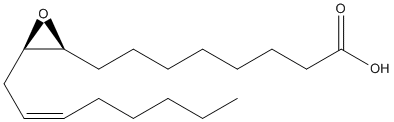
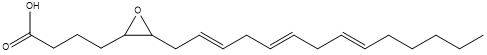
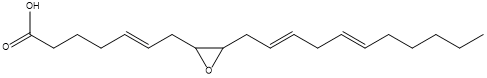
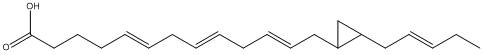
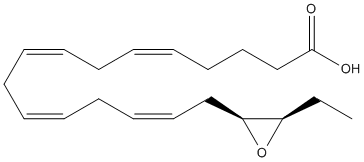
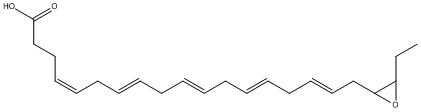
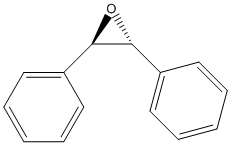
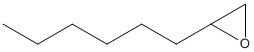
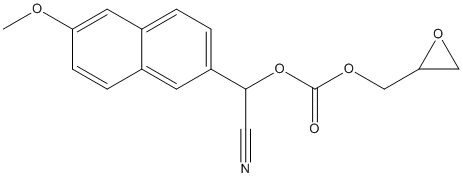
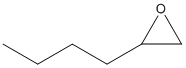
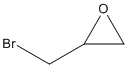
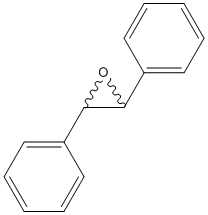
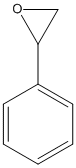
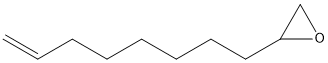
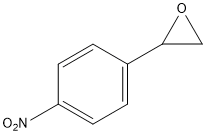
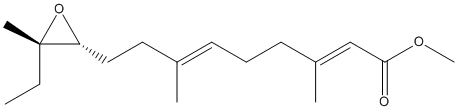
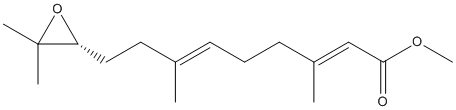
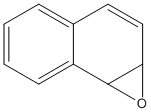
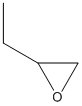
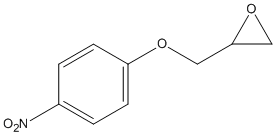
Epoxide
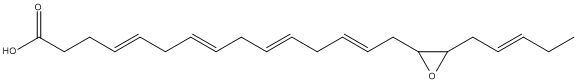
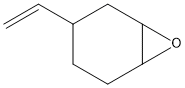
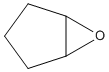
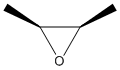
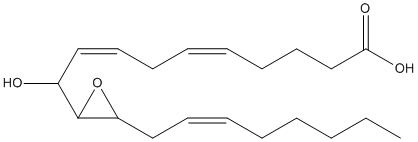
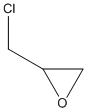
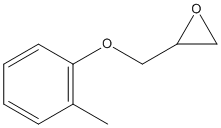
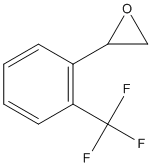
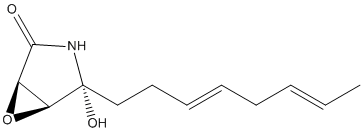
An epoxide is a cyclic ether (R1R2-C-O-R3R4) with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. Epoxides are uncommon in nature. They arise usually via oxygenation of alkenes by the action of cytochrome P450. They are substrates of epoxide hydrolases




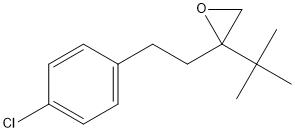

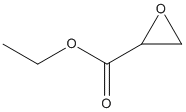
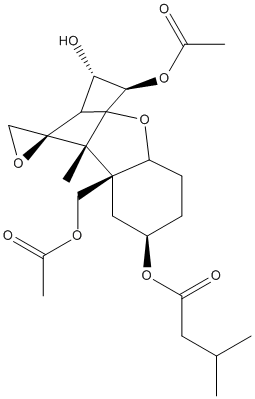



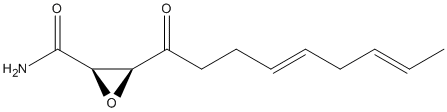
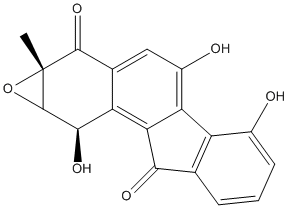
-EpOME.gif)