate molecule in an enzyme-catalyzed chemical reaction and can bind more tightly to the enzyme than the actual substrate
-butane-2-sulfonate.gif)