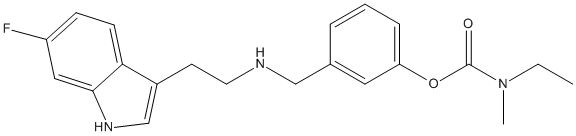
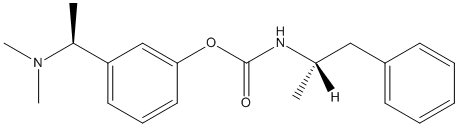
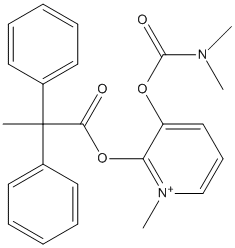
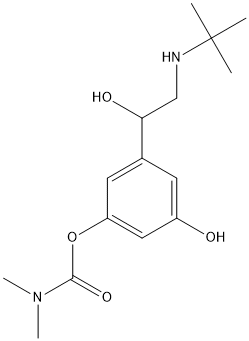
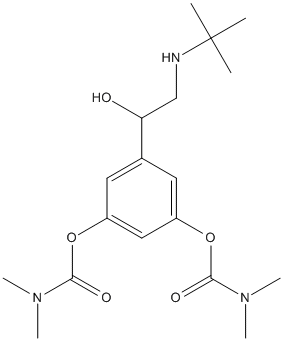
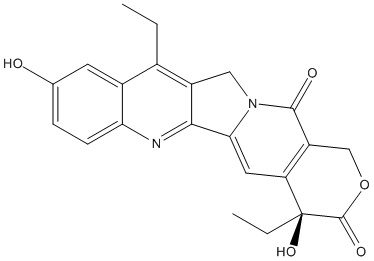
Pro-Drug
General
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after administration, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. For example, salicin is a beta-D-glucopyranoside that is cleaved by esterases to release salicylic acid. Aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid, first made by Felix Hoffmann at Bayer in 1897, is a synthetic prodrug of salicylic acid. Many prodrugs are synthetized to slow down the delivery of the active compound. Esterases often hydrolyze prodrugs and are targeted for that role. Genetic variants of these esterases may act differently and explain variation of response in patients bearing these variant