Palmostatin-B
Palmostatin B inhibits other protein thioesterases, such as APT2 (human-LYPLA2) (Ki = 34 nM)
General
Type : Oxooxetan
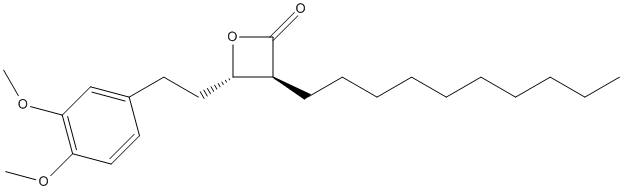
Chemical_Nomenclature : (3S,4S)-3-decyl-4-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]oxetan-2-one
Canonical SMILES : CCCCCCCCCCC1C(OC1=O)CCC2=CC(=C(C=C2)OC)OC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C23H36O4\/c1-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-19-20(27-23(19)24)15-13-18-14-16-21(25-2)22(17-18)26-3\/h14,16-17,19-20H,4-13,15H2,1-3H3\/t19-,20-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : ASVWFAVGLYUDFD-PMACEKPBSA-N
Other name(s) : Palmostatin B,PalmB,Palm B,CHEMBL1673415,PalmostatinB,BDBM50336546
MW : 376.52
Formula : C23H36O4
CAS_number :
PubChem : 45100481
UniChem : ASVWFAVGLYUDFD-PMACEKPBSA-N
Target
Families : Palmostatin-B ligand of proteins in family
ABHD16
Thioesterase
5_AlphaBeta_hydrolase
ABHD17-depalmitoylase
ABHD6-Lip
LYsophospholipase_carboxylesterase
S9N_PREPL_Peptidase_S9
Protein :
human-ABHD16A
human-ABHD6
human-FASN
human-ABHD17A
human-ABHD17B
human-ABHD17C
human-LYPLA1
human-LYPLA2
human-PREPL
References (10)
| Title : Trypanosoma brucei Acyl-Protein Thioesterase-like (TbAPT-L) Is a Lipase with Esterase Activity for Short and Medium-Chain Fatty Acids but Has No Depalmitoylation Activity - Brown_2022_Pathogens_11_1245 |
| Author(s) : Brown RWB , Sharma AI , Villanueva MR , Li X , Onguka O , Zilbermintz L , Nguyen H , Falk BA , Olson CL , Taylor JM , Epting CL , Kathayat RS , Amara N , Dickinson BC , Bogyo M , Engman DM |
| Ref : Pathogens , 11 : , 2022 |
| Abstract : Brown_2022_Pathogens_11_1245 |
| ESTHER : Brown_2022_Pathogens_11_1245 |
| PubMedSearch : Brown_2022_Pathogens_11_1245 |
| PubMedID: 36364996 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: tryb2-q7yxi0 |
| Title : Prolyl endopeptidase-like is a (thio)esterase involved in mitochondrial respiratory chain function - Rosier_2021_iScience_24_103460 |
| Author(s) : Rosier K , McDevitt MT , Smet J , Floyd BJ , Verschoore M , Marcaida MJ , Bingman CA , Lemmens I , Dal Peraro M , Tavernier J , Cravatt BF , Gounko NV , Vints K , Monnens Y , Bhalla K , Aerts L , Rashan EH , Vanlander AV , Van Coster R , Regal L , Pagliarini DJ , Creemers JWM |
| Ref : iScience , 24 :103460 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Rosier_2021_iScience_24_103460 |
| ESTHER : Rosier_2021_iScience_24_103460 |
| PubMedSearch : Rosier_2021_iScience_24_103460 |
| PubMedID: 34888501 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-PREPL |
| Title : Chemical proteomic analysis of palmostatin beta-lactone analogs that affect N-Ras palmitoylation - Suciu_2021_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_53_128414 |
| Author(s) : Suciu RM , Luvaga IK , Hazeen A , Weerasooriya C , Richardson SK , Firestone AJ , Shannon K , Howell AR , Cravatt BF |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Lett , 53 :128414 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Suciu_2021_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_53_128414 |
| ESTHER : Suciu_2021_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_53_128414 |
| PubMedSearch : Suciu_2021_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_53_128414 |
| PubMedID: 34666187 |
| Title : Human leukocytes differentially express endocannabinoid-glycerol lipases and hydrolyze 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol and its metabolites from the 15-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase pathways - Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| Author(s) : Turcotte C , Dumais E , Archambault AS , Martin C , Blanchet MR , Bissonnette E , Boulet LP , Laviolette M , Di Marzo V , Flamand N |
| Ref : J Leukoc Biol , 106 :1337 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| ESTHER : Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| PubMedSearch : Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| PubMedID: 31556464 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-ABHD6 , human-ABHD12 , human-ABHD16A , human-CES1 , human-LYPLA2 , human-PPT1 |
| Title : Acyl protein thioesterase 1 and 2 (APT-1, APT-2) inhibitors palmostatin B, ML348 and ML349 have different effects on NRAS mutant melanoma cells - Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| Author(s) : Vujic I , Sanlorenzo M , Esteve-Puig R , Vujic M , Kwong A , Tsumura A , Murphy R , Moy A , Posch C , Monshi B , Rappersberger K , Ortiz-Urda S |
| Ref : Oncotarget , 7 :7297 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| ESTHER : Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| PubMedSearch : Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| PubMedID: 26771141 |
| Title : ABHD17 proteins are novel protein depalmitoylases that regulate N-Ras palmitate turnover and subcellular localization - Lin_2015_Elife_4_ |
| Author(s) : Lin DT , Conibear E |
| Ref : Elife , 4 : , 2015 |
| Abstract : Lin_2015_Elife_4_ |
| ESTHER : Lin_2015_Elife_4_ |
| PubMedSearch : Lin_2015_Elife_4_ |
| PubMedID: 26701913 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-ABHD17A , human-ABHD17B , human-ABHD17C |
| Title : Biochemical and Pharmacological Characterization of the Human Lymphocyte Antigen B-Associated Transcript 5 (BAT5\/ABHD16A) - Savinainen_2014_PLoS.One_9_e109869 |
| Author(s) : Savinainen JR , Patel JZ , Parkkari T , Navia-Paldanius D , Marjamaa JJ , Laitinen T , Nevalainen T , Laitinen JT |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 9 :e109869 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Savinainen_2014_PLoS.One_9_e109869 |
| ESTHER : Savinainen_2014_PLoS.One_9_e109869 |
| PubMedSearch : Savinainen_2014_PLoS.One_9_e109869 |
| PubMedID: 25290914 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-ABHD16A , mouse-Abhd16a |
| Title : A mechanism regulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling that requires cycles of protein palmitoylation and depalmitoylation - Jia_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_6249 |
| Author(s) : Jia L , Chisari M , Maktabi MH , Sobieski C , Zhou H , Konopko AM , Martin BR , Mennerick SJ , Blumer KJ |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 289 :6249 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Jia_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_6249 |
| ESTHER : Jia_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_6249 |
| PubMedSearch : Jia_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_6249 |
| PubMedID: 24385443 |
| Title : Identification of acyl protein thioesterases 1 and 2 as the cellular targets of the Ras-signaling modulators palmostatin B and M - Rusch_2011_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_50_9838 |
| Author(s) : Rusch M , Zimmermann TJ , Burger M , Dekker FJ , Gormer K , Triola G , Brockmeyer A , Janning P , Bottcher T , Sieber SA , Vetter IR , Hedberg C , Waldmann H |
| Ref : Angew Chem Int Ed Engl , 50 :9838 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Rusch_2011_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_50_9838 |
| ESTHER : Rusch_2011_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_50_9838 |
| PubMedSearch : Rusch_2011_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_50_9838 |
| PubMedID: 21905186 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LYPLA1 , human-LYPLA2 |
| Title : Small-molecule inhibition of APT1 affects Ras localization and signaling - Dekker_2010_Nat.Chem.Biol_6_449 |
| Author(s) : Dekker FJ , Rocks O , Vartak N , Menninger S , Hedberg C , Balamurugan R , Wetzel S , Renner S , Gerauer M , Scholermann B , Rusch M , Kramer JW , Rauh D , Coates GW , Brunsveld L , Bastiaens PI , Waldmann H |
| Ref : Nat Chemical Biology , 6 :449 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Dekker_2010_Nat.Chem.Biol_6_449 |
| ESTHER : Dekker_2010_Nat.Chem.Biol_6_449 |
| PubMedSearch : Dekker_2010_Nat.Chem.Biol_6_449 |
| PubMedID: 20418879 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LYPLA1 |